
In-Use / USA Residential V6 /
Part 1
Information correct as of 26thFebruary 2026. Please see kb.breeam.com for the latest compliance information.
Alarm systems – Intent of Criterion 2 - KBCN1707
The intent of Criterion 2 is as follows:
A documented plan is in place to ensure that when the alarm is triggered, whether due to a fire or security incident, a system fault or a false alarm, building staff and occupants understand what actions to take. This must include any necessary communication with ARC staff, emergency services and other building users.
This clarification will be incorporated in the next update of the technical standard.
Benchmark energy performance value – clarification - KBCN1724
The benchmark energy performance value is a performance level which achieves the
median performance within a local energy performance standard's range of values.
Example
The asset is being benchmarked using the Energy Star Portfolio Manager.
Under this system, assets can receive a score from 1 to 100.
A score of 50 represents median performance, which equates to the benchmark energy performance value.
27-Mar-2025 - Published.
Carbon monoxide detection – Combustion appliances located outside - KBCN1586
Where all combustion appliances are located outside in the open air, no flues pass through an occupied space and there are no enclosed parking areas, the associated credits can be filtered out as per Criterion 1
Clarification – percentage of end uses - KBCN1650
This percentage is measured by the energy consumption (kWh) of significant energy uses, not by the number of end uses.
Combined system for heating / cooling and domestic hot water - KBCN0329
It is permissible to have combined metering for a shared on-site or district system that combines heating / cooling, and domestic hot water generation.
In all cases, justification is provided in the QA report for the combined metering, and explains why it is not technically feasible to provide separate meters.
21-Sep-2022 Applicability of KBCN added to BIU V6. Amended to include district heating and cooling networks.
Condition survey – refurbishment in the last 5 years - KBCN1522
Where an asset has been refurbished, refurbished elements listed in criterion 2 can be excluded from the condition survey if:
- The refurbishment was carried out less than 5 years ago.
- The refurbishment addressed any and all major defects with the element.
- The records of the refurbishment allow asset management to effectively maintain that element.
The intent of Rsc 01 is to give asset management a complete understanding of the condition of the asset. The requirement for 5 years is to make sure that this information is relatively up-to-date, and allows effective maintenance of the asset and management of any minor defects.
All example scenarios below assume that the refurbishment was carried out less than 5 years ago. Any refurbishment works carried out more than 5 years ago must follow the full criteria of this issue.
[accordion]
[accordion_block title="Scenario 1"]
A major refurbishment to a Commercial asset covered and effectively documented refurbishment to:
a. Structure.
b. Mechanical components.
c. Electrical components.
d. Plumbing.
e. Fire protection.
It did not cover:
f. Communications and life safety systems.
g. Health and safety conditions.
All major defects were resolved.
Credits for the condition survey, and for rectifying defects are awarded based on elements f. and g. only.
[/accordion_block][accordion_block title="Scenario 2"]
A major refurbishment has covered and documented all items in criterion 2. All major defects were resolved, but there are some outstanding minor defects that are being monitored and maintained by asset management.
BIU V6: This issue is filtered out as per criterion 1.
BIU 2015: The relevant credits are awarded.
Minor defects are common after major building or refurbishment works, and typical building contracts provide a period for the resolution of minor defects. As long as major defects are resolved by the refurbishment, and asset management are aware of and managing minor defects, these items can be excluded from the condition survey.
[/accordion_block][accordion_block title="Scenario 3"]
A major refurbishment covered all elements, but there is no record of the refurbishment of mechanical and electrical components.
A condition survey covering these items is required. Relevant credits are awarded for surveying and addressing any defects for these elements.
[/accordion_block]
[/accordion]
District heating / cooling / hot water – entering data into the Online Platform - KBCN1536
For assets which use district heating / cooling / hot water, information on the district systems are entered into Ene 09a and 09b.
In Ene 05 / 06 / 09, answer 'no' to first question
"Is space heating / cooling / hot water generated on-site?" then navigate to:
- Ene 09a to answer questions on district cooling.
- Ene 09b to answer questions on district heating and hot water.
A district heat network will also provide hot water, so information on the system which provides both is entered into Ene 09b.
The Online Platform differs from the manual structure, however it does not affect scoring in any way. All data entered contributes to the asset energy calculator.
Assets with on-site and off-site systems
Only answer questions on the system which provides the most signifcant heating or cooling to the asset. If an asset includes both on-site and off-site systems, choose the one which delivers the most energy annually.
Ecological features – Answer D – Planters and planted areas - KBCN1543
Outdoor planters and traditional planted areas can be considered as
one feature for the purposes of Answer D, provided there is enough planting on the site to meet the intent of the issue.
To meet the requirements of Answer D, the following must be demonstrated:
- Outdoor planters, containing live plants and/or traditional planted areas
- Other planted areas such as green roofs or green walls
- Features to assist local fauna
20-Dec-2023 – The intent of this KBCN was to simplify compliance with Answer D. This has now been updated to clarify that it only applies to Answer D, thereby removing the potentially negative impact on meeting the requirements of Answer C.
Electric vehicle charging stations (EVCS) – Priority spaces - KBCN1429
The current criteria for EVCS do not address provision for priority spaces, such as those allocated to disabled use and car sharing.
The assessor and design team should, therefore, take a pragmatic approach to this and, where the overall number of required EVCS permits, an appropriate proportion of these should be provided for priority spaces. This will not be deemed as 'double-counting' as the number of EVCS required should be considered independently of other requirements.
The intent is that electric vehicle charging spaces are available to all building users (where possible).
Electric vehicle charging stations – faster charging - KBCN1497
The number of electric vehicle charging stations required for compliance cannot be reduced by installing faster/higher power charging stations.
This would not necessarily increase the availability of the charging stations for users.
Enhanced waste collection in the asset - KBCN1528
Where the asset collects 6 or more unique residential waste streams on-site, answers G and H are available without the need for additional off-site collection points.
If the asset can provide enhanced waste collection and sorting on-site, then this is effectively the same as having a compliant collection point in the local area.
Example scenarios
[accordion]
[accordion_block title="5 waste streams on-site"]
An apartment building has compliant facilities or kerb-side collection for 5 residential waste streams. There is no collection for composting or garden waste.
The asset achieves the requirements for answer C only if all relevant criteria are met. There aren't enough waste streams to meet the threshold for answer G.
[/accordion_block]
[accordion_block title="7 waste streams on-site"]
An apartment building has compliant facilities or kerb-side collection for 7 residential waste streams. There is no collection for composting or garden waste.
The asset achieves the requirements for answer C, and answer G if all relevant criteria are met.
[/accordion_block]
[accordion_block title="7 waste streams on-site, with off-site collection point within 0.3 miles"]
An apartment building has compliant facilities or kerb-side collection for 7 residential waste streams. There is no collection for composting or garden waste.
An off-site collection point within a compliant distance can collect 5 waste streams, however only 2 are unique (different from what the asset already collects on-site).
In total there are 9 unique waste streams collected on-site, kerb-side, or within a compliant distance.
The asset achieves the requirements for answer C, and answer H if all relevant criteria are met.
[/accordion_block]
[/accordion]
Erratum – scope of issue - KBCN1498
Criterion 1 states:
"Where external lighting or car park lighting are not necessary from a safety perspective, the associated credits can be filtered out of the assessment."
What this means is:
- Where external lighting does not exist, filter out the relevant credits.
- Where car park lighting does not exist, filter out the relevant credits.
- Whether or not the lighting exists for safety reasons has no effect on credit filtering.
The inclusion of the word 'safety' in this criteria is misleading and will be removed in future versions.
28-Feb-2024 - Wording clarified.
Erratum – up to V6 – methodology – no default energy assumptions - KBCN1630
The scope of the issue applies only to systems with
significant energy use.
The methodology section states that the online platform will calculate
default values, and use this to indicate which systems are in scope.
This is incorrect, as default values are
not automatically calculated.
The energy use of each system will need to be manually estimated. This can be done based on:
- Typical benchmark values, and / or,
- Estimates based on the capacity of equipment, and annual equivalent full load hours of use.
Erratum – up to V6.0.0 – compliant cycle storage - KBCN1595
Criteria
Instead of answer C, criterion 3 should refer to answers D and E.
Evidence
The criteria references for this issue are incorrect, and will be corrected in the next re-issue.
Checklists and tables
- Answer D awards 2 credits for achieving the minimum number of cycle storage.
- Answer E awards 1 additional credit for achieving additional cycle storage.
The headings in Table 20 do not match these answers. Table 20 will be revised with these updated headings:
| Home size |
Answer D
Minimum cycle storage
2 credits |
Answer E
Additional cycle storage
+1 additional credit |
| Studio or 1 bedroom |
1 cycle space / 2 homes |
1 cycle space / home |
| 2 - 3 bedrooms |
1 cycle space / home |
2 cycle spaces / home |
| 4+ bedrooms |
2 cycle spaces / home |
4 cycle spaces / home |
Erratum – V6.0.0 – cooling efficiency parameter – EER / SEER - KBCN1560
In the asset energy calculator guidance, the parameter given for cooling efficiency is 'SEER' (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio).
This is incorrect and should say '
EER'.
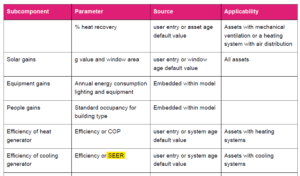
This affects the following tables:
|
International |
USA |
| Commercial V6.0.0 |
Table 19 |
Table 18 |
| Residential V6.0.0 |
Table 16 |
Table 16 |
This will be updated in the next manual re-issue.
Erratum – Electric Vehicles (EV) charging stations criteria - KBCN1701
In the BREEAM In-Use International Technical Manual, the Electric Vehicles (EV) charging criteria and their evidence were incorrectly referenced. The requirements for EV charging stations should read as follows
Answer G Electric Vehicles (EV) charging stations are provided for ≥5% of the car parking capacity.
Methodology
The methodology indicates the number of charging stations required should be calculated as a percentage of the total car parking capacity.
The ≥5% in Answer G indicates that at least 5% of the total parking spaces in the residential development should be equipped with EV charging stations.
If the number of charging facilities that should be supplied is not a whole number, it must be rounded up to the nearest whole number. For example, where the number of charging facilities that should be provided is calculated to be 10.2, the actual number of facilities that must be provided is 11.
Charging stations for Car Clubs cannot count towards the percentage provided for residents.
Evidence
The manual incorrectly referred to criterion 7 for the EV charging stations in the evidence section. The evidence requirement should refer to Criterion 5 and should be read as follows:
| Criterion |
Evidence requirement |
|
5
|
Calculations showing the percentage and number of charging stations |
|
5
|
Site plan showing the location and number of electric vehicle charging stations |
Evidence of no risk – Use of Approved Standards and Weightings List - KBCN0959
The current BREEAM International Non-Domestic New Construction Approved Standards and Weightings List (ASWL) can be used as evidence to demonstrate that a country has ‘no risk’ to all natural hazards apart from flooding (which is considered within POL 02 of BREEAM USA In-Use 2016 and Rsl 01 of BREEAM In-Use Version 6).
Any country which has a weighting of 0% for Hazards within the current ASWL (within Weightings INC 2016 and V6 tab) can provide this to BRE Global as evidence. As flooding is not included within the Hazard section of the ASWL, it must be evidenced separately. Therefore, in order to achieve maximum credits within MAT 05 or Rsl 03, the assessment must also provide evidence that the asset is in a ‘low or zero flood risk area’ under the requirements of POL 02 (BREEAM USA In-Use 2016) or Rsl 01 (BREEAM In-Use Version 6).
Note: BREEAM In-Use International Assessors who are not BREEAM International Non-Domestic New Construction Assessors, will be unable to access the ASWL. In this instance please send a technical query to BRE Global outlining the country which the asset is located, and BRE Global can confirm the current weighting for that country.
18-Aug-2025 added '(within Weightings INC 2016 and V6 tab)' to clarify where in the ASWL the weightings can be found
16-Aug-2016 Amended to clarify situations where there is no access to the ASWL
01-Oct-2022 Updated to apply to BREEAM In-Use Version 6
Fire hydrants and sprinklers – Leak detection - KBCN0680
Where it is confirmed by an appropriate project team member that it is not possible to fully meet the leak detection criteria for fire hydrants or sprinklers, an alternative approach can be implemented for these systems.
This must demonstrably meet the aim of the issue by detecting and alerting the building management to major water leaks.
11 Sep 2024 - Applicability to BIU USA V6 and INC V6 confirmed. New guidance introduced to clarify that BREEAM compliance should not compromise the operation of building safety-critical systems.
Flood risk – use of flood maps only in FRA - KBCN1524
Answer option E (Commercial) or F (Residential)
If a flood risk assessment considers flooding from rivers and seas only, flood risk is zero / low, and the following requirements are met:
- There are local or national flood maps available covering these sources of flooding.
- The maps are accurate, up to date, and have sufficient detail to clearly identify flood risk for the asset.
- The maps are approved by local or national government, and based on robust data.
It is acceptable for the flood risk assessment to be carried out by a relevant member of the team. It does not require a competent individual (see manual definition) to do this.
Most sources of flooding are site-specific and require specialist input and calculation to quantify. However, flood maps meeting the criteria above can provide an acceptable level of assurance of overall flood risk from rivers or seas without the need to engage a specialist.
Answer option B (Commercial) or C (Residential)
Where the risk of flooding is medium or high, flood mitigation measures are required (criterion 3).
These mitigation measures must be defined by either:
- A local authority (the measures must be relevant to the asset).
- Or a competent individual.
The FRA can still be produced by a relevant member of the team.
Relevant member of the team
A ‘relevant member of the team’ would typically refer to an individual directly involved with the management and operation of the asset, such as the building owner, client, tenant (if they have management responsibility), or the facilities/building manager. The aim is to ensure the flood risk assessment is carried out by an appropriate party to inform the owner/management about the flood risk to the property, whilst upholding the independence of the BREEAM Assessor for verification.
The relevant person cannot, therefore, be the BREEAM assessor, as they must be impartial and cannot produce evidence which they then verify for compliance. If another person in the assessor organisation were to undertake this role, it would need to be demonstrated how potential conflicts of interest would be managed - see
KBCN1708
Exemplary credit
This option is only available if a site-specific FRA was carried out by a competent individual, and cannot be based only on flood maps that give an allowance for climate change.
Example scenarios
[accordion]
[accordion_block title="Low / zero flood risk"]
National flood maps cover flooding from rivers and seas. The flood risk from these sources is zero / low.
The compliant FRA can be produced by a relevant member of the team.
[/accordion_block]
[accordion_block title="Medium / high flood risk"]
National flood maps cover flooding from rivers and seas. The flood risk from these sources is medium / high. Flood mitigation measures are required.
The local authority provides some general flood mitigation measures for the area, but these are not relevant to the assessed asset.
Instead, a competent individual is consulted on relevant flood mitigation measures for the asset - their recommendations are recorded in the FRA.
The compliant FRA can be produced by a relevant member of the team.
[/accordion_block]
[/accordion]
19-Jun-2025 - Relevant member of the team - Definition added
06-Nov-2024 - Answer C guidance title now corrected to point to Answer B for Commercial manuals.
Inclusive design – Access4you - KBCN1826
BREEAM recognises the use of Access4you certification as an approved alternative to the credits available in Hea12 Inclusive design as set out below:
| Hea 12 Inclusive design |
Access4you |
| 2 credits |
Bronze level |
| 4 credits |
Silver level or higher |
Evidence of Access4you certification must be provided at the final BREEAM certification stage.
AboutAccess4you
Access4you International is an organization that evaluates, certifies, and qualifies the accessibility of the built environment. Their self-developed criteria system consists of 1000 aspects, which are based on the usability aspects of 8+1 stakeholder groups, including people with special mobility, visual, hearing, and cognitive needs. The rating system consists of Certified location, Bronze, Silver, or Gold qualifications.
Access4you has two schemes, the Design & Building certification scheme which is aligned with a new construction or major refurbishment project and the Building certification scheme which is aligned with an assessment of an existing building. The most appropriate scheme, advised by Access4you should be used for certification.
Installed controls – ‘Asset does not have both heating and cooling’ - KBCN1678
In the technical manual, the intent is that Q1, Q2 and Q3 allow the credits to be filtered where the asset has 'neither heating nor cooling', in line with the assessment tool.
This will be updated in the next reissue of the technical manual.
Interlock controls – clarification - KBCN1491
An interlock is a control that is wired so that when there is no demand for heating / cooling in a space, the heating / cooling generator and the associated pumps are switched off. Use of thermostatic radiator valves (TRVs) alone does not provide interlock.
Partial interlock means that the cooling and heating interlock controls are separate. However, the control function may be set up to minimise the possibility of simultaneous heating and cooling.
Total interlock means the controls are wired so that simultaneous heating and cooling is not possible. Where there are separate local heating or cooling units present, these will also need to be wired into the control system for total interlock to avoid the possibility of simultaneous heating and cooling.
Intruder alarm systems – apartment buildings or similar - KBCN1572
Scope
The scope of this KBCN applies to any residential asset that:
- Is comprised of multiple self-contained dwellings within a single building envelope, and
- Share common entrance(s) and circulation.
A typical example is an apartment building.
Principle
The asset as a whole is protected by systems that are fit for purpose to ensure the safety and security of the asset, its users and their property
Implementation
Security requirements for apartment buildings will vary greatly depending on factors such as:
- Scale and configuration.
- Access strategy.
- Local context.
- Which areas are under building management control.
Because of this, BREEAM cannot provide specific guidance on how intruder alarms and access control are configured to meet the principle.
It is the role of the assessor and a competent third party (for instance, this can be a 'competent person' as defined in Rsl 10) to evidence how this principle is achieved for the asset as a whole.
Evidence from a compliant security risk assessment carried out in line with Rsl 10 can be used to support this issue.
Management-based solutions
As a Part 1 issue, this intent must be achieved by systems which are intrinsic to the asset.
Management-based solutions (such as a concierge service, or security guards) cannot be used to achieve answer E (intruder alarm systems).
Answer F (alarm receiving centre) can only be achieved with a system that complies with Answer E.
Intruder alarms – Requirement for these to be audible when activated - KBCN1597
Where it is justified by the security consultant, project team or building management that a 'silent' intruder alarm system is more suited to the asset’s overall security strategy, this can be considered as meeting the Definition in our guidance.
Methodology – Procedure for measuring illuminance - KBCN1721
The following guidance, found in the Methodology section of BIU USA V6 Commercial, can also be applied to BIU USA V6 Residential assessments:
For assets with identical lighting systems and floor layouts across multiple areas or floors, illuminance levels in a representative sample of areas or floors may be measured, if in the professional opinion of the suitably qualified person, these are likely to give measurements that reflect the performance of the lighting in all relevant spaces within the asset. Illuminance measurements must be taken at least every five years and after any changes to lighting systems. Where the asset is less than five years old and illuminance levels were assessed as part of the design or construction of the asset that demonstrate compliance with the criteria in this assessment issue, then the results of these studies may be used as evidence (assuming there have been no changes to the lighting systems in the intervening period).
Minimising flicker – scope of issue - KBCN1639
Principle
Flicker from
all lighting systems is eliminated. This means eliminating flicker in:
- All lighting within management control, common areas, and tenanted areas.
- Occupied, un-occupied and external spaces.
Only emergency lighting is excluded. See
KBCN0185.
Lighting flicker is undesirable regardless of location or length of exposure.
Commercial scope
Eliminate flicker in all lighting.
Residential scope
Eliminate flicker in:
- All communal areas (internal and external, occupied and unoccupied).
- Management offices, and all areas under management control.
Minimizing watercourse pollution – Areas to be assessed - KBCN1633
Criterion 2 should be interpreted as follows:
The intent is to provide a list of areas that are likely to present a risk of watercourse pollution. All the listed areas must be considered, however, where a listed area is not present, or it is present but poses no risk of watercourse pollution, this should be justified with supporting evidence.
Where the development does not include any of the listed areas, or none of the areas present poses a risk of watercourse pollution, justification and evidence must be provided and this issue should be filtered out, in line with Criterion 1.
ModeScore Sustainable Transport certification - KBCN1705
Achieving
ModeScore Gold or Platinum certification can be submitted as part of the supporting documentation
to award credits for implementing sustainable transport options,
provided the BREEAM criteria were targeted, as follows:
| Scheme |
Issues |
Credits |
| BREEAM International NC 2016 and V6 |
Tra 03a Alternative modes of transport |
2 + Exemplary credit |
| Tra 03b Alternative modes of transport |
2 + Exemplary credit |
| Tra 04 Maximum car parking capacity |
1 |
| BREEAM UK NC 2018 and V6 * |
Tra 02 Sustainable transport measures |
10 |
| BREEAM Int RFO 2015 |
Tra 01 Sustainable transport solutions |
5 |
| Tra 04 Maximum car parking capacity |
2 |
| BREEAM UK RFO 2014 |
Tra 01 Sustainable transport solutions |
3 |
| Tra 03 Cyclist facilities |
2 |
| Tra 04 Maximum car parking capacity |
2 |
| BREEAM In-Use Commercial and Residential (International and USA) |
Tra 01 Alternative modes of transport |
8 |
| Tra 02 Proximity to public transport |
3 |
| Tra 04 Pedestrian and cyclist safety |
2 |
* BREEAM UK NC 2018 and V6 credits can be awarded provided the transportation assessment and travel plan (criterion 1) are met
When the assessor submits a ModeScore certification as evidence, they should include their report and highlight the BREEAM criteria or credits that were targeted.
About ModeScore Sustainable Transport certification:
ModeScore assess and certify sustainable transport facilities and services in buildings. ModeScore encompasses ActiveScore within its assessment criteria, covering four pillars of sustainable transportation while incorporating accessibility into each:
- Public Transportation
- Environmentally-Friendly Private Vehicles
- Active Transportation
- Site-Wide Mobility
ModeScore evaluates the connectivity potential of any building in any location, offering four levels of certification with a total scorecard of 120 points. ActiveScore (Travel Facilities) counts for 10 points:
- Certified (0-39%)
- Silver (40-59%)
- Gold (60-79%)
- Platinum (80-100%)
See more information and details at https://modescore.com/
Multiple ratings in a single assessment - KBCN1725
Sometimes the boundaries for energy performance ratings for meeting building regulations are split in a different way to the BREEAM assessment boundary.
If the BREEAM assessment boundary covers multiple energy ratings, for this issue only enter data on the rating which covers the largest NIA (Net Internal Area).
27-Mar-2025 - Published.
Night-time operation – requirement for controls - KBCN1048
Projects
or areas of an asset which operate at night-time can adapt or omit the requirement to provide controls or presence detection to align with the building’s hours of operation.
This could, for example, include service yards or car parks.
The aim of this Issue is to reduce the energy use for external lighting and should not interfere with the building’s operation.
02 Oct 2024 - Updated to clarify the scope of the this guidance and applied to NC V6 and BIU.
Occupant control – spaces requiring user controls - KBCN0170
This guidance is intended to clarify the types of area for which user controls are required or would be considered beneficial.
Zoning is required in all areas of the asset where specified in the assessment criteria. Please refer to the specific requirements of the applicable BREEAM standard to interpret this guidance appropriately.
User controls required
Spaces where users are expected to have independent control over their environment.
- Owned spaces: small rooms for a few people.
For instance, cellular offices, owned spaces in residential assets.
- Temporarily owned spaces: where occupants expect to operate the environmental controls while they are there.
For instance, meeting rooms and hotel bedrooms.
- Shared spaces.
For instance, multi-occupied areas such as open-plan offices or workshops.
User controls not required
Spaces where users are not expected to have independent control over their environment.
- Managed spaces: where environmental control is expected to be centrally managed.
For instance, atria, circulation areas, concourses, entrance halls, function halls, restaurants, libraries, and shops.
- Occasionally visited spaces.
For instance, storerooms, bookstacks in libraries, aisles of warehouses, toilets.
14-Dec-2022 - KBCN applicability updated to include BIU. Wording clarified, and amended for compatibility with BIU criteria.
On-site LZC – whole site shared connection - KBCN1424
To be recognised in BREEAM, the on-site Low and Zero Carbon (LZC) technology must have a direct physical connection to the assessed asset.
OR
Where the LZC technology is;
- Located on the same site,
- Is owned and managed by the same organization as the assessed building, and
- Where it is impractical to physically connect the assessed building to the system,
It is acceptable to allocate the renewable energy generated proportionally as a calculation of the asset's predicted energy consumption compared to the total energy consumption of the whole site.
To allocate renewable electricity by proportional consumption:
- Obtain the total annual renewable electricity generated on-site.
- Exclude all renewable electricity which has been exported to the grid.
- Determine the respective electricity consumption of all assets on the whole site (predicted for new builds and measured for existing assets).
Where consumption data is missing, renewable electricity must not be allocated to the assessed asset. In this case, it is assumed that all electricity consumed is sourced from the grid.
17-Jan-2024 - Applicability BIU V6 Ene 13 removed, as this approach is not applicable to assessing the area of PV fitted.
21-Dec-2022 - Applicability to In-Use V6 confirmed.
On-site or curbside storage and collection – Additional recyclable residential waste streams - KBCN1722
Answer C rewards on-site or curbside storage and collection of recyclable residential waste streams.
Answers G and H reward local storage and collection of additional recyclable residential waste streams.
Where Answer C is met and further recyclable residential waste streams are available with on-site or curbside storage and collection, these can be considered under Answer G or H.
Presence detection – illuminated signs - KBCN1671
The requirements for presence detection do not apply to illuminated signs.
In BIU V6, presence detection requirements are included as part of automatic energy saving controls. All other requirements in this criteria must still be met.
Refrigerant charge – issue filtering - KBCN1717
Criterion 1 states that if all systems have ≤11lbs refrigerant charge, this issue is filtered out.
In the asset, there may be a mixture of systems above or below this threshold.
In this scenario, this issue
still applies to all other systems with
>11lbs refrigerant charge.
All systems with refrigerant charge ≤11lbs are excluded from assessment, but if other systems are still in-scope, this issue still applies.
11-Feb-2025 - Published.
Resources inventory – Scope - KBCN1667
The inventory only needs to include resources that belong to the asset owner (or those which the asset owner or manger is responsible for maintaining or replacing). It does not need to included tenant-owned fittings and furnishings
Risk assessment – flooding is the only natural hazard - KBCN1552
Where:
- Flooding is the only natural hazard identified and,
- The flood risk assessment (FRA) from Rsl 01 is used as evidence for this issue,
then Answer D ('the asset is in an area where no risks exist') is only available where the FRA shows zero or low flood risk from
all sources of flooding listed within criterion 1 of RSL01 with the exception of:
d) Groundwater: most common in low-lying areas underlain by permeable rock (aquifers)
e) Sewers: combined, foul or surface water sewers
Assessing flood risk from rivers and seas only does not cover all risks.
13 November 2025 Updated to exclude groundwater and sewers from the requirements for Rsl03.
Safe pedestrian routes – Definition, measurement and verification - KBCN0238
Definition
Safe pedestrian routes include sidewalks and safe crossing points, which may be controlled or, for example, be identified by tactile paving, a crossing island or a dropped curb. An element of judgement may be required, in which case justification should be provided.
Measurement
Distances could be measured, for example, along a sidewalk, across a road at a safe crossing point and along the sidewalk on the other side. The distance should not be measured diagonally across a road, following the most direct route.
Verification
The assessor’s site inspection is an important aspect of the assessment and may help to confirm that all relevant information is current and can include photographs of any key areas. This can also help to identify safe crossing points or hazards which may not be apparent from a desktop study. However, web-based evidence may also be used where the assessor is satisfied that it is robust and demonstrates that it is up to date.
Where web-based navigation maps (e.g. Google Maps/Street View) are used as supporting evidence, this must include:
• Dated and marked-up site plan or a web-based navigation map viewer highlighting:
• Current location and type of transport nodes and local amenities.
• Current route and distance from the building via a safe pedestrian route.
• Plan or map scale.
When using web-based evidence for post-construction stage, the assessor must, additionally, provide verification that the information provided for the nodes/amenities is still accurate and up to date.
29 Aug 2025 - Approach to web-based map data at post-construction stage updated and related wording amended accordingly
07 Mar 2024 - No changes have been made. This appears as 'updated' due to an administrative error.
11 Jan 2024 - Wording re-structured for clarity
19 Dec 2023 - Applicability to BIU V6 confirmed
Shower with multiple shower heads - KBCN0855
To calculate the water use of a shower with more than one shower head, one of the following should be done:
- If all of the shower heads can be turned on at once, the flow rates should be added up.
- If the shower heads can only be used one at a time, the highest flow rate should be used
22 Feb 2024 - Applied to BIU, BREEAM NC and RFO standards
Sub-metering technologies – Compliance principle - KBCN1561
Where it can be demonstrated that alternative sub-metering technologies can meet or exceed the capabilities of systems set out in the BREEAM guidance, subject to approval, these can also be considered compliant.
It is the role of the Assessor and the project team to provide evidence and justification in a compliance principle query (see
KBCN1555).
The following metering standards or technologies are currently recognized as alternatives to pulsed output meters:
- M-bus.
I.e. systems that comply with the EN 13757 series of standards.
Also includes systems complying with the OMS (Open Metering System) standards.
Systems serving <10% overall floor area - other affected issues - KBCN1542
The methodology for Ene 01 states:
"Heating / cooling systems can be excluded from the calculation where the heated or cooled area equates to less than 10% of overall floor area."
Systems which heat or cool < 10% overall floor area
are not assessed in:
- Ene 01 Building services.
- Ene 05 Cooling.
- Ene 06 Heating.
Ene 01, 05 and 06 all feed into the asset energy calculator and so their inputs must be consistent. All other issues relating to these excluded systems are still assessed such as:
- Ene 11 Installed controls.
- Ene 15 and 16 Monitoring energy issues.
- Pol 03 Local air quality.
- Pol 04 Global warming potential of refrigerants.
User controls – Thermal comfort - KBCN1813
The requirement for user controls does not mandate a specific type of control; e.g. local manual adjustment.
Where control is provided indirectly, e.g. via BMS or central management, the assessor must demonstrate that this approach meets the intent of the user comfort and accessibility criteria and is informed by end-user discussions or relevant design guidance.
Please refer to
KBCN0170 for clarification of the types of space requiring user controls.
Using water from natural underground sources to offset water consumption - KBCN00094
Water from natural underground sources (for instance aquifer water accessed via boreholes) cannot be used to offset:
- NC / RFO: potable water consumption.
- IU: utility supplied water consumption.
A significant amount of water used for public consumption is already drawn from aquifers. Private boreholes may be drawing water from the same sources as public utility companies.
27-Mar-2024 - Title and text updated to broaden definition. Scheme applicability updated.
View out – Calculating the glazing to wall ratio - KBCN1506
This should be calculated based on the glazed area of window, expressed as a percentage of the area of the external wall in which the window sits.
Where the ceiling height of the room is unusually high, relative to the window height, the wall area can be calculated based on a standard ceiling height for the building type.
Washer dryers - KBCN0699
Where a washer dryer is specified, the water consumption figure for the wash and dry cycle should be used.
The drying cycle of a washer dryer is taken into account because it usually uses water during this drying process (e.g. for cooling during the drying cycle) and in some cases, this water usage can be significant.
18-Nov-2022 - Updated to apply to BREEAM In-Use Version 6
Washing machines and dishwashers – Water consumption data - KBCN1571
The water consumption data used to demonstrate compliance may be based on the lowest full wash cycle (i.e. not a pre-wash cycle, for example).
Waste streams – clarification - KBCN1526
Scope
The focus of the criteria is on
recyclable materials only. Any facilities / spaces for managing recyclable materials must be
in addition to spaces / facilities for managing general waste.
Definition
“Waste streams are flows of specific waste, from its source through to recovery, recycling or disposal. Waste streams can be divided into two broad types:
- Streams made of materials (such as metals or plastics).
- Streams made of certain products (such as electronic waste or end-of-life vehicles).”
Source
For BREEAM, a waste stream is a material / product with its own recycling process. This means each stream needs to be separated from other materials before it can be effectively processed into new materials / products. This separation can happen in the asset, or (in the case of co-mingled waste) after collection from the asset.
Residential waste streams
In most cases, this is defined by how it will be how be sorted and collected by municipal waste authorities. Where no local guidance exists, the list below may be used as a guide.
Recyclable waste streams (answer option C in BREEAM USA In-Use Residential V6):
- Paper and cardboard.
- Glass.
- Plastics.
- Metals.
- Wood and wood-based products.
- Oils.
- Batteries.
- Electrical and electronic equipment.
Compostable / recyclable waste streams (answer option D in BREEAM USA In-Use Residential V6):
- Food waste.
- Garden waste.
Commercial waste streams
Commercial assets will generate specialised waste streams specific to the asset's function. These are typically:
- Generated consistently, and in large volumes.
- Are specifically separated for recycling.
In these cases, waste streams such as metals, plastics and paper / cardboard may be sub-divided into specialised waste streams where they meet the above.
Example scenarios
[accordion]
[accordion_block title="Scope"]
A vehicle repair workshop generates the following waste streams:
- Metals.
- Paper / cardboard.
- Plastics.
- Engine oils.
- General waste.
The engine oils and general waste cannot be re-processed into other usable materials. Only 3 recyclable waste streams can be considered for BREEAM assessment.
[/accordion_block]
[accordion_block title="Residential"]
The local authority collects co-mingled waste for the asset. This waste mixes together:
- Metals.
- Paper and cardboard.
- Plastics.
This co-mingled waste can be counted as 3 waste streams.
[/accordion_block]
[accordion_block title="Commercial"]
A supermarket consistently generates large quantities of cardboard packaging. This cardboard forms a significant portion of recycable waste generation. It is baled up and collected separately by a specialised waste contractor.
In this case, cardboard waste can be considered a separate waste stream from paper.
[/accordion_block]
[/accordion]
18-Jan-2024 - Clarified list of residential waste streams (separated compostable waste streams and added relevant answer options).
Information correct as of 26thFebruary 2026. Please see kb.breeam.com for the latest compliance information. This affects the following tables:
This affects the following tables:
