
Refurbishment and Fit Out
Information correct as of 9thMarch 2026. Please see kb.breeam.com for the latest compliance information.
Absence of regulated/prohibited wood preservatives - KBCN0740
This requirement for wood panels means that PCP (pentachlorophenol, a regulated / prohibited substance) must be absent.
In this case, 'absent' is defined as <5 parts per million.
This must be verified by testing.
11-Oct-2022 - Title amended to standard naming format for clarity and consistency. Wording clarified.
Acceptable alternative strategies to sub-metering by floor plate - KBCN00071
An alternative sub-metering strategy, not based on a by-floor-plate basis, would be acceptable provided that:
- it provides an equivalent, or more useful level of detail than sub-metering by floor plate.
- it divides the assessment in a logical manner which provides useful information to building management re: energy use.
- the approach does not conflict with requirements for sub-metering other functional areas.
The intent of sub-metering by floor plate is to allow a large homogenous function (such as office space) to be split up into smaller areas that will allow building management to monitor, identify and influence areas of high energy use. Alternatives that also meet this intent are also acceptable.
Acceptable deviations – ISO 7730:2005 category B - KBCN1714
Acceptable deviations from category II thermal modelling criteria can be made in accordance with CEN 16798-2:2019 Anne E, only when the thermal comfort assessment uses CEN 16798 to demonstrate compliance. Where this is the case, up to a 6% deviation based on yearly occupied hours can be accepted when demonstrating compliance.
Note: this KBCN no longer allows the deviations to be used for ISO 7730:2005. However, for assessments where the assessor has advised the project team based on the original KBCN, prior to this update, this will be honoured if you provide evidence of this in your assessment.
KBCN wording 16 Jan 2025 - 10 Jul 2025:
~ Acceptable deviations from the ISO 7730:2005 category B criteria thermal modelling criteria can be made in accordance with CEN 16798-2:2019 Annex E. Up to a 6 % deviation based on yearly occupied hours can be accepted when demonstrating compliance ~
10 Jul 2025 - KBCN updated following further review of relevant standards
Accessibility of energy metering systems - KBCN0580
Energy metering systems should be accessible and the energy consuming end uses visible to building users, such as the facilities manager, where present, and/or other building occupants responsible for the management of the building.
Accreditation – sampling and testing laboratories - KBCN1337
Analysis / testing laboratory
NC 2016 or newer: Where an organisation used for the analysis of indoor air or emissions from building products is not accredited to ISO/IEC 17025, the organisation must be accredited, either by a national accreditation body, or by a member of any one of the following accreditation groups:
European Cooperation for Accreditation
International Accreditation Forum
International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation
The accreditation must specifically cover the analysis of indoor air or emissions from building products.
Other schemes: Accreditation to ISO/IEC 17025 is
not required in the criteria. However, this KBCN has been applied to encourage a consistent approach towards accreditation.
Accreditation by a national or internationally recognised organisation helps to ensure rigorous, consistent and reliable testing results.
Sampling organisation
If another organisation carries out sampling on behalf of the analysis / testing laboratory, this organisation does not need to be accredited to the above. However, they must provide a brief report justifying:
- The sampling methodology used.
- Appropriate environmental conditions during the sampling.
- The number and location of samples taken.
This report is provided to the BREEAM assessor and submitted as supporting evidence for this issue.
31-Oct-2022 Wording clarified. Scheme applicability updated.
10-Oct-2022 Title amended for clarity. Scheme applicability updated.
24-May-2022 Updated to differentiate between sampling and analysis requirements.
07-May-2021 Added clarification regarding alternative qualifications.
10-May-2021 Updated scheme applicability.
Acoustic performance standards - KBCN0922
For the Acoustic performance standards credits it is possible to use either:
- the building regulation requirements or other appropriate good practice local standards
or
- the good practice criteria outlined in the BREEAM manual.
If assessors want to use standards that have not been approved yet, they should submit these to BRE along with all relevant documents detailed in the standards approval process. The extent and scope of these local standards and the SQAs justification statement will be checked by BRE acoustic experts to ensure that the overall effect is similar to the stated BREEAM requirements.
Adaptability for a projected climate change scenario – Winter conditions - KBCN1715
Where future climate change scenario projections in winter indicates a higher temperature and, therefore, more thermally comfortable climate compared to the current winter temperatures, it can be assumed that the winter conditions within the climate change scenario are met based on the thermal modelling of current winter conditions. Justification must be provided for each project confirming that the future winter conditions will be met with the current heating system.
In a warming climate the heating system needs to be sized for the beginning of its lifespan, whereas the cooling systems need to be sized for the end of their life span (Ref: CIBSE TM55: 2014)
Adaptation to climate change strategy study – timing - KBCN0533
Late consideration of the climate change adaptation strategy study, might reduce the study to a ‘paper exercise’, with minimal value to the project.
However, if the assessor is satisfied that there is clear justification for the strategy being developed at a slightly later stage (i.e. early RIBA stage 3) AND there is clear evidence that the strategy has achieved the intended outcomes (i.e. the later consideration has been in no way detrimental to the outcomes of the strategy study/appraisal and the benefits can still be realised on the project), then this will be sufficient for compliance. In any case, all other requirements of the issue must be met for the credits to be awarded.
The requirements for the timing of the climate change adaptation strategy are intended to ensure that the benefits of these strategies are realised through early consideration.
Adoption of road in the development - KBCN0331
Where a development includes roads, these are often adopted by a statutory authority (for example the Highways agency or the local authority in the UK).
Where the authority will be taking responsibility for the roads, the following guidance should be followed to determine if the water run-off from the roads needs to be considered as part of the assessment:
- If the road drainage system bypasses the new development's network to connect directly to the local drainage network, then the water running off from the roads does not need to be considered for this assessment. Evidence will need to be provided to demonstrate if this is the case.
- If the road drainage system connects to the development drainage network before connecting to the local drainage network, then the water run off from the roads must be considered for the assessment.
Where the authority will NOT be taking responsibility for the roads, the BREEAM criteria should be followed for all drainage on site.
Aftercare – speculative developments - KBCN0101
For speculative projects (i.e. where the end occupiers are unknown), the Aftercare issue will be filtered out. Any relevant minimum standard will not be applicable in such cases.
Where the end-user is unknown it is not possible to demonstrate compliance with the Aftercare issue requirements.
AI calculation – changes to public transport services during the assessment - KBCN1527
The AI is calculated as part of the design stage transport analysis and its value relates to the site location and to informing transport-related design decisions. This must be based on current information, including any planned and publicly-notified changes at the time the transport assessment is carried out. This should be used as the AI benchmark for the assessment.
Where later, unforeseen changes to public transport availability are implemented before post-construction certification, the AI benchmark should not be updated at post-construction stage.
Assessments should not be disadvantaged by, or benefit from such changes.
Air-conditioned spaces - KBCN00035
Air-conditioned spaces are assessed to ensure appropriate thermal comfort levels are achieved. Cooling capacity should be sufficient to comply with the requirements of CIBSE Guide A, however providing sufficient space to install additional capacity to meet the requirements at a later date in line with projected climate change scenarios is also acceptable.
In addition, if it can be demonstrated that the air-conditioning system can achieve the thermal comfort criteria in accordance with CIBSE Guide A, Table 1.5, thermal modelling does not need to be carried out. The “time out of range” (TOR) metric should be reported as 0%.
Aircraft safety – developments in the proximity of airports - KBCN0977
Where it can be demonstrated that an assessed development, within or adjacent to an airport or similar must restrict the ecological value of the site for reasons of aircraft safety (mitigating the risk of bird-strikes to meet ICAO/EASA/CAA or equivalent regulations), the approach for some issues in the Land Use and Ecology category can be adjusted. If in these circumstances, the client wishes to enhance ecological value on an external site, outside of the main development site, this can be considered in the following way for each issue:
Ecological value of site and protection of ecological features: The development site only must be assessed, but the recommendations may be tailored to suit the requirements of the relevant legislation.
Enhancing site ecology: The development site and the external site must be included in the SQE’s report and recommendations, albeit that, for the development site, the approach may to be to restrict biodiversity. Enhancements implemented in-line with the recommendations of the SQE are likely to apply to the external site.
Long term impact on biodiversity: Both sites must be considered in the SQE’s report, albeit that, for the development site, the approach may to be to restrict biodiversity. Credits for additional measures to improve the site’s long-term biodiversity can be awarded on the basis of adopting these for the external site only, in line with the guidance.
Alignment between BREEAM and the Fitwel certification system - KBCN0737
BRE, as an independent and impartial research-based organization, is working with the Center for Active Design (CfAD) and International WELL Building Institute (IWBI) to promote and improve health and well-being in the built environment. The aim of both these agreements is to support our clients who want to pursue either Fitwel or WELL alongside the BREEAM standard.
To simplify the process for project teams pursuing both assessment methods, BRE has worked together with the respective organizations to compare performance requirements, identify specific documented credits and evidence that will be recognized by both organizations to streamline the process of achieving dual certification. This work demonstrates the significant synergies between the various methods and the efficiencies that exist between their respective assessment and certification processes. Because of BRE’s unique position as an impartial organization, it is possible to form these important collaborations with like-minded organizations to work together to harmonize approaches to health and wellbeing in the built environment across their standards, research programs and services.
Further information can be found in the Resources section of the BREEAM website:
For Fitwell –
https://bregroup.com/brebreeam/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2017/06/98107-BRE-BREEAM-USA-briefing-paper-fitwel-216x279-002.pdf
For WELL –
http://files.bregroup.com/breeam/briefingpapers/BREEAM-Briefing---Assessing-Health-and-Wellbeing-in-Buildings---January-2017--93678-.pdf
Alignment of RFO fit-out with New Construction shell only and shell and core assessments - KBCN0731
Where seeking a fully-fitted certificate for a shell only or shell & core project assessed against the BREEAM NC 2014 scheme, the advice provided within the scope section of the RFO manuals has been superseded.
The original concept to provide ‘fully-fitted’ ratings and certificates following BREEAM New Construction shell or shell and core certificate has been dropped in favour of separate independent assessments, certificates and scores in the normal way. This is partly due to lack of demand and partly due to the complexities of mapping, managing and scoring one set of criteria against another at completely different stages.
For a comprehensive BREEAM assessment of a project that has two separate construction stages, two separate BREEAM assessments should be undertaken. For example, a shell only BREEAM New Construction assessment, the same as Part 1 in BREEAM Refurbishment and Fit-out (RFO), will have a certificate for the original design. Later on, the fit-out (RFO Parts 2, 3 and 4) can be undertaken and will have a separate certificate. The two separate certificates will then represent a comprehensive BREEAM assessment and best reflect the different scopes of the different project stages.
This will be be updated in the next reissue of the technical manual.
Alternative calculation method - KBCN0547
Where it is not possible to use the standard approach to determine the building’s total water consumption, the assessment can be completed on an elemental basis. This applies even in cases where the Wat 01 Excel calculator tool has a section for a broader building type, but the defined activity areas do not match the specific project under assessment. For example, although Wat 01 calculator includes a retail calculator, bars and restaurants should be assessed using the alternative calculation method, as no relevant data is available for the specific activity within retail.
Where the activity areas of the building under assessment do not allow using the relevant building type’s calculator, then the alternative calculation approach should be used.
Alternative transport measures not applicable to the project - KBCN0965
It is acknowledged that certain alternative transport measures may be considered not applicable to the project under assessment, due to building type, scope of refurbishment, etc.
Upon provision of clear justification for the exclusions, in such instances, in order to ensure a fair assessment, an alternative calculation method has been introduced.
This method is only applicable where there are less than six measures deemed to be appropriate and in all other instances the methodology outlined in the manual applies.
The Assessor will:
- Identify the number of measures applicable to the assessment;
- Determine the number of measures that have been complied with;
- Determine the percentage of measures achieved, and based on this, the proportion of credits achieved.
Please see the worked example below, where the Assessor:
- Deems that five alternative transport measures are appropriate for the project;
- Demonstrates compliance with three of these measures;
- Determines the percentage of compliance, ie 60% (three out of five measures). This results in the awarding of 60% of the three credits available to this assessment, ie 1.8, which, to ensure robustness, will be rounded down to the nearest whole number, with a final one credit achieved.
The number of credits achieved is proportioned to the percentage of compliant measures against the total number of measures applicable to the project.
Alternatives to composting - KBCN0465
In anaerobic digesters, organic waste is digested by micro-organisms which break down fats, oils and grease. Digesters where the only output is water that is safe to discharge into drains and sewers are acceptable alternatives to composting.
Macerators which simply reduce solids into small pieces through a shredding or grinding process and flush the residue into the drainage system are not an acceptable alternative to composting.
Amenities – Access to cash - KBCN0359
Refers to the availability and convenience of reaching an Automated Teller Machine (ATM) to access cash. Building users should have access to cash at all relevant times of day. This is interpreted as availability during the local community's typical active hours.
For non-residential assessments:
- Relevant times refer to the building’s operating hours or the typical active hours in the local area.
- An ATM inside a building is acceptable as long as its operating hours are convenient for building users.
- This should not require a prior purchase of goods and should provide access to other services, such as checking account balances.
For residential assessments:
- 24‑hour access is preferred; however, access during typical active hours (e.g., 07:00–22:00) is acceptable when 24‑hour provision is not feasible or not available locally.
19-Feb-2026-clarified residential requirements to align with non-domestic schemes. With cash being used far less freque
Amenities – Assessed building is one of the listed amenities - KBCN0264
Where the assessed building is itself included in the list of amenities, that particular amenity criterion can be deemed to be met, e.g. a supermarket development itself meets the proximity to food outlet required for a Retail type building.
Amenities – Pharmacy within a hospital or health centre - KBCN0321
To meet the requirements of 'Over the counter services associated with a pharmacy', a dispensary within a health centre or hospital can be considered as meeting the intent, provided it is publicly accessible and also offers the type of over-the-counter services associated with a stand-alone pharmacy, such as non-prescription medication and health products.
Note: This is a change to the approach outlined in the previous KBCN wording, therefore, for assessments registered before this update, where it can be demonstrated that the the assessor has advised the project team based on the previous wording, this can be accepted:
Superseded guidance:
A publicly accessible pharmacy would typically be required in order to constitute a suitable amenity. If it can be confirmed that an internal pharmacy (in Northern Ireland this may also include an onsite controlled medical dispensary) will provide prescribed medicines for building users, this is acceptable.
18 June 2025 - Title updated and wording amended to clarify the intent. Applied to NC V6 standards.
Amenities – Sandwich van as a food outlet - KBCN0557
A food truck/ mobile catering service would not be sufficient to meet the criteria for this issue.
The aim of this Issue is to assess the location of the built asset relative to amenities.
Amenities – Vending machine as a food outlet - KBCN0653
A vending machine can be considered as a food outlet if a range of items, as can be reasonably expected, are for sale to meet the needs of the building users and it is confirmed to be a permanent fixture.
Applicability – industrial operational areas - KBCN1342
The aim of this issue is to encourage a healthy internal environment. For the operational areas of industrial buildings, the internal environment is dictated by health and safety requirements. This means that the BREEAM requirements should not be made applicable to them, and so the operational areas can be ignored in the assessment of Hea 02.
10-Oct-2022 - Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Made applicable to UK and International NC V6.
Applicability – retail asset with no office areas - KBCN0531
The compliance note regarding industrial and retail areas incorrectly suggests that the minimising sources of air pollution credits are not applicable to retail areas with no associated offices. These credits do apply to retail sales areas, although they are excluded for operational areas in industrial buildings.
The 'potential for natural ventilation' credit is not applicable for retail sales areas, as it applies only to office areas. Therefore, where a retail building does not contain any office, this credit is not applicable.
While the requirements apply to permanently or semi-permanently occupied offices, small admin areas, which are only used occasionally can be excluded.
This also applies to shell only and shell and core new build projects, where it can be demonstrated that no office spaces will be provided as part of the fit-out.
The online tool will award the credit by default in both issue 1.0 of the INC 2016 scheme and up to issue 1.4 of the IRFO 2015 scheme. When assessing against INC 2016 2.0 and V6, the online tool will instead filter this credit out.
22-Oct-2022 Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Made applicable to International NC V6.
11-Sep-2018 Clarification added in relation to spaces that are used occasionally, and shell only/shell and core new build projects.
15-Sep-2017 Clarification added on the procedure for making the 'potential for natural ventilation' credit N/A on the online tool. Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next re-issue.
Applicability of flow control devices - KBCN00057
The criteria are applicable to the cold water supply only and include cold taps, WCs and urinals. Any solution implemented to achieve compliance with this Issue should effectively mitigate the risk of hot-water scalding in showers, in the event that the cold water supply is shut off.
06/03/18 - Wording amended to make the guidance more outcome-driven and to account for solutions other than not providing flow-control devices on the supply pipework to shower areas.
Applicability of prerequisite - KBCN1072
The prerequisite must be met in order to award any credits where refrigerants are used. It is also applicable when the 'leak detection' credit is awarded on the basis of the refrigerant charge being less than 6kg.
Applicable assessment criteria (Parts 2 – 4) - KBCN0896
Due to an error within the publication process of SD225 (issue 1.4 onward), there is incorrect information related to the applicability of assessment criteria to Parts 2 - 4. The following information should be used to determine the applicability to assessment criteria.
Part 2: Criterion 1 - 4, Criterion 5 and 6a, and Criterion 9 and 10.
Part 3: Criterion 1 - 4, Criterion 5 and 6b, and Criterion 9 and 10.
Part 4: Criterion 1 - 4, Criterion 5 and 6b (see CN13 within Man 04), and Criterion 9 and 10.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly at the next reissue
Applying internal partition sound insulation criteria to internal doors - KBCN0665
Where sound insulation criteria apply to internal partitions the calculations do need to include any doors which are part of the wall in question.
While sound insulation performance of a typical door will be lower than for a typical wall, with careful design, specification and detailing, this can be overcome.
Applying the requirements to shell only + shell and core assessments - KBCN00075
A Suitably Qualified Acoustician (SQA) must carry out a quantifiable assessment of the specification of the built form, construction and any external factors that are likely to affect the indoor ambient noise levels. From this assessment, the SQA must confirm that the developer’s scope of works will enable a future tenant utilising a typical fit-out and specification to meet the levels required to demonstrate compliance with the BREEAM criteria.
Where the specific room functions and areas within the building are yet to be defined, the acoustician’s assessment should demonstrate that the criteria for the most sensitive room type likely to be present in the building is capable of being achieved. Where the typical fit out would include a range of requirements (e.g. offices with a mix of open plan, cellular offices, meeting rooms and breakout areas; or retail with sales floor, stock/storage, office and staff rest areas), the acoustician should make an assessment based on a speculative layout and outline specification to determine whether the requirements of the relevant best practice standard are achievable and include examples of the most sensitive room types.
Where the majority of a building’s floor plan will require high performance acoustic environments (e.g. classroom/seminar buildings), then the BREEAM requirements must be achieved for the entire shell where specific layouts are not determined by the built form.
Post-construction testing is not required subject to confirmation from the project team that the built form, construction and any external factors have not changed from those used in the SQA's assessment.
14-Feb-2024 - Scheme applicability updated. Clarified applicability to shell only assessments. Title updated.
Apportioning foundations where not all floors are assessed - KBCN0643
Where a development does not include all the storeys of a building, not all of the aggregates used in the building foundations need to be included in the assessment. Any apportioning must be justified and calculated by a structural engineer, and it is the responsibility of the assessor to ensure that the process used is appropriate, robust and meets the aim of the credit issue.
Approach to thermal model when using BMS - KBCN0169
Where there are smart systems such as BMS in place, modelling must consider normal operating conditions, with the heating and cooling system in operation regardless of the control strategy.
In order for the design team to size the heating/cooling plant, they will carry out modelling to calculate the heat/cold loss throughout the year. Results of these calculations must be submitted, with the heating/cooling plant specification which would demonstrate that the building has been designed to ensure internal winter/summer temperatures will not drop below an acceptable level, and that in effect the winter TOR is zero.
Appropriate project stage to appoint a suitably qualified acoustician - KBCN0256
BREEAM requires that a suitably qualified acoustician is appointed at an appropriate stage of the project, so as to ensure that early design advice on criteria of pre-requisition is met. The aim is to ensure that costly amendments to building designs are not made as a result of late appointment of the acoustician. Ultimately, it is for the assessor to determine at what stage of the project is deemed to be appropriate for this appointment to have taken place given the project specific circumstances and procurement type.
Approved Equivalent Roles List (AERL) - KBCN1809
BREEAM International standards are unique because of their flexibility.
For International projects, Assessors can submit roles to substitute those described in the Technical Manuals. Provided that such roles are equivalent to the BREEAM specified roles, BRE Global will approve them for use in a particular country or region.
The
Approved Equivalent Roles List is a record of all roles that BRE Global has approved to date. The list is periodically updated to reflect recent approvals or withdrawals.
Using existing approved roles
Where you are using an approved role, and not the role described in the criteria in the scheme Technical Manuals, a copy of the AERL should be included as part of your evidence submission for QA.
AERL versions
The version of the AERL that is current at the time of registration is the one that is used for assessment. Newer versions released after this can also be used, however older versions before the registration date cannot be used.
For example: if the version current at registration was v3.0, then v3.0 (or any later versions) can be used, but v2.0 (or any earlier versions) cannot be used.
Proposing new roles
New roles cannot be proposed if they are not of equal competency to the BREEAM requirements. Only roles which are equivalent or more rigorous than the BREEAM default roles are considered.
If you wish to propose a new role which you think is equivalent in your country or region:
- Check what the role needs to cover by referring to the roles described in the scheme Technical Manual definition.
- Complete BF2599 BREEAM Approved Equivalent Roles Application Form and send this to our Technical Team via the Query Webform, adding AERL into the subject field.
The information provided to us within this form must include:
- the names of the proposed role(s)
- confirmation of the scheme and issues the role should apply to
- confirmation of the roles / competent persons you are referring to in the manual
- a detailed explanation of how this work is conducted in your market and how it meets the same level of competency as the BREEAM requirements
- documentation to support your explanation which is clearly marked for our ease of reference. If the documentation is not in English, translations of the relevant sections must be provided.
We will need a few weeks to review the information (please check with us for time scales). If there is missing information, or the information is not clearly referenced, this might take longer.
If successful, we will send you a revised copy of the AERL which includes the new role, and will update this for future versions of the AERL.
Areas consuming less than 10% of the building’s total water demand - KBCN0662
Where water-consuming plants or building areas are required to be sub-metered as a minimum, the requirements apply even if those plant/elements consume less than 10% of the building's total water demand.
Assessing basement external walls - KBCN0241
Only the external walls above ground level are required to be assessed under this issue.
The external walls below ground (i.e. within a basement area) perform a specialist function, these are not comparable with other walls in a building.These are therefore excluded from assessment under this issue.
Assessing equipment to be provided later by the tenant/occupier - KBCN0609
The efficiency of equipment to be provided as part of a subsequent fit-out falls outside the scope of this Issue.
Likewise, in a fully fitted but speculative office, where an unknown future tenant will be providing, for example, their own computers, these computers are to be excluded from the assessment.
Compliance must be demonstrated by the equipment fitted/installed within the scope of the development being assessed and, unless specifically stated otherwise, the use of commitments or legally-binding agreements is not accepted to demonstrate compliance for final certification within this BREEAM Scheme.
24/02/2017 CN amended to incorporate KBCN0701
Assessing industrial spaces – exemptions - KBCN0734
The thermal comfort criteria do not apply to the operational or storage areas typically found in industrial assets or other similar asset types. The criteria is still be applied to the other parts of the asset as appropriate.
Operational and storage areas often have function-related thermal requirements determined by operational or storage needs. These functional requirements override the needs of any occupants.
17-Jan-2024 - Scheme applicability updated.
Assessing thermal comfort – Residential buildings - KBCN1408
CIBSE TM59 can be used to demonstrate compliance with the thermal comfort requirements for residential buildings, instead of ISO 7730:2005.
This is to recognise the most up to date methodology relating to the assessment of homes.
26 Jan 2025 - Updated to apply to multi-residential buildings (long-term stay) and scheme applicability extended to account for this.
Assessment Part applicability - KBCN1165
The scope of this Issue is determined by the RFO Part(s) assessed.
For example, in a Part 3 only assessment, compliance must be demonstrated only for local services.
The same principle applies when assessing against Part 2 only, where only the core services need to comply.
This Issue is not applicable to Part 1 or Part 4.
17.08.2018 Technical manual to be amended in the next reissue.
Assessment parts criteria applicability - KBCN0807
The current criteria applicability in the technical manual contains typos and the below should be followed:
Part 1: Criteria 1-3
Criteria 4-6 (options 1 to 3 listed in CN6 only)
Part 2: All criteria are applicable
Part 3: Criteria 1-3 are applicable to consider local services that utilise passive design
Part 4: This issue is not applicable
Please note that this is not an amendment of criteria applicability, but a clarification in accordance with the original issue intent and with the functionality of BREEAM Projects.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
Asset classification – co-living developments - KBCN1568
The following is a guide only. Every project is unique, and assessors must in all cases review the suitability of the criteria to determine the most appropriate asset classification.
Co-living features
Co-living developments generally combine:
- Self-contained residential apartments with private kitchens and bathrooms.
- Apartments are typically rented for long-term stay (i.e. for periods of more than one month).
- Managed communal areas for work and leisure.
- Managed common facilities.
- Managed landscaping and external areas.
Classification
- For NC or RFO, generally the most appropriate asset classification is 'Residential institutions - long term stay.'
- For BIU, it is Residential.
As a guide, assessors can also consider how their asset is classified according to local regulations.
Astroturf (artificial grass) - KBCN0106
This is not be considered as hard landscaping and should be excluded from the assessment of this issue.
ASWL in Interim and Final assessment stages - KBCN0427
Provided that the same standards are used at both Interim Design Stage and Final Post-construction Stage, it is not necessary to resubmit the Approved Standards and Weightings List at the Final Post-construction Stage.
ASWL location weightings - KBCN0436
As the BREEAM International schemes (New Construction 2013, New Construction 2016, and Refurbishment and Fit-Out (RFO) 2015) allow for the assessment of buildings across the world, the environmental weightings for projects are set per country, or per region if the country has significant land mass with varying climates/ environmental issues. These are listed in the Approved Standards and Weightings List (ASWL). The online tool selects the relevant weightings based on the country selected in the Assessment details tab for International New Construction 2016 and International RFO 2015. Details of newly confirmed country weightings are released periodically in an updated ASWL.
If weightings have not been set for a country, it is because BRE Global does not have sufficient data to determine the appropriate weightings yet. As the scoring cannot be confirmed, it is not possible to submit the assessment for certification until weightings have been set. Therefore we ask assessors to complete, with the help of a local expert if necessary, and submit the BREEAM International Weightings Form, available from BREEAM Projects>Documents and Tools. BRE Global will then review and confirm the weightings for the country or region. Please make sure to complete and submit the BREEAM International Weightings Form related to the scheme under which the assessed project has been registered.
Please note that this automatic selection of weightings is not in place for International New Construction 2013 and 2009 versions.
ASWL submission protocol - KBCN0762
Where a new standard is being proposed the ASWL should be submitted to BRE for approval in advance of any subsequent assessment certification submission to QA.
Where a project is using previously approved standards only, the assessor only needs to submit the ASWL to QA and not prior to this for approval.
ASWL: Approved Standards and Weightings List - KBCN0423
BREEAM International schemes are unique because of their flexibility.
The Approved Standards and Weightings List is a record of all local codes and standards that BRE Global has approved to date. The list is periodically updated to reflect recent approvals or withdrawals.
If stated in the manual, local best practice codes and standards can be submitted to BRE Global to substitute the standards described in the criteria in the scheme Technical Manuals. Provided that such standards are equivalent to the BREEAM specified standards, BRE Global will approve them for use in a particular country or region.
Using existing approved standards
A copy of the ASWL being used should be included in every evidence submission for QA.
If the ASWL is being used without proposing any new standards, the ASWL can be submitted to QA at the same time as the rest of the evidence. It is important to notify QA of which standard (international or local) you are using for each issue.
Default standards
Where no appropriate local standard exists, international, European or UK standards can be used by default. UK standards can be found in the UK country tab. No technical query or permission is required.
ASWL versions
The version of the ASWL that is current at the time of registration is the one that is used for assessment. Newer versions released after this can also be used, however older versions before the registration date cannot be used.
For example: if the version current at registration was v33.0, then v34.0 (or any later versions) can be used, but v32.0 (or any earlier versions) cannot be used.
Standard versions
Where a standard has been updated, it is not automatically added to the ASWL template as the scope of the standard may have changed.
Please provide a copy of the relevant parts of the standard translated into English indicating where in the standard the requirements in the ASWL are met.
Alternatively, if you have evidence demonstrating the scope of the standard has not changed, this is acceptable too for approval.
Proposing new standards
New standards cannot be proposed if they are easier to achieve than the BREEAM requirements. Only standards which are equivalent or more rigorous than the BREEAM default standards are considered.
If you wish to propose a new standard which you think is more relevant to the assessment, or if an existing local standard has been replaced:
- Check what the proposed standard needs to cover by referring to your country tab
- Input the names of proposed standard(s) in the relevant column of your country tab. More than one standard can be proposed, if together, they cover our requirements.
- Identify the relevant clauses in the standards that show how these standards meet our requirements, and make sure these are clearly marked so they are easy for us to check. If the standard is not in English, translations of the relevant clauses must be provided.
- Send the standards and all of the supporting information to us via the ‘Assessor Queries’ section on BREEAM Projects for our review. We will need a few weeks to review the information (please check with us for time scales). If there is missing information, or the information is not clearly marked, we might take longer.
If successful, we will send you a revised copy of the ASWL which includes the new standard, and will update this for future versions of the ASWL.
18-Aug-2025 - Guidance under headings, 'Standard versions' and 'Proposing new standards' updated. Applied to INC V6.
05-Aug-2020 - Broken link to video removed and replaced with explanatory text
05-Jul-2017 - Link to video guidance added
Backup or emergency heating systems - KBCN0936
NOx calculations should be based on permanent heating systems and should not include backup systems used for maintenance or in emergencies.
BREEAM assessments measure the as designed performance level of the building as it normally functions.
Bamboo, cork and other non-timber forest products – Responsible sourcing - KBCN1768
Non-timber forest products, such as bamboo and cork should be responsibly sourced to minimise the environmental impacts and protect local ecosystems. However, as they are not timber or timber-based products, these fall outside the scope of the Prerequisite.
Where such products are integrated into a building, they should, nonetheless, be assessed and included in the calculator under ‘Other materials’.
Boundary Protection - KBCN0753
Only boundary protection specifically forming the site boundary should be included in the calculations. This may not necessarily be located on the boundary of ownership, but is the physical barrier which ostensibly encloses the development.
Any other freestanding walls or fencing within the site can be excluded.
BRE Environmental Profile certificates - KBCN0777
BRE Environmental Profile certificates are compliant EPDs and can be used as evidence for the purposes of Mat 01.
BREEAM Accredited Professional (AP) – Retrospectively applying AP status - KBCN0308
The AP status cannot be applied retrospectively. The purpose of using an AP on a project is that they can advise and steer the development from the outset to maximise its BREEAM and sustainability performance for the least cost/risk. If early AP appointment and involvement does not occur then the aims and criteria of this BREEAM issue are not being met.
BREEAM AP – Achieving the design credit at the Post Construction Assessment - KBCN0215
Where a project will be undertaking a post construction stage assessment only (no interim assessment), to demonstrate that the criteria were met at the design stage a "BREEAM credit monitoring report" should be provided when the assessment is submitted, which shows that at the design stage of the project the building was still on target for the proposed BREEAM rating. This could be an excel document showing the issues that the design is on target for achieving with a short summary of how the BREEAM AP is steering the project for the correct rating.
As long as the criteria are met and the correct information can be gathered for your evidence, a design stage certification is not required.
BREEAM AP – Change of BREEAM APs/Sustainability champions during project - KBCN0295
Whilst it would generally be preferable to retain the same individual in the role of BREEAM AP/Sustainability champion throughout the design and construction of a particular project for the purposes of continuity, we appreciate that this may not always be feasible. It is therefore entirely appropriate that the three credits available for using BREEAM APs/Sustainability champions can still be awarded where the individual performing the role changes (provided the ongoing involvement of an AP/SC is maintained in accordance with the criteria).
BREEAM AP/Sustainability Champion appointment timing - KBCN0738
It is acceptable for the BREEAM AP/Sustainability Champion to be appointed later than the required stage, if it can be demonstrated that the AP/Sustainability Champion was appointed at the earliest appropriate time in the project and that the late involvement will not have a detrimental effect on the setting of BREEAM performance targets that need to be formally agreed no later than the concept design stage.
BREEAM Daylighting – Alternative methods - KBCN1821
Within the BREEAM daylight criteria, there are two detailed calculation options of either using the average daylight factor method or average and minimum daylight illuminance method.
The use of the standards within the table below, can now be used as approved alternative calculation methods. The performance requirement must be met in line with either the standard or exemplary criteria as set out in the table below:
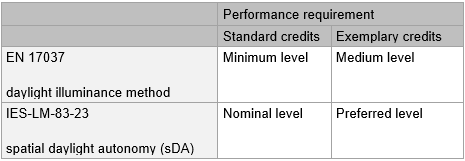
To use either the EN 17037 or IES-LM-83-23 option, the methodology within Guidance Note 50 must be followed. In addition, the minimum percentage area to comply, dependant on the building type and space type, must be met in accordance with the criteria within the relevant BREEAM issue. To calculate the percentage of assessed area that complies, follow
KBCN0471 or
KBCN1081.
Example:
A school using the International New Construction V6 scheme, has used the IES-LM-83-23 sDA method to calculate the daylight performance. The nominal level is achieved in all occupied spaces. The minimum area to comply is set at 80% as per table 10 and 12. As 100% of occupied spaces meet the nominal level, 2 credits can be met.
Building LCA tools recognized by BREEAM - KBCN1118
The following table shows the building LCA tools that are recognized by BREEAM for each BREEAM scheme. Only submissions from the tools listed here will be accepted as part of a BREEAM assessment.
These recognized tools may be either an IMPACT Compliant tool or another type of building LCA tool that has been evaluated by BREEAM and considered suitable for carrying out building LCA according to BREEAM’s scheme specific requirements. To apply for a new tool to be evaluated, please contact:
breeam@bregroup.com
Where more than one version of the same tool is listed for a given scheme version, the most recent version of the tool (that is available at the point building LCA work commences on the project) should be used.
Click on the thumbnail for the full table.
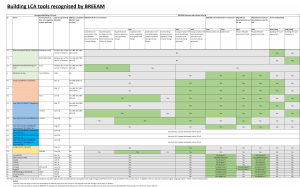
Table updated to include new recognised LCA tools 26/02/2020
Calculating U-values for buildings with extension(s) - KBCN1000
In line with CN ‘Extensions to existing buildings and newly constructed thermal elements’, the performance of the baseline for new thermal elements should be based upon compliance with the appropriate local or national Building Regulations for new thermal elements.
When completing the Elemental level energy model, the existing building U-values for the thermal elements should be calculated as the area-weighted average of the relevant thermal element (e.g, external wall, roof, glazing or ground floor area), excluding any area that is removed to accommodate the extension, and that of the extension, built to meet the local minimum building performance standards.
The U-values for thermal elements of the refurbished building should be calculated as the area-weighted average of the relevant thermal element for refurbished building, including the extension.
This applies when assessing against the 'Elemental level energy model' option.
Campus or campus-type developments – Entrance to consider - KBCN1726
For assessments on sites with multiple buildings (e.g. education campus, business or industrial parks):
- Distances to amenities and public transport nodes can be measured from the site’s main entrance if ≥80% of buildings are within 1000 m. Otherwise, use the assessed building’s main entrance, and in such cases, where multiple buildings are included, calculations must always be based on the worst-case scenario (the entrance furthest from the node or amenity)
- Where the site has more than one main entrance, either entrance may be used for the calculation.
Purpose: To ensure fair assessment on large sites and to encourage the provision or location of amenities and public transport nodes within or at the periphery of the site.
Note: wording update for clarification and including BIU
Campus with multiple building assessments - KBCN0597
If a campus development project has multiple building assessments being built in conjunction with each other, each building should be assessed independently. Where there are noise sensitive buildings; including any new buildings in the process of being built, the criteria requirements must still be met.
Capital cost reporting and LCC measured area - KBCN0438
When assessing the Capital cost reporting and the LCC credits, the area to be considered should be the Gross Internal Floor Area (GIFA), according to the below
RICS definition:
Gross Internal Floor Area
Gross Internal Floor Area is the area of a building measured to the internal face of the perimeter walls at each floor level, which includes:
- Areas occupied by internal walls and partitions
- Columns, piers chimney breasts, stairwells, lift-wells, other internal projections, vertical ducts, and the like
- Atria and entrance halls with clear height above, measured at base level only
- Internal open sided balconies, walkways, and the like
- Structural, raked or stepped floors are treated as a level floor measured horizontally
- Horizontal floors with permanent access below structural, raked or stepped floors
- Corridors of a permanent essential nature (e.g. fire corridors, smoke lobbies, etc.)
- Areas in the roof space intended for use with permanent access (BCIS)
- Mezzanine areas intended for use with permanent access
- Lift rooms, plant rooms, fuel stores, tank rooms which are housed in a covered structure of a permanent nature, whether or not above main roof level
- Service accommodation such as toilets, toilet lobbies, bathrooms, showers, changing rooms, cleaners’ rooms and the like
- Projection rooms
- Voids over stairwells and lift shafts on upper floors
- Loading bays
- Areas with a headroom of less than 1.5m
- Pavement vaults
- Garages
- Conservatories (BCIS)
And excludes:
- Perimeter wall thickness and external projections
- External open-sided balconies, covered ways and fire escapes
- Canopies
- Voids over or under structural, raked or stepped floors
- Greenhouses, garden stores, fuel stores and the like in residential property
- Open ground floors and the like (BCIS)
14.02.18 - KBCN content amended to extend the applicability to LCC and to refer to GIFA rather than GEA, to reflect current industry practice.
Car sharing - KBCN0878
This measure will generally be unavailable to speculative projects.
To fully implement the car sharing option, the building occupants need to be known and signed up to a car sharing scheme in-line with the criteria.
Car sharing – calculation of priority spaces - KBCN0282
The calculation of priority spaces for car sharers should account only for the car parking capacity that is dedicated to the staff working in the building, without considering the spaces for customers or visitors.
As such, car sharing spaces should be clearly segregated from customer/visitor parking areas.
06 Sep 2023 - Title only updated to align with naming protocol
23/03/2017 note added clarifying requirement for segregation
Centralised air handling units (AHU) - KBCN0941
The requirements of the:
- Second sub-metering credit (New Construction).
- Issue (BREEAM In-Use).
do not apply to centralised AHUs, where it is not technically feasible to sub-meter energy use by separate functional, tenanted or floor areas.
The credit(s) will be assessed based on the remaining applicable energy uses.
06-Mar-2024 - Scheme applicability extended to V6.
Certificate validity - KBCN0798
EPDs and Green Guide ratings which have expired or are pending verification at the time the relevant product was specified, cannot contribute to awarding credits.
04/11/2019 Confirmed applicability to UK NC2018
27/03/2020 Added applicability to Green Guide ratings and ISO 14001 certificates
27/05/2020 Reference to ISO 14001 removed - Whilst the same principle applies, the wording relating to product specification does not - See KBCN1401.
Certificate validity – EMS - KBCN1401
The requirement for the principal contractor to operate an EMS relates to the duration of operations on site. Therefore, certification against ISO 14001/EMAS must be valid as above and cannot be expired, pending or applied retrospectively.
Change in main contractor - KBCN0645
In situations where the main contractor changes mid-project, for example where the original contractor goes into administration and is replaced by another main contractor, it is acceptable for the post-construction credits to be awarded based on the new contractor providing information on their activities. This is providing the project is yet to start on site. This is in effect assessing the issue using the Post Construction Assessment route instead of a Post Construction Review.
However, if the project has already started on site and information about the site activities of the previous contractor is not available it would not be appropriate to award the credit solely based on the new contractor activities.
Checklist A1 – not applicable items - KBCN0770
If you can clearly justify and robustly demonstrate that an item in Checklist A1 is not applicable on the assessed project, for the purposes of the BREEAM scoring, this item can be considered compliant.
CHP NOx emission conversion - KBCN0592
If the CHP manufacturer cannot provide the NOx emissions in mg/kWh it is not possible to award any credits. The CHP manufacturer must provide the NOx emissions in mg/kWh, the conversion factors provided in the Technical Manual can only be used for boilers.
Classification of offices on education sites - KBCN0410
If an admin office situated on a higher or further education campus is used exclusively for admin and support services (i.e. it will not be used by teaching staff or students), then such offices must be assessed under the Offices scheme classification.
Where a building is mixed use, containing multiple unrelated functions and user groups with no clear dominant function, separate assessments are required.
CN1 – Part 1: Fabric and structure - KBCN0854
CN1 is applicable to more projects than simply Part 1 only assessments (as stated in the Technical Manual). It states where a Part 1 only assessment cannot demonstrate full compliance with the criteria defined in the relevant tables, 1 credit is available (unless multi-residential) where an SQA completes the tasks listed within CN1.
Instead of being relevant to Part 1 assessments only, this text is actually relevant to any assessments which include Part 1, and do not include Part 4.
This covers the following combinations of Parts:
- Part 1 only assessments;
- Part 1 and Part 2 assessments;
- Part 1 and Part 3 assessments;
- Part 1, Part 2 and Part 3 assessments.
Please note: In relation to projects which are not multi-residential, one credit is available where the project demonstrates compliance through CN1 for 'indoor ambient noise and sound insulation', and one credit available where the project demonstrates compliance through CN1 for 'reverberation times'.
Combined sub-metering – electric space / water heating and small power - KBCN00068
For bedrooms and associated spaces in:
- Multi-residential or residential institution building types (New Construction).
- Hospitality or supportive housing asset types (BREEAM In-Use).
It is acceptable for an electric space or water heating system to be combined with lighting and small power, provided that sub-metering is provided for each floor plate or other appropriate sub-division.
For these asset types, sub-metering electric heating in multiple bedrooms may be costly and technically challenging. Where occupants have individual control but are not responsible for paying the utility bills, the building manager may have little influence on their energy consumption. Therefore, sub-metering electric heating would provide little or no benefit in meeting the aim of the issue.
06-Mar-2024 - Scheme applicability extended to V6.
15-Dec-2023 - Title updated to clarify that this approach can be applied to both space heating and domestic hot water heating, where appropriate.
Combined system for heating / cooling and domestic hot water - KBCN0329
It is permissible to have combined metering for a shared on-site or district system that combines heating / cooling, and domestic hot water generation.
In all cases, justification is provided in the QA report for the combined metering, and explains why it is not technically feasible to provide separate meters.
21-Sep-2022 Applicability of KBCN added to BIU V6. Amended to include district heating and cooling networks.
Commercial dishwasher appropriate data - KBCN0687
If the component is present in the building but the appropriate data is unavailable from the manufacturer's product information i.e. uses a different unit of measurement, then the baseline performance level for the specified component should be used in the WAT 01 calculator.
BRE Global is unable to provide a calculation method to convert data in to the correct unit for the WAT 01 calculator tool.
Commissioning – Monitor and specialist commissioning manager - KBCN00051
The commissioning monitor is typically a project team member who will monitor the systems commissioning and testing programme for the building. The individual may combine that role with that of the specialist commissioning manager to deal with complex systems if they have the necessary knowledge. However, if the building has several specialist systems it is unlikely that the same person would be able to carry out all of the commissioning and more than one specialist would most likely be required.
Commissioning – Role of the specialist commissioning manager - KBCN0604
The specialist commissioning manager for a complex system will generally be be a specialist contractor. They must provide independent design review, oversee the commissioning and independently verify the work carried out by the installer, in line with the criteria.
It may be possible for the specialist commissioning manager to be part of the principal contractor's organisation, provided it is demonstrated that they are independent of the design and installation and that any potential conflict of interest has been managed.
22 Nov 2021 - Wording updated to clarify the intent.
Communal Laundry Facilities – Domestic or Commercial Washing Machines - KBCN0613
The table provided in the manual highlights the criteria for an appliance to be considered domestic or commercial. However, for multi-residential projects (or other building types containing laundry facilities), the BREEAM assessor should use their judgement to determine whether the appliance is commercial or domestic, and justification of the category selected must be provided. For instance, commercial and domestic sized washing machines can be defined based on load size or power rating.
Communal Laundry Facilities- Commercial Sized Tumble Dryers - KBCN0555
Tumble dryers should be taken in to account when calculating the total annual unregulated energy consumption of communal laundry facilities with commercial sized appliances.
Heat recovery from a commercial sized tumble dryer exhaust can be used as an alternative to the solutions listed within the Ene 08 credit issue provided it will achieve a meaningful reduction of energy demand, and justification can be given as to why this method has been implemented over those recommended in the manual.
The list of equipment types and compliance requirements is not intended to be exhaustive, however where alternative solutions are proposed, the design team must provide justification and evidence as outlined above, to the satisfaction of the assessor.
Community transport schemes in rural areas - KBCN00013
In rural areas, where scheduled public services are insufficient to gain credits via the calculation of the Accessibility Index, community transport schemes, including 'on-demand services', can be used to achieve the 'dedicated bus service' option. In such cases evidence must be provided to demonstrate:
- It serves a rural area
- It is available to all potential users
- The service is established at the time of the assessment being submitted
- The service is of an appropriate scale for the community it serves
Content reworded to highlight the availability of the on-demand service to all potential users. 24/04/2017
Compliance: Applicability of criteria to subsequent schemes’ versions - KBCN0554
When assessing a project under a certain scheme, criteria or compliance notes from a previous scheme cannot be used to demonstrate compliance.
Compliance: Applicability of criteria to scheme’s previous versions - KBCN0430
Criteria set for a scheme version are not applicable retrospectively to previous versions.
Compliance: Manufacturer/supplier does not comply - KBCN0571
Where equipment is required to meet specific criteria to achieve compliance it is important to ensure the client seeks out manufacturers/suppliers that provide equipment which meets these criteria. If the chosen product / supplier cannot meet the criteria then the credit cannot be awarded.
BREEAM seeks to recognise the use of equipment which offers the latest sustainable solutions.
Compliance: Statutory requirements - KBCN0395
BREEAM is an assessment method which promotes best practice in sustainable buildings.
Matters critical to health and safety, as well as any mandatory requirements from statutory authorities which conflict with BREEAM criteria may take precedence over BREEAM requirements. In this instance, evidence would be required to demonstrate that this is the case.
Note, this does not change the criteria requirements, and where BREEAM requirements are not met the design team must explore alternative options or specifications if the relevant credits are to be awarded.
17/04/18 Wording amended to clarify
Compliant attenuated noise levels - KBCN00047
BS 4142 noise level requirements can be used to demonstrate compliance provided the best practice testing methodologies for noise attenuation outlined in BS 7445 are followed.
Compliant test body – alternative compliance route using a Suitably Qualified Acoustician - KBCN1412
Where acoustic testing and measurement has not been performed by an organisation or individual that meets the definition of a compliant test body, compliance with this requirement can still be demonstrated where a Suitably Qualified Acoustician has reviewed the relevant test report(s).
The test report must:
a) Be countersigned or authorised by a Suitably Qualified Acoustician
b) Include a clear statement that the acoustic testing and measurements have been carried out in accordance with the BREEAM or HQM testing requirements
AND
c) Include evidence that the verifier meets the definition for a Suitably Qualified Acoustician within the relevant BREEAM or HQM technical manual
Compliant wheelchair and buggy storage facilities - KBCN1200
In sheltered housing or care homes and supported living facilities assessments, compliant wheelchair and buggy storage facilities are those that meet the following:
- Charging points for electric buggies (at least two) provided within the
storage space
- Storage area must be secure yet easily accessible
- Lighting of the storage facility must be compliant with the external (or
internal where relevant) lighting criteria defined in BREEAM Issue Hea 01
Visual comfort. The lighting must be controlled to avoid operation during
daylight hours, where there is sufficient daylight in or around the facility.
- Where access to and from the building main entrance needs to be tightly
controlled for the safety/security of residents, and it can be demonstrated
that compliance with points 2 and 3 above impact on this (e.g. where
residents include those with mental health problems), these two items can
be excluded from the compliance requirements.
Considerate construction – corporate registration - KBCN0905
Where credits are awarded for the assessment of the site against a compliant scheme, corporate registration, which assesses the contractor's overall operations and performance across multiple sites, is not in itself recognised.
To award considerate construction credits, BREEAM requires the assessment of the specific assessed development, in line with the criteria.
Considerate construction: Checklist A1 – Photo card identification - KBCN1632
Checklist A1 Reference 4.e. requires the following:
'Operatives’ identification; all operatives to be provided with a photo identification clip card'
However, since this was introduced into 'considerate construction' requirements, data protection legislation and expectations around privacy have progressed. This requirement can, therefore, be disregarded.
Considerate constructors exemplary criteria - KBCN0843
Where the exemplary criterion has been met, the exemplary credit will be awarded in addition to the two standard credits for considerate construction. There is no need for the assessor to demonstrate compliance with the standard credits in this case, just the exemplary one.
Considering Sand and Cement Replacements - KBCN0181
Neither sand or cement replacements should be taken into account when assessing the percentage of recycled or secondary aggregate used in a project.
The recycled aggregates issue only assesses the use of coarse aggregates.
29/03/2017 Title amended and additional reference to cement substitutes added
Contractor not yet appointed at the design stage - KBCN000002
Where the contractor has not been engaged at the design stage certification, it is acceptable to award the credits based on a commitment. This commitment must be from a suitable member of the design team, and must detail the targets and criteria which must be met. Evidence must also confirm that the details in the commitment will form part of the contractual requirements.
Contractual agreements for Shell Only / Shell & Core assessments - KBCN0942
For Shell Only and Shell & Core (RFO Part 1, Part 2, and combined Part 1 & 2) assessments, all relevant criteria are applicable. Contractual agreements confirming future provision of spaces are not acceptable.
Evidence must be provided showing waste storage space(s) that are suitably sized, dedicated and unlikely to be used by the future tenants for other purposes.
While the location of the space/spaces may change when fitting out, at this stage a space that is conveniently located for the deposit and collection of operational waste must be provided.
Counterbalancing ratio fixed - KBCN0327
The requirement to analyse the counterbalancing ratio can be omitted if the project team can provide a statement confirming that it has been set by the manufacturer due to existing standards and to maximise efficiency. The remaining criteria must be met.
Criterion 3 – Error in the manual - KBCN0736
Only 1 credit is available for LE 04 issue (except for prisons) and all recommendations of the ecology report for the enhancement of site ecology must be implemented for criterion 3 to be met.
In the versions 1.1, 1.2 and 1.3 of the technical manual the table under criterion 3 is wrong.
This table will be removed in the next update of the scheme.
Cut-off - KBCN0598
The current CN 'Route 1 Cut- off See step 1 in the Methodology section' in the technical manual should refer to Route 2 and 3 as well.
CN in technical manual to be updated accordingly in next re-issue
Cut-off threshold for responsible sourcing - KBCN1409
For projects pursuing the one separate credit under Responsible Sourcing of Materials (where at least three of the material types listed in the material categories have been responsibly sourced), any material type which clearly accounts for less than 1 m³ per 1000 m² of gross internal floor area, can be excluded from the assessment. This applies for materials in any location or use category.
The volume considered should be taken as the construction product's overall external dimensions, including any internal voids and air spaces. Minor fixings (brackets, nails, screws etc.), adhesives, seals and ironmongery would normally fall below this threshold.
Cycle spaces – Minimum and maximum requirements - KBCN0637
These remain applicable where the 50% reduction allowed for building locations with a high level of public transport accessibility is in effect.
This means that, for instance, a large retail will still need to provide at least ten customer cycle storage spaces and could meet compliance with a maximum of fifty.
22-Nov-2023 Scheme applicability updated.
18-May-2017 Previous KBCN on large retail adapted to include any minimum requirement for cycle storage spaces.
Cycle spaces – Compliant types of storage - KBCN0257
Due to the number of different types of cycle storage facility available and the variation in site conditions, BREEAM New Construction is less prescriptive about the dimensions and type of cycle parking which can be used to demonstrate compliance. The Assessor is expected to exercise their professional judgement to determine whether the cycle parking spaces meet the aims of the Issue and the requirements listed in the compliance notes.
BREEAM is used to certify buildings, not products. Cycle parking systems cannot, therefore, be considered inherently 'BREEAM compliant'. These must be assessed in context with reference to their location and the intended user profile.
Cycle Spaces – Electric cycle charging stations - KBCN1238
Electric charging stations can be considered as compliant, provided they also meet the criteria for cycle storage spaces.
However, where these are dedicated spaces, (ie they are not available for non-electric cycles), these should not constitute more than 10% of the provision required for compliance.
Cycle spaces – Folding bicycles and scooters - KBCN00024
The provision of cycle storage that is only suitable for folding bicycles or scooters is not compliant.
Providing reduced storage space for folding bicycles or scooters in place of compliant cycle storage may limit future travel options.
14 03 2018 Wording clarified and reference to scooters included.
Cycle spaces – Prominent location - KBCN00053
The requirement to provide cycle storage facilities in a prominent location on site, within view of building users, is intended to encourage use through advertising their presence to building users. Providing these facilities inside the assessed building, such as in the basement, may be compliant so long as there is prominent signage to indicate their location to all building users.
Cycle spaces – Provision for extensions - KBCN0707
When assessing an extension to a building, partial refurbishment or a stand-alone building, which extends an existing facility to be occupied by the same building users (such as a classroom block in an existing school), a site-wide approach should be used to determine the number of new, compliant cycle spaces required.
In such instances a stand-alone approach cannot generally ensure that the new cycle spaces for the assessed extension would be dedicated and available to the occupants of the assessed extension, refurbishment or building. This can only be used where it can be demonstrated that the use of the new cycle storage can be effectively restricted to only those using the assessed extension, either by effective positioning and or management.
Cycle spaces – Provision for regular, large visitor numbers - KBCN0546
Where there are large numbers of visitors on a regular basis, provision of cycle storage for visitors should be based on the maximum number at any given time.
This is to ensure that at peak times enough cycle storage is provided.
Cycle spaces – Similar buildings assessments - KBCN0570
Where cycle storage and/or facilities are provided for individual units, a site-wide approach cannot be used to include all units. If, however, these are a shared facility, provided in a suitably-located communal area, this may be acceptable.
When assessing using the 'similar buildings' approach, each of the similar buildings has to be assessed separately and credits have to be awarded, based on the worst performing building.
14 03 2018 Clarified to account for suitable shared facilities
Cycle spaces – Small retail – multiple units - KBCN0187
In a development of multiple small retail units, to achieve credit, 10 compliant cycle storage spaces in total are required where it can be shown that these are accessible to all units. However, where such developments consist of multiple units over a large area or are separated by barriers such as roads, the assessor should ensure that the provision is both adequate and conveniently located for all units.
The 50% reduction allowed for building locations with a high level of public transport accessibility is not applicable in this case.
17/11/2016 Note related to the 50% reduction added.
14/03/2018 Note added regarding multiple units over a large area or separated by barriers.
Cycle spaces and facilities – Rounding calculations - KBCN0445
The calculation for the required cycle spaces and facilities must always be rounded up. If the calculation works out as 5.3 cycle spaces, 6 cycle spaces must be provided.
To determine the requirements for developments with multiple types of building user, calculate the requirement for each user group separately (rounding up to the determine the number of spaces) and then add the number of cycle spaces for each user group together.
04/10/2018 Wording amended to clarify the correct calculation method for developments with multiple user groups.
Cycle spaces – Determining compliant provision where occupancy is unknown - KBCN1741
Where occupancy is unknown, the default occupancy rates given in the table in the Additional Information section of BREEAM issue ‘Tra 04 - Maximum car parking capacity’ can be used to help determine a default number of users.
Alternatively, the number of building occupants in an existing development of similar type and size can be used. The assessor must justify the methodology and number of spaces provided in their certification report
Cyclists’ facilities – Adequately sized lockers - KBCN0961
The requirement for adequately sized lockers is so that cyclists have a dedicated space to store their cycling equipment and clothes. It is not compliant for the space requirement to be met by providing two or more inadequately-sized lockers for each cyclist.
Requiring cyclists to separate their equipment into different lockers/storage spaces could create a barrier to uptake of commuting by bicycle.
Cyclists’ facilities – Combining different facilities - KBCN0683
Cyclists’ facilities can be combined, provided that all relevant compliance requirements are met and it is demonstrated that there is no conflict impacting on their use. For example, compliant showers can be combined with compliant lockers in one room, subject to the principle below.
For combined facilities to count as multiple facilities, they must be capable of being used independently of each other at the same time (where relevant) with reference to any space requirements, access, gender and privacy issues.
11 Jan 2023 - Applicability to BIU V6C confirmed
Cyclists’ facilities – Provision of only one shower - KBCN0566
Where only one shower is provided, this needs to cater for users of both genders.
For a changing facility to count as an additional amenity, it must be capable of being used independently of any showers, otherwise it could not be considered as two facilities.
A shower which is a mixed gender facility must be capable of being used privately. As such, it requires adequate private changing space associated with it.
Amended to provide further clarification and to add the general principle.
10/11/2016
Cyclists’ facilities – Shell only/shell & core assessments - KBCN0882
Cycle parking must be provided as part of the base-build for all assessment types.
Where compliance is sought for additional cyclists’ facilities, the developer should provide all aspects of the installation which fall within the scope of their work and facilitate the future completion of any aspects which do not.
For shell & core assessments, if additional facilities, such as showers and drying space, are not provided in core areas and internal walls are not provided to tenanted areas, these must be indicated on design drawings and all relevant services provided. This would include capped-off supplies and electrical points as necessary in order to facilitate the completion of the compliant facilities by the tenant.
Where internal walls are within scope, a compliant changing area must be provided, however for lockers, compliance can be achieved by providing a design drawing showing that there is an adequately sized and suitably located space for the required number of compliant lockers.
The developer should do as much as they can, within the scope of their work, to facilitate the future installation of compliant facilities and should not do anything which would make future installation more onerous.
01 Oct 2024 - Addition paragraph added to clarify the approach for changing areas and lockers.
25 May 2018 - Wording amended to clarify the intent.
Cyclists’ facilities – Shower provision for male and female users - KBCN0536
Where a deviation from the guidance for a 50:50 split can be fully justified, (for example, based on actual occupancy data from a similar development of the same building type) this can be deemed as compliant by the assessor.
If such justification cannot be provided but design teams wish to provide a flexible arrangement for showers to suit the anticipated building occupancy, providing unisex showers accessible to all building users would be acceptable.
Cyclists’ facilities – to match additional bicycle spaces - KBCN00093
The minimum number of showers/lockers/changing facilities required for BREEAM compliance is determined by the minimum number of compliant bicycle spaces required, not by how many total compliant bicycle spaces have been provided. Where more than the minimum number of compliant cycle spaces has been provided, there is no requirement to provide more than the minimum number of showers/lockers/changing facilities.
01 Feb 2022 - Applicability to BIU USA Commercial V6 confirmed
Cyclists’ facilities – Visitors - KBCN00014
Where the cycle spaces requirement is based on the number of staff plus visitors, customers or patients, the number of cyclist facilities required to demonstrate compliance is based on the number of cycle spaces for staff only.
Visitors, customers or patients would not be expected to have access to showers and lockers within a building.
Daylighting – speculative building - KBCN0269
Where the building is speculative and therefore the final layout is not defined (e.g. only an open plan shell is provided in each tenanted space), the required percentage of each open plan shell should meet the daylighting requirements. However, where it is possible to designate separable ancillary areas that would be required in the space (such as toilets or server room), these can be excluded from the calculation.
For daylight calculations in speculative projects where the layout and colours are unknown, a realistic notional layout may be used.
Daylighting – ‘Internal association or atrium areas’ - KBCN1267
This term refers to areas intended to replace outdoor recreation spaces, typically found in prisons, but which may also be present in hospitals and residential accommodation for elderly people.
The requirements relating to such spaces are, therefore, not generally applicable to other building types.
Daylighting – calculation procedures - KBCN1339
For all spaces in the building where daylight provision is relevant (these are defined in the defintions for the relevant building areas), calculate the area weighted percentage improvement in daylight (Σ A
i P
i) / (Σ A
i ). Here A
i is the floor area of space i and P
i is the percentage increase in daylight in it. The Σ operator means to sum over all the relevant spaces.
In order to demonstrate compliance with criteria 4 and 5 for an improvement in existing daylighting, for each space, the percentage increase in daylight (Pi) is calculated in one of the following ways:
Where only the window area or glass transmission will increase:
- If window area has increased but all other aspects remain the same, Pi = ((increase in glass area)/(original glass area)) x100%.
- If glass transmission has increased but all other aspects remain the same, Pi = ((increase in glass transmission)/(original glass transmission)) x100%.
Where many aspects will change (e.g. room size, a combination of reflectance and window size etc.):
- Calculate the average daylight factor (ADF) in the space ‘before’ and ‘after’. Pi =( (ADF after – ADF before)/ ADF before) x100%.
- Calculate the average illuminance in the space that is exceeded for 2000 hours per year. Pi =( (Average illuminance after – Average illuminance before)/ Average illuminance before) x100%.
This will be amended in the next version of the manual.
Daylighting – Changing rooms - KBCN1132
The daylighting criteria are not applicable to changing rooms.
Daylighting – communal kitchens (multi-residential) - KBCN0217
Communal kitchens should be assessed under 'Non-residential / Communal Occupied Spaces.
Communal kitchens outside of self-contained dwelling units, for example a kitchen within a self-contained student flat shared between several students would be classed as a private kitchen for the purposes of this issue. However, if it was shared between rooms along a communal corridor it would be considered a communal kitchen, and assessed under 'Non-residential buildings - occupied spaces'.
Daylighting – Floor areas for average daylight calculations - KBCN0471
Where the room size is comparable and the function is the same, such as ‘kitchen’, the percentage rule needs to be applied to the total floor area. As the average daylight factor is a measure of daylight across the whole room, only whole rooms can be compliant. This is why we refer to rounding up the '80% of the floor area' requirement to the rounded up number of compliant rooms.
This rule applies to rooms of a similar size and function and compliance note ‘percentage of assessed area’ includes a simple example, where all the rooms are the same size. However, this rule can still be applied to rooms of different sizes.
Spaces whose size is substantially larger should meet the average daylight factor requirement on their own. In these cases, the percentage requirement is still applicable to the floor area of the remaining rooms.
Where a building contains different area types, the 80% minimum floor area must be calculated by each separate area type. For example, a multi-residential building that contained kitchen areas and living room areas would need both of these areas to comply with the 80% minimum floor area requirement separately.
Daylighting – requirements differing by area - KBCN0176
Where areas within a building have different daylighting requirements for the same credit, all relevant areas must meet the requirements to award the daylighting credit(s).
The aim is to improve daylight conditions in all applicable area types of an assessed building.
Daylighting – retail cafe / dining areas - KBCN0968
Customer seating/dining areas in a cafe or restaurant should be considered as 'sales areas'. Sales counters, staff areas or food preparation areas, for example, should be assessed as 'Other occupied areas' in accordance with the definition of 'Occupied space'..
The requirements for 'Sales areas' are applied to transient spaces.
Daylighting – studio flats - KBCN0866
In the case of studio flats, where there are no separating walls between occupied spaces, the minimum area of compliance for the average daylight factor requirement is based on the combined area of kitchen, living room, bed and study area. The required daylight factor for the open-plan space (subject to percentage requirement) should be based on the highest daylight factor required for any of the spaces.
It is impractical to separate the open-plan space and assess the daylight according to notional lines. In order to maintain robustness, the highest daylight factor should be applied throughout.
Daylighting – uniformity ratio applicability - KBCN0584
The uniformity ratio requirements apply to the percentage of the building’s relevant areas specified in the table. In the NC 2013 scheme, this is 80%.
Daylighting uniformity criteria – Multi-residential/Residential institutions - KBCN1129
The view of sky criteria (Table 11 (b)) are applicable to Multi-residential/Residential institutions where the room depth criterion (Table 11 (c)) is used.
Other requirements for Multi-residential/Residential institutions in the Daylighting table should read 'Either (a) OR [(b) and (c)]'
11/02/2019
Removed applicability to 2018 as this has been corrected in the latest version of the manual
Dedicated transport service - KBCN1823
A dedicated transport service, such as a dedicated bus, coach, or minibus, provided or managed by the building owner or management, can be considered for any building type with a fixed usage pattern. The dedicated transport must provide a transfer to the local population centre or public transport interchange, or it may be a door-to-door service.
Generally, a dedicated service must be available to all regular building users. However, for primary and secondary schools, a dedicated service available to students only can be considered compliant
Dedicated transport service - KBCN1823
A dedicated transport service, such as a dedicated bus, coach, or minibus, provided or managed by the building owner or management, can be considered for any building type with a fixed usage pattern. The dedicated transport must provide a transfer to the local population centre or public transport interchange, or it may be a door-to-door service.
Generally, a dedicated service must be available to all regular building users. However, for primary and secondary schools, a dedicated service available to students only can be considered compliant
Deemed to comply solutions – alternative proposals - KBCN1214
The solutions listed for each category in the Table are examples deemed to comply with the requirements, without further justification or calculations to demonstrate a meaningful reduction in unregulated energy consumption.
If an alternative solution is proposed, justification and/or calculations are required to demonstrate this.
Definition – Critical value - KBCN1006
Critical value aims to
maximise whole life value of the building based on client requirements, and differs from minimising life cycle cost. This is a more specific analysis of how the building's ongoing maintenance and operation can impact business needs. For instance:
- Where any disruption to business is costly, a specification with long periods between maintenance cycles and reduced maintenance time may be desirable.
- Where maintaining aesthetics are important, a maintenance cycle may be based on aesthetic upkeep rather than functional lifespan.
- Where maximum recyclability and re-usability is important, an alternative, costlier specification may be required.
- Where capital costs are constrained, the specification with the lowest LCC may not be affordable, and instead, the best available option within the budget is chosen.
Definition – Project value - KBCN0552
The term ‘project value’ represents the total project cost, which includes all costs such as construction, design, land acquisition etc.
Definition – Reused in situ with minor repairs - KBCN1160
This item in Table "Allocation of points awarded" refers to the Relevant definitions section.
This reference is incorrect and should, instead, point to the Compliance Note "Repairs to existing
in situ elements", which indicates that, 'Materials used to repair existing
in situ elements may be excluded provided no more than 20% of the total area; or volume of the existing element is subject to minor alternations, repair or maintenance'.
To be amended in the next re-issue of the technical manual.
Definition of ‘total useful floor area’ - KBCN00079
The total area of all enclosed spaces measured to the internal face of external walls. In this convention:
- The area of sloping surfaces such as staircases, galleries, raked auditoria and tiered terraces should be taken as their area on plan
- Areas that are not enclosed, such as open floors, covered ways and balconies, are excluded
Definition of concourse - KBCN0386
A concourse is an open area within or in front of a public building which is used primarily for circulation, short term waiting, or incidental interaction, analogous to the concourse of a train station. It should not be considered occupied space.
Definition of NIA (net floor area) for assessment registration purposes - KBCN0569
Net Internal Area (NIA) is broadly the usable area within a building measured to the face of the internal finish of perimeter or party walls ignoring skirting boards and taking each floor into account.
NIA will include:
- Perimeter skirting, moulding, or trunking
- Kitchens
- Any built in units or cupboards occupying useable areas (subject to height exclusion below)
- Partition walls or similar dividing elements
- Open circulation areas and entrance halls, corridors and atria (but see 9 and 10 below)
NIA will exclude:
- Toilets and associated lobbies
- Cleaners' cupboards
- Lift rooms, boiler rooms, tank rooms, fuel stores and plant rooms other than those of a trade process nature
- Stairwells, lift wells, those parts of entrance halls, atria, landings and balconies used in common or for the purpose of essential access
- Corridors and other circulation areas where used in common with other occupiers or of a permanent essential nature
- Areas under the control of service or other external authorities
- Internal structural walls, walls (whether structural or not) enclosing excluded areas, columns, piers, chimney breasts, other projections, vertical ducts etc
- The space occupied by permanent air conditioning, heating or cooling apparatus and ducting which renders the space substantially unusable having regard to the purpose for which it is intended
- Areas with headroom of less than 1.5m
- Car parking areas
Source: Valuation Office Agency
Therefore, the usable area within a building measured to the face of the internal walls should be provided.
Whilst this is not expected to be accurate to the nearest 1m
2, the closest estimate possible for the NFA should be entered. This is to allow for any possible subsequent adjustment to the size of the development.
Demand-based bus services in AI calculation - KBCN1338
Demand-based bus services operated by public transport providers can be included in the calculation of the Accessibility Index. The project team will need to determine an average number of stops per hour to allow input into the AI tool.
Dementia care homes - KBCN0820
For dementia care homes, there may be instances where the resident profile, and hence design and use, result in some BREEAM criteria being considered inappropriate or not applicable. Where this is the case assessors should seek confirmation from BREEAM through the technical query service, providing a clear justification for why specific criteria cannot be met.
Before submitting a query, however, please review the BREEAM Knowledge Base under the relevant Scheme and Issue, to check for a specific, published compliance note.
Assessors will be required to provide evidence. This could be from suitable individuals/organisations regarding the specific project, detailing how the criteria is not relevant for the individual project.
Demolition – external guidelines (incl BS 6187) - KBCN0630
Independent standards exist and some are referenced in the BREEAM manual and can be used to provide additional guidance for clients/design teams. Unless explicitly stated they are not 'deemed to satisfy' BREEAM criteria and assessors must demonstrate that BREEAM criteria have been met in the usual way.
One such standard is BS 6187:2011 which gives good practice recommendations for the demolition (both full and partial) of facilities, including buildings and structures. The standard is therefore applicable to demolition activities undertaken as part of structural refurbishment. It also covers decommissioning.
Unless explicitly stated external standards do not automatically satisfy BREEAM criteria and assessors must demonstrate that BREEAM criteria have been met in the usual way.
Demolition records not available - KBCN1009
Where demolition records are missing, either wholly or in part, the credit available for diversion of construction and demolition waste from landfill cannot be achieved. This includes instances where demolition was conducted under a separate contract or by a third party on behalf of the developer.
Demonstrating CO2 reduction with no existing building information - KBCN0575
When there is no information about the existing building, any reduction resulting from the incorporation of passive design measures should be demonstrated by comparing the CO2 emissions for the building with and without the proposed passive design measures adopted.
Design stage requirements where specific product details are unknown - KBCN1483
The Mat 03 tool must be completed in accordance with the Methodology, providing all available details and submitted as evidence.
Where products or materials are subject to a performance specification and a specific manufacturer and certificate reference cannot be provided, the missing details should be completed as 'tbc'.
This ensures that a strategy for compliance can be demonstrated, even where some specific details are unavailable.
Design team meetings via conference call - KBCN0201
Design team meetings can be conducted via conference calls.
It can be difficult for design team members to be in the same place at the same time. Conference calls are a more sustainable way to conduct meetings.
Designed-out or integrated finishes - KBCN1066
The requirements for this credit are met when either:
- No finishes within the scope of the issue have been specified, or
- Finishes are integrated into the asset and designed in a way that the finish cannot be removed.
For instance, a self-finished timber floor or exposed soffit which cannot be removed and does not require additional finishes when installed.
This issue recognises avoiding unnecessary waste of materials.
16-May-2023 - Scheme applicability updated. Name updated for clarity.
Display lighting - KBCN00097
The display lighting listed in the table includes internal lighting only. External lighting is covered in issue Ene 03.
District cooling – Used in combination with local cooling - KBCN1634
Where district cooling can be considered outside the scope of the assessment, either in accordance with the Methodology section of the technical manual or in line with
KBCN0759, compliance must be based on calculating the DELC for all systems.
However, where the district cooling system is exempt from assessment, as described above, this should be based on a GWP of zero for the district cooling system.
District cooling systems - KBCN0759
Where a district cooling facility is servicing the assessed building, the building will have an environmental impact in terms of refrigerants, albeit in this case indirectly. As such the district cooling system must be considered against the BREEAM criteria for refrigerants.
Where connection to an off-site district cooling system, over which the developer has no control, is mandated by a local authority or other statutory body, the maximum number of credits can be awarded for Issue Pol 01. However, where this is not mandatory and the developer has the option whether to connect, regardless of encouragement or incentives by the local authority, the district cooling system must be considered against the BREEAM criteria for refrigerants to award the credits.
27/04/2017: Clarified the number of credits awarded
District heating systems - KBCN0979
District heating systems serving the assessed building must be assessed for NOx emissions.
- Where the developer has no choice over this connection, the maximum number of credits available for the asset type is awarded for this issue.
For instance, the connection is mandated by a local authority or other statutory body.
- Where the developer has choice over their connection, the district heating system must be assessed against BREEAM criteria.
This is regardless of any incentives to connect.
14-Dec-24 - Wording clarified.
07-Dec-17 - Reference to NOx emissions clarified
District heating systems – fuel mix - KBCN0885
Where the feasibility study is considering connection to a district heating system and this burns a mixture of fuels, only the proportion of output generated from second generation bio-fuels (or waste incineration that complies with BREEAM requirements) can be considered for this issue.
For instance, a system burning a 25/75 mix of compliant biofuel vs fossil fuel can only count 25% of its output towards a meaningful reduction in CO2 emissions (where relevant to the BREEAM scheme) against the baseline building.
As fuel mixes may vary over time, at least one year or more of historical information must be provided to balance out any seasonal variations. Where the system is new or proposed, robust evidence must be provided of the anticipated fuel mix.
The fuel mix must be calculated based on the energy content of the input fuels in kWh.
19/12/2017 Wording clarified
District heating systems which off-set grid electricity - KBCN0857
District heating systems which incinerate waste usually have NOx emissions higher than the levels set to achieve any BREEAM credits.
However, where a district heating system also generates electricity, this can be used to off-set NOx emissions from grid electricity. In such cases, the calculation methodology for CHP systems can be used to calculate NOx emissions for the district heating network.
Domestic hot water supplied by a circulation loop - KBCN1017
Where a circulation loop is used on the domestic hot water supply, it is acceptable to only sub-meter the cold water supply.
Sub-metering such systems may be impractical and the occupant can use the cold water meter readings as a proxy for overall water usage in relevant areas.
Drop-down menus in the tool - KBCN0789
When using the Mat 03 calculator tool, some of the entry fields are no longer restricted to drop-down menus but allow free-text entry. This provides greater flexibility of use for the tool making allowance for updates to Guidance Note GN18.
If a responsible sourcing scheme is not in the drop-down menu, assessors should check Guidance Note GN18 for the scheme and manually enter the name of the recognised scheme and its point score.
Drying space in hotel/ hostel projects - KBCN0174
The Drying space issue is not applicable to projects where occupancy is transient, such as hotel or hostel type developments, but does apply to long term residential buildings.
There is little potential in reducing the energy from drying clothes in hotel and hostel bedrooms compared to long term residential buildings.
Ecological enhancements – large mixed use/multi-building developments - KBCN0588
At the Post Construction stage of assessment, for large mixed use/multi-building developments, where the whole site has not been completed and ecological enhancements have not yet been added, or where features are being added at a later date in an appropriate planting season: evidence from the client or principal contractor confirming planting will be completed within 18 months from completion of the development is acceptable.
Ecological value – timing of planting - KBCN0479
Where the 18 month deadline for the completion of the planting is likely to be exceeded due to the timing or phasing of the construction, the project team will need to clearly justify the reason for this variation, and provide a written commitment to carry out the planting within a reasonable and justifiable timescale.
Education – Boarding schools - KBCN00089
The number of cycle spaces and facilities should be calculated based on the number of day pupils and boarders and these should be available to pupils and staff as appropriate.
For boarders, the cycle storage and cyclists' facilities requirement may depend upon a number of factors, such as the age of the pupils/students, distance of the residential accommodation from the school buildings and the school’s policy on cycling. Therefore, the assessor is required to calculate the appropriate number of cycle storage spaces and facilities for pupils and staff based on the relevant criteria.
Calculations, justification and supporting evidence should be provided in the assessment report.
14 03 2018 - Heading and wording clarified and amended to remove requirement for assessors to submit a technical query prior to certification.
Education – Different age ranges and/or non-acute SEN - KBCN0224
For a combined school campus the number of cycle storage spaces and compliant facilities will need to be calculated individually for each user-group of the building; e.g. the number of facilities for nursery schools, primary schools and secondary schools should be calculated as per the criteria defined for each of these education types and totalled.
Where this includes non-acute SEN facilities and the unusual structure of the classes prevents standard assessment, the assessor should use their judgement to determine whether to apply the pre-school criteria or base on the total number of staff and students.
While within the scoring and reporting tool the dominant education building type category will be selected, calculations need to be provided as supporting evidence, with the assessor's comments/notes used to clarify the calculation used to demonstrate compliance.
14 03 2018 - clarified and key information incorporated from KBCN0424
Education – Secondary schools - KBCN0119
Cycle spaces:
Cycle parking spaces may be shared between students and staff, and are calculated based on the total number of staff and students as per the technical guidance.
Students:
Compliance for students can be based on the provision of compliant lockers only based on the following logic:
• Where secondary schools have sports facilities, compliance shall be based on the provision of compliant lockers only. The provision of showers or changing spaces is assumed to be included with the sports facilities are do not need to be assessed.
• Where secondary schools do not have sports facilities, cyclist facilities are assessed as per the technical guidance.
Secondary schools will, in almost all cases, will already have sports facilities including enough showers and adequate changing facilities to meet the BREEAM requirements by default. For most students however, the most important facility is likely to be adequate locker storage rather than showers or changing facilities.
Staff:
Separate shower and changing facilities must be provided for staff. Locker facilities may be shared with students if appropriate, but staff lockers should be suitably located in relation to the other staff facilities.
The number of showers for staff should be based on the total number of staff and one shower for every 100 staff*, subject to a minimum of one shower being provided.
*This is based on 1 cycle storage space per 10 staff, and 1 shower per 10 cycle storage spaces.
10 03 2020 Further clarification of the intent
14 03 2018 Heading and wording clarified
Electric vehicle (re)charging stations/points/spaces - KBCN0934
For BREEAM purposes, a vehicle charging station/space includes a facility that is dedicated to charging vehicles. Provision of a mains-powered electrical socket will not be deemed compliant.
13 October 2023 - Title and wording updated to align with terminology used elsewhere in our guidance.
Electric vehicle charging stations - KBCN0684
As per the 'Alternative transport measures' criteria, the percentage requirement for electric charging stations should be based on the total car parking capacity for the building.
Where the assessment covers only part of a building or development this must be based on the total car parking capacity unless the parking for the assessed development is clearly segregated and available only for the use of its building users.
23 03 17 Reference to car sharing spaces removed. See also KBCN0282
Electric vehicle charging stations (EVCS) – Priority spaces - KBCN1429
The current criteria for EVCS do not address provision for priority spaces, such as those allocated to disabled use and car sharing.
The assessor and design team should, therefore, take a pragmatic approach to this and, where the overall number of required EVCS permits, an appropriate proportion of these should be provided for priority spaces. This will not be deemed as 'double-counting' as the number of EVCS required should be considered independently of other requirements.
The intent is that electric vehicle charging spaces are available to all building users (where possible).
Electric vehicle charging stations – Availability - KBCN1128
This option requires the number of electric vehicle recharging stations (EVCS) to be based on a percentage of the total car parking for the building.
To meet compliance, the intent is that recharging stations be available to all building users, including customers and visitors. However, where overall parking numbers are low, it may be difficult to effectively distribute the EV charging spaces between general users and priority groups.
In such cases, the design team must provide evidence that this aspect has been considered when locating the EV spaces, however, the decision on how to distribute these may be made by the client or, for speculative development, by an appropriate member of the design team.
In situations where parking is limited to priority spaces only, the above guidance still applies.
11 Jan 2023 - Applicability to BIU V6C confirmed and updated to allow more flexibility in relation to how EV spaces are allocated.
02 Jun 2020 updated to clarify how this applies where the only on-site car parking is for special user groups.
Electric vehicle charging stations – faster charging - KBCN1497
The number of electric vehicle charging stations required for compliance cannot be reduced by installing faster/higher power charging stations.
This would not necessarily increase the availability of the charging stations for users.
Electric vehicle charging stations – Requirement to demonstrate that electric vehicles have lower CO2 emissions - KBCN1622
This requirement is now considered obsolete and it is no longer a requirement where compliant electric vehicle charging points are installed.
Electric vehicle charging stations – shell & core assessments - KBCN1247
For shell & core and partially-fitted residential developments, compliance can be demonstrated by installing all the necessary infrastructure, (i.e. capacity in the connection to the local electricity distribution network and distribution board, as well as sub-surface ductwork to receive cabling to parking spaces), to enable the simple installation and activation of charging points at a future date.
15/11/2019 Incorrect reference to pre-installation of 'cabling' removed.
Electric vehicle charging stations – Short-term visitor spaces - KBCN1735
Where it can be demonstrated that parking spaces for visitors will only be used for short-term parking (a maximum of 15 minutes), these spaces can be excluded from the calculation for EV spaces.
This exclusion will typically apply to certain types of retail outlet, where visitors are, for example, collecting or dropping off orders. However, other situations can be considered, where justified.
Elemental U-values for assessments against Parts 2 and 3 - KBCN1011
Where Part 1 is not being assessed, improvements to the performance building fabric cannot be recognised, whether these be designed or consequential. In order to fully recognise the services efficiency improvements, however, where changes to the building fabric have been made, the post-refurbishment elemental U-values should be used for both pre-and post-refurbishment.
Where a project seeks recognition of improvements to the performance of the building fabric, this must be assessed against Part 1.
Emergency lighting - KBCN0185
Maintained systems featuring emergency light fittings which are also used for normal operation, are assessed for this issue.
Non-maintained lighting which is only activated in an emergency can be excluded from the assessment.
NC / RFO / BIU V6 Ene 17: The aim of these credit(s) is to encourage and recognise energy-efficient fittings. Non-maintained emergency lighting will very rarely be activated and in such extremes the emergency requirements must not be compromised.
BIU V6 Hea 05: Flicker is eliminated from maintained systems only.
24-Jan-2024 - Scheme applicability updated to include BIU V6.
Emissions – measuring heating demand - KBCN0182
Emissions for all heat sources should be measured under normal operating conditions which are when all heat sources from the building plant are operating to their maximum design heat outputs to meet the building's heating demands.
Where plant is designed to operate below maximum capacity, for example multiple or modular systems or standby boilers,the emissions should still be calculated for the plant operating to meet the building’s heating demand. Any redundant capacity or standby plant should not be included.
Emissions from products – ‘no formaldehyde’ declaration - KBCN1137
Where a product manufacturer’s declaration confirms that a product contains no formaldehyde, this can be used to demonstrate compliance with both the standard and exemplary level criteria.
However, where a manufacturer has made a declaration of formaldehyde class E1 without testing, this can only be used to demonstrate compliance with the standard criteria.
An E1 declaration only confirms that emissions of formaldehyde are ≤0.12 mg/m3, so this would not be valid evidence to demonstrate compliance with the exemplary level criteria emission limits.
The manufacturer would need to provide additional information (e.g. test report) to show that emissions from the product meet the exemplary level emission limit.
11-Oct-2022 Title amended for clarity and consistency.
Emissions from products – BS EN ISO 12460-5 standard - KBCN0118
Products tested to the BS EN ISO 12460-5 standard can show compliance with the BREEAM 'emissions from products' criteria only for the following products:
- Wood panels.
- Suspended ceiling tiles.
These products must be made from unfaced particle board, unfaced OSB or unfaced MDF.
Factory production control testing must demonstrate that the product has a formaldehyde content of ≤ 8mg/100g oven dry board.
10-Oct-2022 - Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Wording clarified.
01-Dec-2017 - Previously referenced standard EN 120 superceded by BS EN ISO 12460-5 Wood-based panels. Determination of formaldehyde release. Extraction method.
Emissions from products – Building materials for M&E purposes - KBCN1740
All M&E materials are excluded from VOC assessment requirements. However, from V7 onward, while finished M&E products may be excluded, all on-site applications of paints, coatings, adhesives and sealants used for M&E purposes must be included in VOC assessments under their relevant material categories.
02 July 2025 - Inclusion of duct insulation removed
Emissions from products – earlier versions of AgBB standard - KBCN0655
Guidance Note GN22 lists the standard AgBB (2015) as a recognised scheme for emissions from building products for pre-December 2015 launched BREEAM schemes.
Previous versions of the AgBB scheme are not listed as recognised schemes because earlier versions of AgBB did not include any requirement for the testing of Formaldehyde.
If an earlier version AgBB has been used, further evidence will be required to provide additional information on the required Formaldehyde testing.
10-Oct-2022 - Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Made applicable to International NC V6.
Emissions from products – exemplary level formaldehyde requirements - KBCN1124
The exemplary level criteria for formaldehyde emission levels are not applicable to the following product types:
- A paints and varnishes.
- G flooring adhesives.
- H wall coverings.
Formaldehyde emission levels should be assessed on all other product types.
This applies also to any approved alternative VOC schemes for these product types listed in GN22.
11-Oct-2022 - Title amended for clarity and consistency.
Emissions from products – installations manufactured off-site - KBCN0137
Internal finishes to installations manufactured off-site such as elevators need to be assessed for the emissions from products criteria.
The specification of internal finishes (regardless of whether they are installed on site or in the factory) will impact on VOC emissions. By specifying low VOC finishes, design teams will be encouraging manufacturers to consider the environmental impacts of their products.
10-Oct-2022 - Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Made applicable to UK and International NC V6.
Emissions from products – manufacturers’ calculations for paints and varnishes - KBCN0452
Manufacturers' calculations of VOC content, based on the constituent ingredients, can be used to demonstrate compliance with the testing requirement for paints and varnishes.
10-Oct-2022 - Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Scheme applicability updated.
Emissions from products – resin flooring - KBCN0980
Resin flooring products (such as epoxy floor coating) are assessed as ‘Resilient textile and laminated floor coverings’.
11-Oct-2022 Title updated for clarify and consistency. Wording simplified.
Emissions from products – rigid wall covering adhesives - KBCN00076
Rigid wall covering adhesives need to meet the standard listed for flooring adhesives.
11-Oct-2022 - Title renamed to standard naming format for clarity and consistency. Scheme applicability updated.
16-Jun-2015 - Published pending reissue of the technical manual UKNC2011/REISSUE UKNC2014/REISSUE UKRFO2014/REISSUE.
Emissions from products – scope of assessment - KBCN0212
General
This issue covers any product installed or applied inside the inner surface of the building’s infiltration, vapour or waterproof membrane.
Where this membrane is not present, it applies to the inside of the building envelope’s interior-facing thermal insulation layer.
Only products that are installed or applied in parts of the building where their emissions are likely to affect indoor air quality need to be assessed.
Paints and coatings
Any decorative paints and varnishes that occupants are exposed to should be assessed.
This is likely to include paints and coatings applied to walls, ceilings, floors, doors, etc.
Whole products
A finish applied to a product in the factory is assessed as a whole product, and not separately as a paint or coating.
For instance, a wood panel has a finish applied in the factory. The whole panel, including all the elements that make up that panel, would need to comply with the requirements set for wood panel products in this issue.
The finished product as a whole must meet the performance requirements / emission limits set in the manual.
11-Oct-2022 - Title amended for clarity and consistency. Content merged with KBCN871.
10-Oct-2022 - Wording simplified. Scheme applicability updated.
16-Jun-2017 - Title and general principle amended to extend the applicability of the KBCN to all finishes. Paints specified for specialist applications covered in KBCN0872.
Emissions from products – specialist paints and coatings - KBCN0872
Where a paint or coating falls within:
- A category in Annex II of the EU Directive 2004/42/CE or,
- A category in the relevant product emission table of the technical manual,
then the paint or coating must be assessed.
Specialist paints and coatings are exempted from meeting the VOC content and emission limits where there are no alternative products available that can perform the function, and still meet the emission limits.
This must be clearly evidenced.
02-Oct-2025 Reference to 'VOC content' added and KBCN applied to INC V7 to clarify CN2.1
27-Oct-2022 Wording clarified. New compliance principle added from UKNC V6.
10-Oct-2022 Title amended for clarity. Scheme applicability updated.
13-Mar-2020 KBCN amended to clarify exceptions and applicability.
16-Jun-2017 Content merged with KBCN0212.
Emissions from products – testing to ISO 16000-10 - KBCN1134
Results of testing to ISO 16000-10 can be considered compliant with the relevant testing requirements of the emissions from construction products credit where the product manufacturer can demonstrate the results generated by testing to ISO 16000-10 correlate to results that would be achieved using EN 16516 or ISO 16000-9.
This is because EN 16516 classifies ISO 16000-10 as an ‘indirect method’, which means “any simplified, screening, secondary, derived or alternative method. An indirect method can be applied if it provides a result that is comparable to or that correlates with the result of the reference method under the conditions applied. The validity of the correlation with the reference method is limited to the field of application for which it has been established.”
11-Oct-2022 - Title amended for clarity and consistency. Scheme applicability updated.
Emissions from products – wall covering fabric - KBCN0724
For the 'Volatile Organic Compound emissions levels (products)' criteria:
Any fabric specified as part of a wall covering should be assessed as part of the 'wall covering' requirements.
It should not be assessed as part of the 'resilient textile and laminated floor coverings' requirements.
11-Oct-2022 Title amended for clarity and consistency. Wording clarified.
Emissions from products – alternative testing standard for paints - KBCN1003
Where stated in EU Directive 2004/42/CE, ASTMD 2369 can be used as an alternative the testing standard for paints where reactive diluents are present.
11-Oct-2022 - Title amended for clarity and consistency. Wording simplified.
Ene 01 Assessment - KBCN0985
For the assessment of Ene 01 in International Refurbishment and Fit-Out 2015, the elemental level energy model is the only assessment route available to demonstrate compliance.
Compliance Note CN3 'Approved Building Energy Calculation Software' has been included within the International Refurbishment and Fit-Out manual in error and should be disregarded.
Technical manual to be amended in the next re-issue.
Energy consumption and carbon emissions of untreated spaces - KBCN00049
Where the assessment contains a mix of treated and untreated spaces, untreated spaces can be excluded and the performance based on the treated spaces only. Where the entire assessment is untreated, the whole of the structure(s) must be assessed on the basis that this issue is critical for certification.
BREEAM is primarily designed to assess permanent, treated and occupied structures. Untreated structures are unlikely to gain many credits when being assessed.
Energy efficient laboratories – scope - KBCN1254
This Issue is also applicable to 'Offices with Research and development areas' and other buildings with research and development facilities that contain laboratory space and containment devices/areas.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
Energy modelling a change of use project - KBCN0574
The energy model for the existing building in a change of use project should include the physical characteristics of the existing building but with the use class of the proposed refurbished building to enable a comparison to be made between the performances of the two buildings.
Moreover, the existing building energy model needs to include the existing services as they were before the refurbishment. Where a particular system to be installed in the refurbished building is not present in the existing building, then the baseline system needs to meet the minimum requirements required to pass building regulations for it.
22/02/2017 Added content clarifying building services
Energy monitoring and management systems and small useful floor areas - KBCN1361
The requirement for an energy monitoring and management system (Building Management System – BMS) applies to useful floor areas that are greater than 1,000 m2. For developments where useful areas are monitored by single utility meters (of the same fuel) and are smaller than 1,000m2, the BMS requirement is not applicable. This is because the value of monitoring given by a BMS is not appropriate for such small areas.
For example, in a situation where a large building is served by several utility meters (of the same fuel), with none of them covering a useful floor area greater than 1,000 m2, the requirement for BMS is not applicable.
Energy performance assessment for part of a whole building - KBCN0596
If the assessment is only covering part of a whole building, the energy performance assessment must be representative of the part of the building being assessed. Simply taking the energy performance assessment of the whole building would not therefore comply, especially if the non-assessed parts of the building were of a different use. A separate energy assessment of the part of the building is likely to be required.
The energy performance assessment must be representative of the parts of the building being assessed.
Energy sub-metering – Single occupancy & function - KBCN0491
In large buildings of single occupancy/tenancy where there is only one homogeneous function (e.g. hotel bedrooms, offices), sub-metering should be provided per floor plate.
Environmental management – no principal contractor - KBCN1213
In order to achieve compliance where there is no principal contractor, the criteria must be met by the party which fulfills an equivalent role in managing the construction.
The intent of the criteria is to ensure that the site is managed in accordance with demonstrably sustainable principles by the party having overall control of site management and operations.
Environmental management – Timing of obtaining ISO 14001/EMAS certification - KBCN0229
The contractor must be in possession of the ISO 14001/EMAS certification prior to starting works on the development under assessment.
This is to ensure that the aim of the issue, to ‘encourage construction sites managed in an environmentally sound manner’, can be achieved. To uphold the robustness of BREEAM, the date of certification to ISO 14001/EMAS must be prior to initial works starting on the site.
Erratum – Criterion 1 – Exemplary level credit - KBCN1494
Within the list of requirements, Criterion 1.a.vi was included in error. The requirements for the Exemplary credit are listed under Criterion 2.
One credit - Adaptation to climate change – structural and fabric resilience
1 Conduct a climate change adaptation strategy appraisal for structural and fabric resilience by the end of Concept Design (or equivalent), in accordance with the following approach:
1.a Carry out a systematic (structural and fabric resilience specific) risk assessment to identify and evaluate the impact on the building over its projected life cycle from expected extreme weather conditions arising from climate change and, where feasible, mitigate against these impacts. The assessment should cover the following stages (see Methodology):
1.a.i Hazard identification
1.a.ii Hazard assessment
1.a.iii Risk estimation
1.a.iv Risk evaluation
1.a.v Risk management
1.a.vi Exemplary credit – Responding to adaptation to climate change
This will be corrected in the next reissue of this technical manual.
Erratum – up to v1.4 – VOC emission levels - KBCN0442
The technical manual is missing the following requirement for the VOC emission levels for the product categories, which should follow the wording in criterion 8:
"At least five of the seven remaining product categories listed in Table 'VOC criteria by product type' meet the testing requirements and emission levels criteria for volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions (listed in the table)."
11-Oct-2022 Title amended for clarity. To be amended in the technical manual re-issue.
Erratum: Minimum requirements for an Excellent or Outstanding rating - KBCN1486
The minimum requirements for Excellent and Outstanding ratings in table 26 are incorrect. Please, instead, refer to table 5 in the Minimum Standards section of the manual.
For example, to meet the minimum requirement for an Outstanding rating when assessing all 4 parts, 10 out of 12 credits are needed, which equates to 83.33% of the maximum score. The same 83.33% is required, regardless of the number of credits available.
Escalators or moving walks – variable speed drive - KBCN1621
The requirements refer to 'a load sensing device that synchronizes motor output to passenger demand through a variable speed drive'.
The intent is that the inverter must operate full-time to moderate output based on passenger demand.
Evacuation lifts - KBCN0437
Evacuation lifts, which will be used during an emergency only, can be excluded from the relevant BREEAM criteria. However, if these lifts are used during the normal operation of the building, then they still need to be assessed.
Evidence requirements for Mat 01 Calculator - KBCN0675
The following evidence requirements, taken from the BREEAM International New Construction 2016 manual, give further information on the evidence that can be used to demonstrate compliance. This will be added to the next manual re-issue and will be required as evidence.
Evidence requirements
Note: Aside from the likely benefit to the environment from teams using LCA tools, the objective for BREEAM is to gather LCA performance data in order to create benchmarks and inform future updates of the scheme. The evidence requirements below are generic, but BRE Global understand that some tools are not able to fulfil all of the criteria. Where this is the case, the tool operator should submit results as close as possible to that required for the tool.
IMPACT compliant tools
A copy of the full IMPACT project or building file submitted by the assessor to BRE Global must be transmitted in the following format:
- For 3D CAD or building information model (BIM) based IMPACT compliant tools: In Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) or the IMPACT Compliant tool’s native format.
- For spreadsheet-based IMPACT compliant tools: IFC, MS Excel or comma-separated variables (CSV) file format.
- Building element categorisation to be according to New Rules of Measurement (NRM) Royal Institution of Chartered surveyors (RICS).
- A table in MS Excel or CSV file format listing each building element with, for each one, the information listed under 2 b, c and d (from the 'other tools' section), along with the NRM classification.
Other tools
An electronic data table or tables of results (suitably cross referenced) generated by the tool, submitted by the assessor to BRE Global must fulfil the following criteria:
Submit a total building environmental impact result for year 0 (installation only) and year 60 study periods, as follows:
- To include individual results for all environmental issues or indicators that the tool or data permits, showing issue or indicators names and units used. Where issues or indicators according to BSEN 15978:2011 are available, these should be used
- Include individual results for each life stage or module, e.g. stages A, B and C (see BS EN 15978:2011). Where the tool further permits, or where complete measurement of the aforementioned stages is not possible, more detail should be provided. For example, BS EN 15978:2011 modules should be used
- The reporting format should be to BS EN 15978:2011 (or equivalent).
Results for each element as follows, to enable project team members and assessors without an IMPACT Compliant tool to check the accuracy of the model:
- Element impact per issue (as above), with units
- Element kg kgCO2e per life stage or module (as above)
- Element quantity, with units
- Element description
- For each material in the element:
- Installed quantities, with units
- Site wastage quantities, with units
- Replace, repair, refurbish quantities, with units
- Reuse, recycling or disposal (landfill, incineration) quantities, with units.
Transmitted in IFC, MS Excel or CSV file format.
Data permissions
Submission of information to BRE Global for the purpose of assessing this issue will be required at QA stage. The submission is deemed to grant permission for the BRE Group of companies to use the information to:
Fulfil BREEAM quality assurance requirements
Conduct further research (using anonymised data), including for the establishment of robust building level life cycle performance benchmarks in BREEAM and BRE associated tools and methodologies.
Technical manuals to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
Evidence: Final design/’as-built’ drawings as evidence - KBCN0393
Where drawings are not clearly marked to indicate their 'as-built' status, additional evidence would need to be provided by the design team to confirm the drawings represent the completed development and that there have been no changes relevant to the BREEAM/HQM assessment. This could, for example, be a written confirmation from the architect or the contractor, as appropriate.
Evidence: Photographs not permitted for security reasons - KBCN0389
Where photographs are not permitted during a post-construction site visit for security reasons, in addition to any alternative evidence requirements listed in the Schedule of Evidence for each issue, the assessor will also need to provide a detailed site inspection report and/or as-built drawings (where permitted by the client). If following this approach, full justification and documentary evidence from the client will be required for QA purposes.
Evidence: Post construction assessment evidence - KBCN0407
For the purposes of robustness and completeness, both design AND post-construction stage evidence is required for a post construction assessment. However, it is possible to provide only post construction stage (PCS) evidence where it is clear that this completely supersedes the design stage (DS) evidence and renders it unnecessary.
Excluding applications from assessment - KBCN0875
Where a structural engineer has determined that recycled or secondary aggregate cannot be used in line with the criteria for a particular application, or where they will not allow the minimum BREEAM level to be used, that application can be excluded from the assessment. Where the engineer allows some content to be used, this percentage must still be specified in the excluded application. The engineer's decision must be suitably justified (for example following the BS8500 series and associated standards) and must be provided as evidence for the BREEAM assessment.
Exemplary level criteria applicability - KBCN0973
Criterion 16 mistakenly refers to criteria 5-19, but should refer to criteria 5 to 15.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in the next re-issue.
Exemptions from hard landscaping and boundary protection - KBCN00062
Where a third party, such as the local authority, enforces strict constraints on the materials that can be used by the project for hard landscaping or boundary protection, and these materials do not achieve a Green Guide rating of A/A+, it is possible to exempt these materials from the assessment of this issue, on the condition that robust evidence confirming this is given.
In this instance the developer does not have control over the materials specified, therefore it is not appropriate to include them in the assessment.
Existing lift shaft retained - KBCN0971
Where existing lift shafts are being retained, with a new lift system installed, all criteria for this Issue can still be assessed and credits awarded accordingly, despite the limitations of the existing shafts. The transport analysis should still be carried out as this will inform the developer of any shortfall in capacity and may influence the design of the new lift system.
Despite the limitations of the existing building, BREEAM seeks to reward the installation of an energy-efficient lift system.
Existing lifts outside the scope of assessment - KBCN0793
Transportation systems should be considered as within the scope of the assessment where these serve the assessed area. However, in cases where the developer cannot influence their specification or carry out work to these, they should not be assessed.
This would, for example, include situations where, in an assessment of a tenancy area, the lifts are under the landlord's control or, in a first fit-out assessment of a shell and core development, which includes newly-specified lifts which will not undergo any further work.
Reference in the criteria to compliance for existing lifts is intended to apply where existing lift systems are being refurbished, or where existing lifts are within the control of the developer and are being retained . (Refer also to other relevant compliance notes).
In such cases, where these are the only lifts and transportation system present in the building, this Issue should be filtered out of the assessment by responding ‘no’ to the relevant filtering question in the online scoring and reporting tool.
This Issue is intended to assess transportation systems, which fall within the scope of the refurbishment and where their specification can be influenced as part of the assessed project.
30.11.17 Re-worded for clarity.
22.11.17 Wording amended to clarify that such lifts will not be assessed.
16.11.17 Clarification added on how to filter out this Issue.
Existing materials recycled on site - KBCN0813
When existing elements are recycled (ie crushed and used as aggregate) on site, they can contribute to awarding credits as recycled aggregates.
This issue aims to recognise and encourage the use of recycled and secondary aggregates and addresses waste rather than materials. It refers to recycled aggregate obtained on-site or off-site, based on materials identified as waste and removed during construction works.
Previous incorrect KBCN text amended. CN 'Aggregates in existing applications' to be amended accordingly in next reissue of the RFO Technical manuals.
Existing plant – Noise impact assessment - KBCN0640
The existing background noise level should not include existing plant associated with the assessed building (criterion 2.a.i). Both existing and newly specified externally mounted plant should be considered within the noise impact assessment as part of the ‘rating noise level’ (criterion 2.a.ii).
However, for Part 2 only and Part 3 only assessments, as indicated in the relevant CNs within the manual, only the noise impact of existing or new externally mounted plant specified within the scope of that Part is to be considered.
For example, in a Part 3 only assessment, where existing plant forms part of the core services and new plant is installed as part of the local services, only the impact of the noise generated by the new plant should be considered. The existing plant noise should be included as part of the existing background levels.
Issue Pol 05 assesses the impact of existing and newly specified externally mounted plant and the impact of any fabric measures on reducing the impact of noise on any nearby noise-sensitive buildings. Its applicability is relevant to all treated buildings where Part 1 is included, even where the existing plant is not being upgraded and is scope dependent when Part 2 or Part 3 only assessments are carried out.
13.08.18 KBCN content amended to include consideration of Part 2 or Part 3 only assessments.
This will be clarified in the next manual re-issue.
Extending a lift shaft - KBCN0802
Where the scope of works regarding a lift only includes extending the lift shaft to other floors, then assessment of this lift is not appropriate. Where changes are made to the lift system, then assessment is required.
Where changes to lift systems are made, these lifts need to be included in the assessment to encourage specification of energy efficient transport systems.
External lighting – architectural façade lighting - KBCN0650
Architectural facade (or other decorative) lighting which does not provide users with lighting to perform tasks outdoors does not need to be included in the assessment of external lighting.
This Issue seeks to ensure that lighting levels are appropriate for tasks which building users will be undertaking outdoors.
External lighting – High frequency ballasts - KBCN0278
The requirement for all fluorescent and compact fluorescent lamps to be fitted with high frequency ballasts does not apply to external lighting.
External lighting inside wider building - KBCN0906
Where a building undergoing assessment is located inside of another building, for example a retail unit within a shopping centre, Ene 03 External lighting and Pol 04 Reduction of night time light pollution should be assessed as follows;
Ene 03
'External lighting' that is inside of the wider building, using the example above the lighting is external of the retail unit itself but inside of the wider shopping centre, criteria relating to the luminous efficacy should be applied as presented within the manual. For the criteria relating to controlled for prevention of operation during daylight hours and presence detection in areas of intermittent pedestrian traffic, however, instead of demonstrating that the lighting is not operational during daylight hours, it should be demonstrated that the lighting is not operational outside of the operational hours of the wider shopping centre. Any external lighting within the scope of works being assessed that is located outside of the wider shopping centre, for example if the retail unit had an entrance or exit that leads on to the street outside, this would need to be assessed against the criteria presented within the manual.
Pol 04
If the building undergoing assessment has no external lighting that is outside of the wider building, it can be considered that the building has no external lighting. However, as above, any external lighting within the scope of works of the assessment that is located outside of the wider building will need to be assessed as the criteria is presented within the manual.
10/05/2019 Reference to specific criteria numbers removed and made applicable to UK NC2018
External wall area – inclusion of doors - KBCN00088
21/12/17 Previous guidance removed. Please refer to the relevant building energy modelling software guidance.
External works – waste reporting requirements - KBCN1379
Waste arising from external works does not need to be included within the calculations for construction resource efficiency. To do so would be incongruous with reporting waste relative to the building's floor area. This follows the logic of excluding excavation waste from this criterion.
However, waste from external works should be addressed in the RMP and should also be reported in the calculations for the Diversion of resources from landfill credit, which is not reported relative to the building's floor area.
Fabric testing and inspection in hot climates - KBCN0790
The requirements for thermographic survey and air tightness testing are applicable to both, cold and hot climates. A suitably qualified professional will advise on the appropriate testing conditions and specific methods in order to address this issue in different climatic conditions.
Building fabric air tightness is important in different climates in order to ensure than no additional energy is consumed due to increased heating or cooling demand originating from the lack of integrity of the building fabric.
Feasibility study – comparison with connection to existing LZCs - KBCN0563
In carrying out a feasibility study (covering all the areas required as stated in the manual) the primary intent is to demonstrate to a reasonable level of certainty that the chosen LZC is the most appropriate of all those available.
Some of the options (for example community heating/cooling schemes) may not allow for a simple like for like comparison but a comparison can be made overall across many factors. For example in a community heating scheme the life cycle costing estimate might need to be simply the cost of using and maintaining the system for the measuring period, if upfront costs and payback period information is not available. Similarly for an existing community scheme, planning would not be a barrier but land use and noise impacts could be compared.
The feasibility study must include a comparison of all criteria and for it to show that each has been factored into the final option being made. While some options may provide information in different formats and differing levels of detail making direct comparisons not straightforward, a comparison can still be made and this should aim to be as comprehensive and representative as possible. This will serve to demonstrate with reasonable certainty that the chosen option is the most appropriate.
Fire hydrants and sprinklers – Leak detection - KBCN0680
Where it is confirmed by an appropriate project team member that it is not possible to fully meet the leak detection criteria for fire hydrants or sprinklers, an alternative approach can be implemented for these systems.
This must demonstrably meet the aim of the issue by detecting and alerting the building management to major water leaks.
11 Sep 2024 - Applicability to BIU USA V6 and INC V6 confirmed. New guidance introduced to clarify that BREEAM compliance should not compromise the operation of building safety-critical systems.
First fit-out of a shell only/shell and core development - KBCN00099
For assessments of a first fit-out of a new building the 'pre-refurbishment audit' credit is filtered out from the assessment.
Flood risk – Site situated across numerous flood zones - KBCN0532
Where a site is situated across more than one flood zone, the flood zone with the highest probability of flooding, i.e. the worst case scenario, must be considered for the purpose of the BREEAM assessment. An exception to this would be where the areas in the higher probability zone include only soft landscaping and it can be demonstrated that access to the building will be maintained in a flooding event.
This is to ensure that the site has adequately managed the worst case scenario level of flood risk associated with the site's location.
07/03/2018 Updated to include circumstances where an exception may apply.
Flood Risk Assessment older than five years - KBCN1744
This sentence appears in the definition of ‘Flood Risk Assessment’: Where more than five years have passed since the FRA was carried out, evidence would be required to demonstrate that the basis of the FRA has not changed in that time.
The requirement for evidence that the basis of the FRA has not changed where more than five years have passed is applicable only at Design Stage. It is not required at Post Construction Stage where a compliant FRA was undertaken at Design Stage and the development was carried out in accordance with that design.
Flow control devices – Use of devices on individual sanitary fittings - KBCN1550
The intent of the requirement for flow control devices is to minimize the impact of undetected wastage and leaks from sanitary fittings and supply pipework.
The use of flow control devices on individual sanitary fittings alone does not, therefore, fully meet this aim.
Flow control devices for multiple blocks - KBCN1186
The criteria are set to encourage isolation of the water supply to each WC block when it is not being used. If a single flow control device, for example one programmed time controller, is adequate to switch the water on at predetermined times that suit the usage patterns of more than one WC blocks or facilities, this can be used to demonstrate compliance.
Please note that if only one timed controller is used for a large area/number of facilities, the assessor must justify that this is appropriate to the usage patterns within the building and confirm that multiple timers would be redundant (i.e. they would all be set to the same time). Consideration should be given of any facilities that may be open longer than others, requiring these timers to be programmed differently in different areas.
As long as the aim of the credit (‘to reduce the impact of water leaks that may otherwise go undetected’) can be achieved through the specification of an appropriate number of flow control devices, the credit may still be achieved if timers cover more than one WC area/facility to prevent minor water leaks.
14 Apr 2023 - Applicability to BIU V6 Commercial confirmed
Flow control devices on rainwater supply for toilets - KBCN0868
Flow control devices will be required on water supplied from rainwater and serving the toilet facilities. Rainwater tanks are topped up by mains water and leaks could reduce levels of stored water and hence increase the use of mains water.
The leak detection requirements apply to all relevant water systems, regardless of the water source.
Flow control on cold water supply - KBCN0417
A shut-off on the cold water supply to the whole WC facility provides a simple and effective way of reducing potential water loss.
Taps which contain built in shut-off valves will not prevent any water leaks from the supply to the tap and so do not fulfil this intent.
The intent of the flow control criteria is to prevent minor water leaks occurring within the pipework of WC facilities.
Flow rate for ‘click’ taps - KBCN0543
The flow rate for click taps should be taken as the maximum flow rate, as quoted by the manufacturer, of the lower range before the water break or 'click'.
All water consumption is based on 'typical' use patterns and it is assumed that most operations of 'click' taps will be at the lower level.
Flow rate for a mixture of taps - KBCN0173
Whichever is the higher of the 'average flow rate' or the 'proportionate flow rate' should be used within the Wat 01 Calculator.
Flow restrictors - KBCN0976
If a flow restrictor can be demonstrated to effectively reduce the flow of water and it is integral to the fitting or supply pipework (ie not easily removed by the building occupant), this can be accounted for in calculations for this Issue.
Such devices must be fit-for-purpose. Proprietary flow restrictors, therefore partly-closed isolation valves, for example, are not an acceptable solution.
FRA more than 5 years old - KBCN1580
Where more than five years have passed since the FRA was carried out, to be able to use the FRA in your assessment evidence would be required to demonstrate that the basis of the FRA has not changed in that time.
Freestanding commercial fridges and freezers - KBCN0577
Freestanding commercial fridges and freezers must be included in the assessment of the Pol 01 issue, even when they are not connected to the building cooling system. Only domestic white goods are excluded from the assessment of this issue.
FSC and PEFC Mixed Sources certified timber - KBCN00091
Products labelled:
- FSC Mix or
- PEFC Mixed Sources
Meet the BREEAM responsible sourcing requirements. This means any such products:
- Meet the prerequisite for legally harvested and traded timber.
- Can be used to demonstrate responsible sourcing.
Products carrying the FSC Mix label contain at least 70% FSC certified and recycled material. These products may contain a small proportion of FSC Controlled Wood (KBCN00054). However for BREEAM compliance, the FSC Mix label is sufficient to meet our requirements.
14-Mar-2024 - Wording clarified and expanded. Relevant prerequisites and requirements clarified. Scheme applicability updated.
FSC Controlled Wood - KBCN00054
The
FSC Controlled Wood label minimises the risk that wood comes from illegal or controversial sources, however it does not eliminate this risk.
Therefore, products which are:
- Labelled as FSC Controlled Wood or,
- Where the majority of material in a product is comprised of FSC Controlled Wood,
Do not meet the BREEAM definition of responsibly sourced.
Where FSC Mix labelled products contain FSC Controlled Wood, see KBCN00091.
This means that any such products:
- Do not meet the prerequisite for legally harvested and traded timber.
- Cannot be used to demonstrate responsible sourcing.
14-Mar-2024 - Wording clarified and expanded. Relevant prerequisites and requirements clarified. Scheme applicability updated.
Functional adaptation strategy study – content - KBCN0930
To achieve compliance with Wst 06, the building-specific functional adaptation strategy study should consider all the items listed in the relevant compliance note 'Functional adaptation strategy study'.
Due to site specific constraints, it may not always be possible to pursue all of the items listed. In these cases, any omissions must be clearly justified in writing when submitting as evidence.
Functional adaptation strategy study – timing - KBCN0730
Late consideration of the strategy appraisal, might reduce the study to a ‘paper exercise’, with minimal value to the project.
However, where the assessor is satisfied that there is clear justification for the study being developed at a slightly later stage (i.e. early RIBA stage 3) AND there is clear evidence that the strategy has achieved the intended outcomes (i.e. the later consideration has been in no way detrimental to the outcomes of the strategy study/appraisal and the benefits can still be realised on the project), this will be sufficient for compliance. In any case, all other requirements of the issue must be met for the credit to be awarded.
The requirements for the timing of the functional adaptation strategy study are intended to ensure that the benefits of the study are realised through early consideration.
Future transport nodes - KBCN0966
Where a transport node is currently inactive but will become active soon after project completion, it can be included when calculating the existing AI.
To demonstrate this, confirmation of the start of service date and service frequency from the appropriate public transport authority or company will be required.
Gabion as boundary protection - KBCN000008
A gabion can be excluded from the assessment if it acts as a retaining wall or any other form of a supporting structure. If it acts purely as a boundary and a generic Green Guide rating cannot be found for a specification, the BREEAM assessor will need to submit a Bespoke Green Guide Query proforma detailing the specification details.
Glare control – adjacent buildings - KBCN1211
It is acceptable to account for surrounding buildings, structures or other permanent environmental features when using simulation modelling to assess the risk of glare, provided this accounts for both direct sunlight and reflected glare from glazing or reflective surfaces.
Glare control – blackout blinds - KBCN0447
Blackout blinds can be used to meet the glare control requirements.
Where the criteria set an upper limit for transmittance value, but no lower limit, blackout blinds will meet this requirement.
Glare Control – no relevant areas - KBCN0429
If the scope of the assessment does not include any relevant building areas, as defined within the manual, the criteria for Glare Control can be considered as met by default.
Only spaces that fall within the definition of relevant areas and are within the assessment's scope need to be assessed.
22/06/17 Wording clarified
16/06/17 KBCN amended to exclude content of KBCN0146.
Glare control – no windows in relevant areas - KBCN0146
Where a ‘relevant area’ as defined in the manual does not include any windows, the glare control criteria can considered as met for this area.
Note that the view out and daylight criteria would not be achieved in rooms with no windows.
Where there are no windows in a room there would be no potential for disabling glare, so the aim of the credit would be achieved.
Glare control – residential institution and multi-residential bedrooms - KBCN0666
Assuming that occupants are generally elsewhere during daylight hours, lighting and resultant glare are not considered to be problematic for bedrooms in residential institution and multi-residential assessments.
The only exception to this is where designated additional office working space is provided. In these circumstances it is the role of the assessor to determine if individual spaces should be determined as 'relevant building areas' in accordance with guidance provided.
Glare control criteria apply to building areas where lighting and resultant glare could be problematic for users.
Glare control – transmittance value - KBCN0709
Transmittance values should be based on those quoted for 'visible light'.
Glare control – use of tinted windows - KBCN0862
Solar control or 'tinted' glazing could potentially support the attainment of this requirement. However, the assessor must be satisfied and provide evidence to demonstrate that the particular glazing type, when used on the assessed building for a given location, is meeting this overarching aim of preventing disabling glare. It should be noted that whilst certain types of glazing, such as low emissivity glazing, may be slightly tinted, they may not necessarily be effective in reducing disabling glare.
For facades receiving direct sunlight, tinted windows alone are unlikely to be sufficient in the majority of situations.
Glare control for roof lights - KBCN0319
Where roof lights are present, they must be considered when demonstrating that the glare control strategy provides adequate control/measures for minimising glare in that space.
All sources of glare need to be considered when designing out the potential for disabling glare.
Glare control in Part 1 assessments - KBCN0100
Although the current technical manual indicates that forms of glare control are applicable to Part1 assessments, this has been reviewed and the BREEAM Projects template now allows the credit to be filtered out for such projects.
This is in line with the NC 2014 scheme and takes account of 'occupant controlled devices' not being within scope.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next re-issue.
Glare control in residential areas - KBCN00040
Glare control criteria apply to building areas such as study bedrooms or facility management offices, where work or study will be carried out and where glare would hinder such activities. It does not apply to other residential areas.
Glare control – Modelling - KBCN1800
The ‘Glare control’ criteria do not require a specific methodology to be used to identify areas at risk of glare, and in most situations, a simple solar path analysis would be suitable. Alternatively, detailed hourly modelling methods, such as DGP and ASE, may be more appropriate. However, in either case, compliance cannot be assumed.
Regardless of the methodology used, the modelling must be supported by robust reporting to demonstrate that each aspect of the criteria has been met.
GN06 Indoor air quality plans - KBCN0618
Latest version: v2.2, July 2025
Guidance Note 6 (GN06) provides guidance to assessors and project teams regarding the content and rigour of an Indoor Air Quality Plan (IAQP) as required by the indoor air quality criteria in BREEAM New Construction and BREEAM Refurbishment and Fit-Out.
It should not be interpreted as BREEAM criteria. It is intended to provide assessors and project teams with further, flexible information and guidance regarding the rigour, content, and tasks of an IAQP.
Download Guidance Note 6
View all Guidance Notes on BREEAM Projects (licensed assessors only)
16-Jul-2025 - Updated for release of v2.2
GN08 – Scope of IMPACT compliant tools and data submission requirements - KBCN0621
Scope of IMPACT Compliant (or equivalent) Tools and Data Submission Requirements - BREEAM UK New Construction 2011 and 2014
Introduction
This Guidance Note relates to complying with the exemplary level criteria for route 2, as defined under the Mat01 issue of the BREEAM New Construction 2011 and 2014 versions. It provides information about IMPACT and the level of detail (the Quality Requirements) and file transmission requirements for the Building Information Model (BIM) from IMPACT compliant (or equivalent) tools. It also outlines criteria for demonstrating the equivalence of a proposed alternative to IMPACT compliant tools for BRE Global approval.
View full Guidance Note (licenced assessors only)
View all Guidance Notes (licenced assessors only)
GN10 Assessing mixed use developments and multiple buildings (or units) of similar function - KBCN0623
Summary
The purpose of this Guidance Note is to assist BREEAM assessors with scheme classifications and the application of BREEAM for mixed use developments and developments with multiple buildings or units on the same site.
This guidance note was revised to v1.0 April 2018
Note, this guidance is applicable to BREEAM standards up to and including V6. For V7 standards, please refer to
KBCN0717
View full Guidance Note (licensed assessors only)
View all Guidance Notes (licensed assessors only)
16 Jul 2025 Applicability clarified and reference to KBCN0717 added.
04 Jun 2018 Note added regarding revision and hyperlink updated
17 Apr 2018 Wording clarified
GN13 Relating ecologist’s report and BREEAM - KBCN0626
Introduction
This guidance note is to be used for registered BREEAM UK New Construction 2014 and RFO 2014 and International New Construction 2016 and RFO 2015 assessments, where an ecologist has been appointed by the client and has produced an ecology report for the proposed development.
The purpose of this guidance note is to help the BREEAM Assessor relate the content of the ecologist’s report to the BREEAM Land Use and Ecology section criteria (assessment issues LE 02, LE 03 (UK only), LE 04 and LE 05). The guidance within this document has been produced to support the assessment of the aforementioned BREEAM issues and should not be interpreted as criteria. If the BREEAM Assessor chooses to use the template provided within this guidance note as evidence in the assessment (use of this document is optional) the assessor or the appointed suitably qualified ecologist must complete all relevant sections
View full Guidance Note (licensed assessors only)
View all Guidance Notes (licensed assessors only)
01/04/2020 Clarified applicability to UK RFO 2014 and International RFO 2015 schemes
GN18 BREEAM Recognised Responsible Sourcing Certification Schemes and BREEAM Scheme Applicability - KBCN0723
Latest version: v3.7, May 2023
BREEAM awards credits for responsibly sourcing construction products (typically under the Mat 03 issue) to encourage responsible product specification and procurement in construction. To achieve these credits, applicable specified products (as listed in the relevant technical manual) must be covered by an Environmental Management System (EMS) or a responsible sourcing certification scheme (RSCS) recognised by BREEAM.
Guidance Note 18 lists the responsible sourcing certifications schemes recognised by BREEAM along with the relevant summary scores to be used in BREEAM assessments.
Download Guidance Note 18
Download Guidance Note 18 v2.0 (optional for projects registered prior to release of v3.0 in September 2016)
View all Guidance Notes on BREEAM Projects (licensed assessors only)
GN22 Recognised schemes for emissions from construction products - KBCN0719
Latest version: v3.0, January 2025
Within the Health and Wellbeing category of several BREEAM schemes, credits are awarded for specifying materials that minimise emissions from building products of formaldehyde and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The criteria involve meeting emission level performance requirements in accordance with compliant performance and testing standards.
Guidance Note 22 (GN22) lists schemes that show equivalent or better performance than the current BREEAM and HQM criteria, and therefore can be used to demonstrate compliance with the criteria. This document should be read in conjunction with the relevant assessment issue guidance provided in the appropriate BREEAM or HQM technical manual.
The guidance note contains two tables:
- Table 1 is for use with BREEAM schemes that were first released before December 2015.
- Table 2 is for use with BREEAM (and HQM) schemes that were first released from December 2015 onwards (post-November 2015).
Download Guidance Note 22
View all Guidance Notes on BREEAM Projects (licensed assessors only)
Applying for inclusion in GN22
The list of approved schemes is based on those which have made a successful application to BREEAM. As such, there may be other operational schemes that could potentially be recognised.
To be considered for inclusion, the scheme operator must complete an application form, providing full details of the scheme, and submit this to BRE Global for technical approval. A flat rate charge is payable to cover the costs of administering and reviewing the application. GN22 will be updated following the approval of any schemes via this process.
The application form (BF1648) provides full details of the application process, and licensed BREEAM assessors can request a copy by submitting a technical query using the
webform. Other parties may request a copy by contacting:
breeam@bregroup.com
25-Sep-2025 - Updated to provide details of the approval process and title updated.
30-Jan-2025 - Updated for release of GN22 3.0
30-Sep-2024 - Updated for release of GN22 2.9
01-Feb-2024 - Updated for release of GN22 2.8
31-Jan-2023 - Updated for release of GN22 2.7
10-Oct-2022 - This KBCN merged with KBCN0646. Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Made applicable to UK and International NC V6.
25-Jan-2019 - Link to Guidance Note updated
12-Mar-2018 - Link to Guidance Note updated
GN24 Demonstrating compliance with Mat 03 in BREEAM - KBCN0721
Latest version: v1.1, May 2022
Guidance Note 24 provides additional guidance to assessors and specifiers on demonstrating compliance with the criteria set out in Mat 03. It should be read in conjunction with the Technical Manual for the relevant assessment scheme. It covers:
- How to deal with constituent products/materials including those with certification that is different from the overall product.
- The precision required in estimating quantities:
- For the cut-off volume
- Of products/materials in the building (route 2 only)
- Of different material categories in products/materials.
- An example route 2 calculation.
- ‘Broken chain’ situations.
- How to treat building services.
Download Guidance Note 24 (licensed assessors only)
View all Guidance Notes (licensed assessors only)
Granular fill and capping - KBCN1378
Granular fill and capping only refers to roadworks and not building foundations.
Green lease agreement – applicability - KBCN0898
Green Lease Agreements or other shell & core options (green building guide and developer-tenant collaboration), which were included in UK NC 2011, International NC 2013 and earlier scheme versions are no longer available to demonstrate compliance.
For all other Issues projects are assessed based on the level of works/assessment part(s) being undertaken.
Green-roofs - KBCN0263
When assessing green roofs, only the structural elements of the roof construction need to be considered i.e. the waterproof layer and above can be excluded. Where Green Guide is being used to assess the issue, it is likely that the online Green Guide Calculator will need to be used to provide a rating for the roof construction.
HQM - For the purpose of HQM, green roofs fall under 3.3 Specialist roof systems therefore should be included in the IMPACT model.
Grid NOx emission factors - KBCN0151
The Grid NOx emission factors should be compliant and relevant to the scheme of the development under assessment i.e. BREEAM NC 2011/ 2014 or BREEAM 2008.
In the same way that we do not apply the more stringent requirements of some BREEAM NC 2011 / 2014 Issues retrospectively to 2008 schemes, for a BREEAM 2008 scheme, the emission figures stated in the relevant manual must be used.
Habitat management plan – Level of detail required - KBCN0132
The level of detail required in the landscape and habitat management plan needs to be commensurate with the complexity and extent of the landscaped areas. If there is a limited amount of landscaping, then a simple plan would be acceptable, commensurate with the significance of the area assessed.
Where the suitably qualified ecologist, appointed prior to commencement of activities on site, confirms that a landscaping and habitat management plan is not applicable due to the nature of the site and its surroundings, such as being nearly all or entirely hardstanding or having little or no external space, then full credits can be awarded for demonstrating that the relevant legislation has been followed.
Hazards – Applicability of the issue - KBCN0541
The applicability of issue Hea 07 Hazard is related to the risk of natural hazards in the country, or region, in which the project is situated. This is reflected in the environmental weightings.
The approach to this issue changes according to the country and to the scheme.
BREEAM International New Construction 2013 and BREEAM International Refurbishment and Fit Out 2015
This issue should not be taken into consideration for countries which have a weighting for this issue equal or lower than 1%. The suggested threshold to start considering this credit is more than 1%.
Where no risks are identified in the risk assessment report, this issue will not be applicable, even if the related weighting has a value higher than 1%. Thus before undertaking a risk assessment, it is recommended to investigate if the area might be subject to the natural hazards listed in the technical manual.
BREEAM International New Construction 2016
Countries with no or very low risk, have a weighting of 0% for this issue. Thus, according to the BREEAM scoring and rating system, this issue should not be considered. The suggested threshold to start considering this credit is more than 0%.
Where no risks are identified in the risk assessment report, this issue will not be applicable, even if the related weighting has a value higher than 0%. Thus before undertaking a risk assessment, it is recommended to investigate if the area might be subject to the natural hazards listed in the technical manual.
Head-end systems for smart meters - KBCN0933
As the central component in an Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), head end systems allow data communication and collation from a large and disparate set of smart meters.
Where smart energy meters and sub-meters are to be installed, a head-end system is required for any strategy utilising this technology to be considered for compliance.
Heat pumps powered by renewable energy - KBCN0422
Where renewable energy is used partially to offset grid electricity in heat pumps, this can contribute towards a reduction in equivalent NOx emissions. To account for seasonal variations in renewable energy generation, this must be calculated over the course of a year.
Historic buildings – maximum credits available - KBCN1353
The number of additional credits for historic buildings that can be awarded is capped by the number of energy performance credits available for the assessment, as determined by the Ene 01 assessment option and, for Option 2, the Parts that are being assessed.
For example, for a Part 1&2 assessment using Option 2, the number of credits available for energy performance might be 8, so if it scores 7 energy performance credits, it can only benefit from 1 additional credit by meeting the historic buildings criteria.
The additional credits are intended to recognize cases where the building's performance against the Ene 01 criteria is limited by its historic building status.
22 02 17 Wording updated to clarify.
Home composting facilities – clarification - KBCN0927
Home composting facilities are individual composting containers placed within the kitchen area or communal space for each self-contained dwelling, bedsit or communal kitchen.
These containers are either emptied into local on-site communal facilities or are collected by composting collection services run by the waste collection authority.
Individual composting containers should be:
- Located in a dedicated, non-obstructive position.
- Easily accessible to all users.
- Durable, low maintenance and cleanable.
- Enclosed to manage odour and pest issues.
Hot water supplied by grid electricity - KBCN0549
Where grid electricity is used to supply the hot water heating system, the NOx emissions will be the same as that stated in the guidance for any other heating systems.
Hotels and other short stay accommodation – cycle storage unit of measure - KBCN0676
The cycle storage requirement for hotels and other short‑stay accommodation is
1 space per 10 staff. Guests or visitors staying at the hotel are excluded from the calculation.
Where a hotel includes on‑site facilities such as conference spaces, restaurants, or gyms, visitors to these facilities should also be included in the cycle-storage calculation:
1 space per 10 guests.
Specific Note for Refurbishment and Fit Out International 2015
Table 36 in the technical manual incorrectly refers to “1 staff and 1 visitor, or 1 bed.” Please ignore this error and follow the guidance above.
16-Feb-2026 - Wording update to be applicable across multiple BREEAM Schemes
20-Oct-2025 - Guidance clarified and updated to align with all current BREEAM scheme guidance.
23-Jul-2018 Wording added to include clarification on what to base the calculation of cycle spaces on.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next re-issue.
Hotels and Residential institutions – Short term stay - KBCN0652
For projects registered as 'Hotels and other residential accommodation - short term' two credits can be achieved under this issue:
- One credit - indoor ambient noise and sound insulation, criteria 2 to 5
- One credit - reverberation times, criterion 6
Criteria 7 to 9 are relevant only for multi-residential projects, classified as 'Residential accommodation - Long term stay'.
The pre-requisite is still required in order to achieve the credit for any project type.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
IMPACT compliant software - KBCN0809
For a list of all IMPACT compliant software please see
here
27 Aug 2025 - Corrupted links to resources updated
Impact of refrigerant – Refrigerants with low GWP - KBCN1472
Where systems only use refrigerants with GWP ≤ 10
The Pol 01 calculator
does not have to be completed.
Providing evidence of the compliant systems and refrigerants used is enough to award maximum credits for impact of refrigerant.
Mix of systems with GWPs below and above 10
The Pol 01 calculator
does have to be completed.
The calculator must include systems with GWP ≤ 10 to ensure credits are based on the average value across all systems.
20-Dec-2023 Updated to include scenarios where there is a mix of systems with GWP above and below 10.
Improvements to pre-assessment tools - KBCN1358
Some of our older pre-assessment tools in BREEAM Projects were designed to give a quick indication (or estimation) of the performance of a project at an early stage, prior to registration. They were a simplified version of the main Scoring and Reporting tools and did not contain the same level of filtering.
Following feedback from assessors wanting the two tools to identically match to give accurate performance estimates, we have now released pre-assessments which are identical to the Scoring and Reporting tools. However, pre-assessments created with the previous versions remain on BREEAM Projects. These contain a banner to confirm that they were created using an unsupported version of the pre-assessment tool. All new pre-assessments created will use the updated version, where the filtering and indicative scoring will be consistent with the Scoring and Reporting tools.
Individual and shared drying facilities in larger developments - KBCN0260
Individual bedrooms: an adequate internal or external space with posts and footings, or fixings capable of holding:
- Two metres of drying line per bedroom where drying facilities are provided in each room, OR;
- Two metres of drying line per bedroom for the first 30 bedrooms, plus one metre of drying line for each additional bedroom where drying facilities are shared.
This is to avoid over-provision of shared drying facilities in larger developments.
Indoor air quality plan – later consideration - KBCN1544
Where BREEAM has been engaged at a later stage in the project (for instance, at the beginning of a Post-Construction Assessment) the IAQ plan must still be produced.
The late stage plan must clearly identify opportunities to improve indoor air quality that:
- Were lost during design and construction.
- Remain before hand-over and occupation.
- Can be applied during operation.
The plan is focused on decisions and actions that can still be practically carried out.
The indoor air quality plan is an on-going consideration that extends into the operational life of the asset.
Indoor air quality plan – scope - KBCN0294
Where possible, the indoor air quality plan must cover all items in the criteria. This means the plan must be completed for:
- Situations where BREEAM has been engaged later in the project (see KBCN1544).
- Shell only / shell and core projects - the plan must be completed for the scope of works being assessed.
- Refurbishment projects with a limited scope of works.
Within these requirements, there is flexibility for the design team to use their professional judgement to determine what is appropriate to meet the criteria.
Any exclusions must be clearly evidenced and justified.
As the basis for effective asset management, the indoor air quality plan must be written in a consistent and comprehensive manner. The report must address relevant aspects as fully as possible within the scope of the development.
11-Oct-2022 Title updated for clarity. Wording clarified. Content merged with KBCN0556. Reference to KBCN1544 added. Scheme applicability updated.
Internal lighting levels where computer screens are used - KBCN0283
For areas where computer screens are regularly used projects can specify 300 lux, as referenced in CIBSE Lighting Guide 7, rather than the levels prescribed in the standard EN 12464:2011.
07 Dec 2021 Applicability to BIU V6 Commercial confirmed.
International suitably qualified professionals - KBCN1266
In some issues the International NC and RFO schemes prescribe specific requirements for suitably qualified professionals. We appreciate that some countries might have different recognition schemes in place, and these might differ from the BREEAM requirements. Where this is the case, assessors should submit a technical query with appropriate information, and we will review and approve each situation on a country basis.
Internationally approved Ene 01 calculation software - KBCN1177
The following calculation software are approved internationally and can be used, provided local weather files are available in the country of the assessment.
Please make sure the approved version, in brackets, is used. If you wish to use a different one, please submit a technical query to
BREEAM@bregroup.com providing details of the changes.
- IES VE (all versions from 2014 onwards).
- Design Builder (version 4 onwards).
- TRNSYS (version 17 onwards).
- eQUEST (versions 3.63b and 3.64 onwards).
- Energy Plus (version 3 and version 6 onwards).
- EDSL Tas (v9.5.0 onwards).
- IDA ICE (Version 5.1 onwards)
Any software that has been approved on the ASWL for a particular country can be used in other countries, provided relevant weather files are available.
03-Apr-2025 - IDA ICE Software added.
26-Mar-2024 - Scheme applicability updated.
08-Aug-2022 - Applicability to BREEAM Communities 2012 confirmed.
30-Jun-2023 - Added note relating to software approved for a particular country.
Kitchen and catering facilities – CIBSE TM50 (2021) - KBCN1474
The BREEAM guidance refers to TM50: Energy efficiency in commercial kitchens.
The BREEAM guidance refers to TM50: Energy efficiency in commercial kitchens. The 2009 version has now been superseded by TM50 (2021).
The updated version may be used to demonstrate compliance, however a number of the relevant section numbers have changed. These relate to the current BREEAM guidance, which is based on TM50 (2009) as follows:
|
|
TM50 (2009)
|
TM50 (2021)
|
1
|
Section 8 – Drainage and kitchen waste removal
|
Section 9
|
2
|
Section 9 – Energy controls – specifically controls relevant to appliances
|
Section 8
|
3
|
Section 11 - Appliance specification – excluding fabrication or utensil specifications
|
Section 13
|
4
|
Section 12 – Refrigeration
|
Section 14
|
5
|
Section 13 – Ware-washing: dishwashers and glasswashers
|
Section 15
|
6
|
Section 14 – Cooking appliance selection
|
Section 16
|
7
|
Section 15 – Water temperatures, taps, faucets and water-saving controls
|
Section 10
|
17 Nov 2021 - Re-formatted and applicability to BREEAM International schemes confirmed
Laboratory containment level category definitions - KBCN0943
BRE does not designate or define containment levels for laboratories. The categories listed in the manuals are based on industry standard definitions.
For further information, please refer to HSE/COSHH or DEFRA definitions, depending upon the hazard type.
Laboratory facilities not restricted to building type - KBCN1340
In order to allow buildings with appropriate laboratory facilities to assess the energy performance of their labs, all assessments containing laboratory space and containment areas will be able to assess Issue ‘Energy efficient laboratory systems’, even where the relevant technical manual confirms that the Issue is not applicable to this building type. The Issue remains not applicable to primary and secondary school buildings given the limited scale of their laboratories.
Assessments registered prior to 1 July 2019 have the choice to follow the guidance as stated in the technical manual. They can exclude laboratories by responding negatively to the questions regarding laboratory facilities. For assessments registered after this date, all projects containing laboratories within the scope of the assessment should include the Issue in the assessment.
Landscape and Habitat Management Plan – SQE involvement - KBCN0564
Even if not stated explicitly, it is implied and expected that the Suitably Qualified Ecologist (SQE) does verify the content of the Landscape and Habitat Management Plan to ensure that it is consistent with the whole site ecological strategy.
Late appointment of the SQE and RFO schemes - KBCN0792
The late appointment of the ecologist does not necessarily impinge on achieving the credit, provided they would have had no advice for the early site layout decisions. The ecologist needs to provide an explanation detailing this, that they would have had no advice if they were appointed during the Preparation and Brief stage.
This does not set a precedent. The early appointment of an ecologist has important benefits and must be followed as per the 'Early stage involvement from the SQE' Compliance Note within the technical manual. This KBCN is specific to situations where their late appointment has not had a bearing on the advice they could have provided.
Late appointment of the Suitably Qualified Ecologist - KBCN0603
If the Suitably Qualified Ecologist (SQE) is appointed after the commencement of activities on-site and if the other requirements of this issue are met, then credits can still be awarded, provided that:
- the SQE confirms that all relevant UK and EU legislation relating to the protection and enhancement of ecology has been complied with during the design and construction process
- the SQE confirms that their late appointment has not compromised the adoption of any measures to improve the assessed site's long term biodiversity.
Late confirmation of site boundary - KBCN0307
The ecologist must be appointed and engaged early on (equivalent RIBA Stage 1) so that they are able to inform the design brief. For projects where the site boundary is only confirmed at the next design stage (equivalent RIBA Stage 2), it would be acceptable to delay the full ecology survey until this time. In these circumstances, the ecologist's input at design brief may be based on a desk study or initial viewing of the site and its potential boundaries.
The aim of early engagement with an ecologist is to facilitate and maximise potential ecological enhancement, exact boundary definition does not negate this.
LCA modelling for multiple BREEAM assessments - KBCN0960
Multiple buildings' assessments
Site-wide approaches are not acceptable and each BREEAM assessment needs to have its own Life Cycle Assessment model (using an IMPACT compliant software tool or equivalent).
This applies in all cases, including when the buildings are on the same plot and are built to the same specifications.
Developing assessment-specific LCA models ensures that material quantities are accurate, refer to the actual building (and building type) and account for external works included within the scope of the specific assessment.
Single building with multiple assessments within it
Where multiple assessments are conducted for different parts of a building, it is acceptable to have a single LCA model covering all assessments. In this case, an explanation of the allocation process used should be provided and the following guidance applies:
- Common elements (e.g. roof, foundations, external walls etc): apportion a percentage of the total impact of the element to each assessment based on their percentage share of the total GIFA (e.g. if an assessment accounts for 10% of the total GIFA, 10% of the element’s impact is apportioned to that assessment).
- Elements that are only in a given assessment (e.g. internal partitions, internal finishes etc): 100% of the impact is allocated to the assessment they are in.
LCC – LZC energy sources discounted - KBCN0606
When sufficient information can be provided to justify that LZC energy sources are not appropriate for the development, the LCC analysis, for those LZC sources, do not need to be included in the feasibility study.
The feasibility study (covering all the areas required as stated in the manual) intends to demonstrate, to a reasonable level of certainty, that the chosen LZC is the most appropriate of all those available.
Leak detection – extent of responsibility - KBCN0688
For the credit to be awarded, all the pipework in a development that the owner/occupier has responsibility for must meet the leak detection criteria. In situations where third party organisations place restrictions on the pipework that can be metered, the scope of works (and hence placement of a meter for the use of leak detection) will start immediately after this point. For instance where the utility company's meter is placed midway between the boundary and the building, the scope of leak detection for BREEAM purposes will be between utility meter and the building, not to the boundary (as stated in the guidance).
The scope of the BREEAM criteria is only on pipework that the owner/occupier has control over.
Leak detection – inseparable building and site boundary - KBCN0388
Where there is no distinction between the site boundary and the building; the utility meter being either located on the boundary or within the building, the leak detection criteria apply to the mains water supply within the building only.
The BREEAM criteria apply to the pipework that the owner/occupier has responsibility for.
Leak detection – recycled water use - KBCN0433
The leak detection requirements still apply to all relevant water systems where water recycling systems are specified for toilets and urinals.
Recycled water should be considered as a valuable resource as it replaces potable water use, and in many instances, recycling systems will still incorporate a utility-water back up.
Leak detection – using a BMS - KBCN0439
A BMS can be used for leak detection purposes if it can be demonstrated that its integrated or add-on features meet all the requirements for a leak detection system.
07 Feb 2022 - Applicability to BIU USA Commercial V6 confirmed
Leak detection between building and utilities meter - KBCN1116
For all pipework which is the responsibility of the building owner or occupier leak detection is generally required between the building and the utilities water meter. This requirement is applicable regardless of the length of the pipework.
However, for campus type developments or those with multiple buildings on the same site served by common pipework, leak detection is required both within the building and externally for the length of pipework that exclusively serves that building.
Where it can be demonstrated that it is not physically possible for a meter to be installed on the pipework outside the building, the requirement for leak detection between the building and the utilities meter can be considered not applicable, and the credit awarded based on the leak detection within the building.
02 Jul 2024 - Updated to account for campus type developments. Applicability to INC V6 confirmed.
Leak detection system based on pressure changes - KBCN0326
A system that uses pressure changes to detect leaks is not necessarily compliant. To be deemed compliant the leak detection system would need to monitor the refrigerant pressure and the operating conditions to address the problem of natural fluctuation.
Leak detection system notification - KBCN0245
So long as the compliant system alerts the appropriate person to the leak so they are able to respond immediately, the assessor can judge if the aim of the issue is being met by a reliable, robust and fail-safe means of notification.
Leak detection technologies – Compliance Principle - KBCN1566
Where it can be demonstrated that alternative water leak detection technologies can meet or exceed the capabilities of systems set out in the BREEAM guidance, subject to approval, these can also be considered compliant.
It is the role of the Assessor and the project team to provide evidence and justification in a compliance principle query (see
KBCN1555).
The following alternative solutions are currently recognised:
- Smart leak detection systems that are based on 'self-learning' (machine learning) to determine normal water use patterns are an acceptable alternative to systems that require manual pre-sets or manual programming.
Legally harvested and traded timber – Examples - KBCN0956
The following examples are considered compliant for BREEAM purposes.
Legally harvested:
- Evidence of compliance with the CPET (see here, timber bought inside the UK only)
- FSC, PEFC or SFI certification
- Evidence of compliance with the EUTR (timber bought inside the EU only)
- ASTM D7612-21 (projects in USA and Canada)
- Risk assessment/due diligence documentation demonstrating a low risk of non-compliance with the ‘legally harvested’ requirements given in the manual.
Legally traded:
- Evidence of compliance with the CPET (see here, timber bought inside the UK only)
- FSC, PEFC or SFI certification
- ASTM D7612-21 (projects in USA and Canada)
- Risk assessment/due diligence documentation demonstrating a low risk of non-compliance with the ‘legally traded’ requirements given in the manual.
17-Dec-2025 Reference to ASTM D7612-21 added
Legally harvested and traded/Legal and sustainable timber – Reclaimed/recycled timber - KBCN1402
As an alternative to virgin timber and wood-derived products from a Legally harvested and traded timber/Legal and Sustainable source, ‘recycled timber’ is acceptable. For the purposes of these prerequisites, ‘recycled timber’ is defined by BREEAM as:
Recovered wood that prior to being supplied to the assessed project had an end use as a standalone object or as part of a structure and which has completed its lifecycle and would otherwise be disposed of as waste. The term ‘recycled’ is used to cover the following categories: pre-consumer recycled wood and wood fibre or industrial by products but excluding sawmill co-products (sawmill co-products are deemed to fall within the category of virgin timber), post-consumer recycled wood and wood fibre, and drift wood. It also covers reclaimed timber which was abandoned or confiscated at least ten years previously.
BREEAM requires documentary evidence that all reclaimed/recycled timber products meet the definition of ‘recycled timber’ given above.
Life Cycle Cost - KBCN0385
Life Cycle Costing (LCC) is a methodology that aims at selecting the optimal option amongst a number of option appraisals.
An LCC should therefore consider at least two design option appraisals and should be based on more than one cash flow scenario in order to provide systematic economic evaluation of life cycle costs over a period of analysis.
Life cycle cost – Multiple assessments on the same site - KBCN000003
Where there are multiple assessments on a site and a single life cycle cost (LCC) plan will be carried out, it is acceptable to use this plan as evidence provided that the results of the LCC plan can be applied to all of the assessed buildings and therefore may have a positive influence on the material specification of such buildings. Where the design of some assessments differ to the extent that the LCC plan cannot reasonably be applied, a separate LCC plan is necessary to achieve credits for this issue.
Where multiple assessments are covered under a single LCC plan, there must be sufficient detail for each building to enable them to be adequately assessed.
Life Cycle Cost – Option Appraisals - KBCN0385
Life Cycle Costing (LCC) is a methodology that aims to generate a cash flow prediction over a given period of time for a building and undertake option appraisal studies to evaluate various solutions in order to determine the optimal option.
An LCC should therefore consider:
- At least two design option appraisals (which could be for the base case plus at least one other option) and,
- Include comparison cash flow scenarios for each design stage option appraisal in order to determine the most appropriate option.
This allows project teams and clients to make informed choices about the long term financial implications of different design decisions.
12-Aug-2025 - Title and wording updated to clarify the minimum number of options required
24-Oct-2024 - Updated for clarity
27-Mar-2024 - Wording and requirements clarified. Scheme applicability updated.
Life cycle environmental impact of curtain walling - KBCN0178
Curtain walling performs two functions – the provision of windows and the provision of external walls. Specifications performing the same function are grouped together in the Green Guide to Specification. This means that curtain walling needs to be modelled as two separate building elements (external walls and windows).
The overall performance of the curtain wall will combine the ratings for the two parts according to their areas. It will depend on the curtain walling system selected, the choice of internal lining and the relevant proportion of glazed and opaque elements.
- For the opaque area of the external wall (Area A in the figure below):
- Select the relevant generic specification from the Green Guide (element category – External walls / Curtain walling, then either aluminium or timber framed and the internal skin specification) and note the rating and element number. If your specification is different from all of the generics, please submit a request for a bespoke rating.
- Enter the rating into the BREEAM Materials calculator with the area for the opaque section of the curtain wall (Area A).
- For the glazed (window-like) area of the curtain wall (Area B):
- Select the relevant specification from the Commercial window element category of the Green Guide. There are two specifications: Aluminium curtain walling system (Element no: 831500016) and Laminated timber curtain walling system (Element no: 831500015)
- Enter the rating into the BREEAM Materials calculator with the area for the glazed (window-like) section of the curtain wall (Area B).
The BREEAM Materials calculator will calculate the overall performance for the curtain walling system. It will also calculate the performance of the building elements and the overall number of credits to be awarded.
Lifts with speeds 0.15m/s or less - KBCN1146
Lifts with speeds of 0.15m/s or less fall outside the scope of ISO 25745 and can, therefore, be excluded from the assessment of this Issue. This applies, for example, to lifts in single dwellings or those installed in other low-rise buildings, specifically for the use of persons with impaired mobility.
LZC – Local regulations and private wire arrangements - KBCN1658
Where local regulations do not permit electricity generated by on-site renewables to be connected directly to the building, and where evidence of the relevant regulations is provided at QA, the requirement for a private wire arrangement can be waived.
LZC technologies – energy centre or other LZCs connected at a later stage - KBCN0267
If a project specifies LZCs that have been proposed in the feasibility report which reduce emissions, and/or will be connected to a site-wide energy centre operational at a later stage of the phased development, after the Post Construction Stage review has been submitted, the Energy and Pollution issues can be assessed as follows:
In a phased development where the primary heating system will be upgraded at a later stage than the building being assessed, a commitment to install the new heating source must be made in the General Contract Specification (as per the BREEAM requirements). BREEAM does not specify a particular time for phasing as it is difficult to set parameters, however as a rule building users should have to wait the least time possible before they can use the upgraded heating source.
For the quality audit, two Energy model outputs/EPCs must be produced at the final stage - one with the actual interim system installed for building control, and one for the BREEAM assessment which can include the predicted energy from the proposed energy centre. Additionally, the legally binding general contract specification for the new heating source must be submitted with details of the timescales proposed for the completion of the second phase of work. Where this approach is to be followed BREEAM must be consulted in each case to ensure that the arrangements are sufficiently robust to award the credits.
BREEAM seeks to recognise the environmental impacts of a building's energy use throughout its life, therefore temporary arrangements can be accommodated, provided there is robust evidence on future connection to the permanent systems.
LZC technologies – planning conditions and restrictions - KBCN0535
Where a mandatory planning condition exists (eg to attach to a District Heating Scheme), this will clearly affect the number of options available in a feasibility study. In such cases, compliance can still be achieved where evidence on the planning condition restrictions is provided, and it is clarified how this excludes other technologies from being considered.
The feasibility study will still need to be carried out to cover the remaining energy needs of the building (eg Electrical and lighting load in the case of a district heating scheme).
LZC technologies – shell only feasibility study - KBCN0409
For a shell only project, compliance may be assessed on the built form only i.e. demonstrating that sufficient space and clearance for the installation of future LZCs has been considered, the built form is suitably sited, and that massing and orientation are optimised for the future systems.
Majority of water demand from rainwater harvesting - KBCN0860
If the majority of water use is supplied by sources other than mains or private water, for example rainwater harvesting, and this use will be monitored, additional metering of the smaller water demand that is masked by the larger demand is not necessary.
Manual watering - KBCN0553
Where the design team can justify that manual watering provides a reduction in unregulated water consumption, this can be considered as an acceptable method for reducing unregulated water use.
Manufacturer’s information – system specific data - KBCN0926
The BREEAM technical manual provides a set of default figures, for use within the DELC calculation. Where available, system-specific data, provided by the manufacturer, can be used in the calculation where this is more representative. Any such system-specific figures used must be supported by publicly available, published data, which substantiates the manufacturer’s figures.
Master plans with multiple stakeholders - KBCN0953
Assessment of a building forming part of a master plan co-ordinated by a third party (developer or local authority)
In such cases, it may not be possible for the design team to control elements affecting issues such as land use and ecology, access, external lighting and surface water pollution.
It is therefore acceptable for the assessor to define the assessment boundary according to one of two following options:
- Restrict the boundary only to what the design team can control.
- Extend the boundary to include elements of the master plan, assessing any associated benefits or disadvantages that arise. Relevant Knowledge Base Compliance Notes should be reviewed, and BREEAM Technical contacted for additional guidance if required.
The assessment boundary must remain consistent throughout all issues. Facilities outside of the boundary but serving the assessment (i.e. cycle facilities, parking etc) can be assessed as standard.
Assessment of a building forming part of a master plan co-ordinated by the design team with third party elements
Where there are third party elements in the master plan which are not BREEAM compliant (e.g. external lighting by local authority), evidence should be submitted to QA that efforts have been made with the third party to align these elements with BREEAM criteria.
Where this is not possible, these elements can be excluded. Full justification should be provided when submitting the assessment for certification.
Mat 01 / Mat 03 calculator not big enough - KBCN0647
If a project has more specifications than there is rows available in the tool you can group specifications that have the same green guide rating/responsible sourcing level with each of the specifications with the same rating listed in the same row. The proportion that they contribute to the overall area is also combined. For example where a project has 30 different upper floor specifications, if 10 upper floor specifications are A+, 10 are A, 5 are B and 5 are C then you would only need to use 4 lines.
Mat 01 Calculator Option 1 – verified LCA tools - KBCN0237
Before an LCA tool can be recognised by BREEAM, the tool developer must submit evidence to BRE to verify the tool’s points scored in the Mat 01 Calculator.
The LCA tool is then given its own tab in the calculator, which confirms the maximum score the tool can achieve, if used to its fullest extent. Items coloured green within the calculator are locked because they do not change when using the LCA tool. The items in blue should be edited by the design team to confirm the extent the tool has been used on the project. For RFO schemes, the assessment parts must also be selected.
Items listed as ‘N’ in column W ‘
Included in assessment?’ cannot be changed to a ‘Y’, as the LCA tool cannot be used for this element. For example internal doors cannot be assessed by the Green Guide. An element listed as ‘Y’ can be changed to a ‘N’ if the LCA tool has not been used for the element in the assessment.
Column S confirms if the assessed building includes the element and should be included. For example if there are no stairs in the assessment, then this element is removed from the calculation by saying ‘N’ to cell S15 (in the green guide calculator).
12/01/2017 Reference to LCA approved tools updated.
Meaningful reduction in emissions - KBCN00027
The definition of 'meaningful reduction' is context specific. The required reduction in active cooling demand or CO2 emissions are not specified in the criteria as this is specific to each project. To demonstrate a meaningful reduction, the passive design analysis must show that:
- A rigorous and pragmatic approach was taken in selecting the most suitable strategies / technologies
- The strategies sought to maximise the potential for reduction in energy consumption, taking into account technical and site constraints
As the potential for reduction is context specific, the assessor's judgement can determine whether a 'meaningful reduction' has been achieved. For instance:
Scenario 1: Assessment has multiple site constraints which result in a 2% reduction in CO2 emissions. The assessor is satisfied that the design team have made a significant effort to maximise the potential for reduction having considered technical and site constraints. This would be considered a meaningful reduction.
Scenario 2: The passive design analysis has highlighted a potential for significant reduction with LZCs, however many of these technologies were discounted due to capital cost considerations. The resulting building achieves a 6% reduction in CO2 emissions, however the actual potential was significantly higher. This would not be considered a meaningful reduction.
Measures for protecting features of ecological value - KBCN0583
Where the actions outlined in CN 'Protecting features of ecological value' are deemed not appropriate for a particular site, by a suitably qualified ecologist (SQE), it would be acceptable for alternative means of protection to be used where recommended by an SQE. Where alternative approaches are being used, the assessor must ensure that adequate evidence is collated to demonstrate the ecologists recommendations have been implemented, this should include clear photographic evidence of the solution implemented.
This is to ensure that professional expertise is applied to appropriately address specific scenarios.
Measures in CIBSE TM50 for Kitchen and catering facilities - KBCN0663
The measures are listed in the section summaries (blue boxes) in the guide. The sections that follow each summary in the Guide are explanations of the measures. Therefore you can refer to these parts if you need further clarification about the measures.
When considering which measures to target, first discount any energy efficiency measures which are not applicable to the project, or are specifically excluded in the criteria.
Of the remaining measures, where the criteria requires that two thirds or more are to be achieved always round up any figures. For instance if there are five applicable measures in a section, four will need to be achieved. If there are only two, both will need to be achieved.
Many measures in TM50 require consideration of what is the best option or specification. The intent of our criteria is to demonstrate that these measures have been considered by the relevant specialist and have informed the design and specification of the catering facilities, but energy savings do not need to be quantified.
At design stage it is acceptable for a letter or document to be produced confirming how each measure has been considered along with justification for how this has informed the specification. Where the measures require training to be carried out, relevant training materials could be used as evidence. At post-construction stage, any type of general evidence deemed appropriate by the assessor would be sufficient to confirm the specified measures have been installed.
25/08/2017 Updated to clarify compliance and evidence requirements.
Measuring the flow rate of taps - KBCN0641
On site flow rate testing can be carried out by an appropriate professional to determine the flow rate of taps. This must be overseen by the client’s facilities manager and as-built drawings must be provided to confirm the presence and location of the fitting and any flow restrictors. Note that the conditions under which the testing is completed must be recorded, i.e. the pressure and the temperature of the water. The assessor could conduct the test provided they are able to carry it out accurately.
Meeting the minimum standard requirement – compliance when chain of custody is broken - KBCN1816
Where there is a broken chain in the last link between the purchase and delivery of certified timber from the supplier and the forwarding distribution of the timber to the site under assessment, such as where the timber has been delivered to a subcontractor or fabricator’s premises instead of direct to site (e.g. as part of a bulk order or where limited storage is available on site), compliance can still be achieved if a documented risk assessment confirms that there is
low risk of mixing or substitution of certified and non-certified timber.
Ways to demonstrate compliance:
A. Verification that the subcontractor or fabricator only purchases and uses certified timber.
There must be robust mechanisms in place to verify that all timber materials purchased and delivered originate from sustainably managed sources. This includes maintaining documented timber procurement policies and procedures that mandate certified timber orders and delivery checks. Comprehensive supplier details should be readily accessible for review upon request to demonstrate that all timber is certified.
B. Where non-certified timber is handled/stored or sourced, that there are robust control measures in place to prevent any substitution or mixing of certified and non-certified timber at every stage of the process.
Documentation demonstrating compliance should be maintained and made available upon request. Examples of appropriate control measures are listed below:
Control
|
Evidence required
|
| Purchasing records |
All purchase orders, requisition notes, and contracts must explicitly specify the product details and confirm that materials are to originate from legal and sustainable sources. |
|
Segregated storage of timber
|
Site layout map, stock control processes and records to confirm that certified timber is stored away from non-certified timber. |
| Segregated delivery of timber to site |
- All timber must be thoroughly inspected and verified before shipment to confirm that it is correctly marked/labelled as FSC/PEFC-certified.
- Delivery notes must be accurately maintained.
- A second-party verification process to check tickets and stock, must be carried out upon site delivery to confirm certified status of timber. |
| Documentation |
Comprehensive documentation must enable independent assessors to trace any timber back to its sustainable source. This includes maintaining purchase records, goods-inward notices, stock records, and sales documentation such as orders and invoices. |
The above is guidance and should not replace any local or national requirements for the sourcing of legally traded and harvested timber.
Metering recycled water - KBCN0658
Water-consuming plant or building areas consuming 10% or more of the building’s total water demand need to be sub-metered. This applies to recycled water, such as rainwater, grey water or process water as well as mains water.
The aim of the Issue is to encourage reductions in water consumption, which is beneficial, regardless of its source. Monitoring the use of recycled water, may also help to reinforce the benefits of doing so and encourage further reductions.
Minimising water course pollution – no water courses present - KBCN0550
The credit for 'minimising water course pollution' has to be assessed even in cases where no water courses are in close vicinity to the site under assessment. This is because the aim of this credit is to encourage developments to minimise water course pollution by restricting the discharge of potentially contaminated water from entering the public sewer.
Minimising water course pollution does not focus on water directly entering water courses.
Missing criterion – external lighting standards - KBCN0883
The following criterion, included in the BREEAM INC 2013 scheme, was omitted in error from the BREEAM IRFO 2015 and BREEAM INC 2016.
- The external lighting strategy has been designed in compliance with the limits set for light technical parameters in section 2.7 of CIE 150-2003 and table 2 of CIE 126-1997.
Projects registered after the announcement of this KBCN in the July 2017 Process Note must comply with this and other relevant criteria within Pol 04 in order to achieve the credit.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
ModeScore Sustainable Transport certification - KBCN1705
Achieving
ModeScore Gold or Platinum certification can be submitted as part of the supporting documentation
to award credits for implementing sustainable transport options,
provided the BREEAM criteria were targeted, as follows:
| Scheme |
Issues |
Credits |
| BREEAM International NC 2016 and V6 |
Tra 03a Alternative modes of transport |
2 + Exemplary credit |
| Tra 03b Alternative modes of transport |
2 + Exemplary credit |
| Tra 04 Maximum car parking capacity |
1 |
| BREEAM UK NC 2018 and V6 * |
Tra 02 Sustainable transport measures |
10 |
| BREEAM Int RFO 2015 |
Tra 01 Sustainable transport solutions |
5 |
| Tra 04 Maximum car parking capacity |
2 |
| BREEAM UK RFO 2014 |
Tra 01 Sustainable transport solutions |
3 |
| Tra 03 Cyclist facilities |
2 |
| Tra 04 Maximum car parking capacity |
2 |
| BREEAM In-Use Commercial and Residential (International and USA) |
Tra 01 Alternative modes of transport |
8 |
| Tra 02 Proximity to public transport |
3 |
| Tra 04 Pedestrian and cyclist safety |
2 |
* BREEAM UK NC 2018 and V6 credits can be awarded provided the transportation assessment and travel plan (criterion 1) are met
When the assessor submits a ModeScore certification as evidence, they should include their report and highlight the BREEAM criteria or credits that were targeted.
About ModeScore Sustainable Transport certification:
ModeScore assess and certify sustainable transport facilities and services in buildings. ModeScore encompasses ActiveScore within its assessment criteria, covering four pillars of sustainable transportation while incorporating accessibility into each:
- Public Transportation
- Environmentally-Friendly Private Vehicles
- Active Transportation
- Site-Wide Mobility
ModeScore evaluates the connectivity potential of any building in any location, offering four levels of certification with a total scorecard of 120 points. ActiveScore (Travel Facilities) counts for 10 points:
- Certified (0-39%)
- Silver (40-59%)
- Gold (60-79%)
- Platinum (80-100%)
See more information and details at https://modescore.com/
Multi-Residential: Internal recyclable waste container if waste is sorted off site - KBCN0354
Where the Local Authority or waste management company for the scheme provide evidence confirming that recyclable waste will be sorted after they have collected it from site, it is acceptable to provide one internal storage bin of a minimum capacity of 30 L rather than 3 separate internal bins. The relevant recycling scheme must collect at least 3 of the following materials; paper, cardboard, glass, plastics, metals or textiles.
Multi-residential: Waste storage shared by more than six bedrooms - KBCN0856
Where multi-residential buildings contain communal facilities shared by more than six bedrooms, the requirement for total waste storage can be increased on a pro-rata basis to demonstrate compliance.
For instance, if the standard requirement is 30L for six bedrooms, this equates to 5L per bedroom. Where assessing a flat with eight bedrooms, this requirement increases to 40L (8 x 5L).
The minimum size of individual containers remains unchanged as per the criteria.
Multiple buildings on the same site - KBCN0559
The areas of hard landscaping and boundary protection that need to be assessed on a site that contains several developments/buildings depends on the scope of works and scope of the assessment(s) being undertaken.
Essentially, the areas that need to be assessed are all the areas of hard landscaping (as defined within the relevant definitions of the credit issue) and boundary protection within the construction zone (again defined within the relevant definitions) that are within the scope of works of the building under assessment.
Therefore, if all buildings on one site are being assessed in one BREEAM assessment, then the hard landscaping and boundary protection related to all of these building's scope of works will need to be assessed.
If there are several buildings with individual assessments and their own defined scope of works, then the hard landscaping and boundary protection applicable to the scope of works of each individual building will be assessed for each associated assessment.
The assessment is concerned with the hard landscaping and boundary protection associated to the project under assessment, i.e. the areas under the control of the project under assessment.
Multiple developments monitoring construction waste on a site - KBCN00036
Where the same contractor is working on a site with more than one development, a single Site Waste Management Plan (SWMP)/Resource Management Plan (RMP) can be produced to demonstrate compliance, if it can be justified that separation of the waste would be impractical.
Where the developments are of a similar nature, such as all new-build or all refurbishment with similar scope, the results from the whole development can be apportioned on the basis of floor area to derive the figures upon which the separate developments will be assessed.
Where the buildings are not similar, the design team will need to provide calculations to demonstrate that the waste has been apportioned as accurately as possible according to the project types.
21/11/16 Clarification added in relation to dissimilar projects on the same site.
Natural ventilation – use of CIBSE TM52 - KBCN0935
For a naturally ventilated building, it is acceptable for the thermal comfort limits and calculation methodology in CIBSE TM52: The Limits of Thermal Comfort: Avoiding Overheating in European Buildings to be used in place of ISO 7730:2005.
BREEAM recognises that adaptive comfort models can provide more appropriate thermal comfort limits for naturally ventilated buildings.
Natural Ventilation Heat Recovery Units - KBCN1126
Natural Ventilation Heat Recovery Units (NVHR) systems can be used to support a natural ventilation strategy where it can be demonstrated that openable windows provide sufficient fresh air to the building for the significant majority of the time that the space is occupied.
The assessor will need to use their professional judgement to determine a 'significant majority of time' and be able to justify this within the assessment report.
Night-time operation – requirement for controls - KBCN1048
Projects
or areas of an asset which operate at night-time can adapt or omit the requirement to provide controls or presence detection to align with the building’s hours of operation.
This could, for example, include service yards or car parks.
The aim of this Issue is to reduce the energy use for external lighting and should not interfere with the building’s operation.
02 Oct 2024 - Updated to clarify the scope of the this guidance and applied to NC V6 and BIU.
No car parking provision - KBCN00059
Where the assessment criteria are applicable to a building that has no car parking spaces and where there are no parking spaces accessible to building users, the benchmarks can be considered to be met. If, however, parking is shared with other buildings or parking spaces are available on a campus-type site then the provision must still be assessed.
No data for AI at Design Stage - KBCN0551
If there is insufficient data for a future transport service to include this in the calculation of the AI at the Design Stage, it should not be accounted for.
If at Post Construction stage the data is available, this can be incorporated.
Whilst certain Design Stage requirements can be based on commitments to achieve a certain performance, this must be based on verifiable data.
16/04/18 Wording amended to clarify that this applies to future services and to allow applicability to UK NC 2018
No discharge for up to 5mm rainfall - KBCN0599
The criterion requires no run-off to leave the developed site into the local watercourse(s) for a storm event that results in rainfall depths up to 5mm. It is not acceptable to collect the rainfall within an attenuation tank and allow the runoff to be released from the site at a restricted rate. This simply slows the rate at which it is released to the watercourse(s).
The 5mm rainfall event is considered one of the most common rainfall events and, therefore, a system should be designed to prevent this run-off leaving the site thus protecting a receiving watercourse from pollution.
No external areas controlled by developer - KBCN0608
Where evidence can be provided by the design team that there are no external facades, roofs or external areas within the developer's control, there is no requirement for a SQE or wildlife group to supply evidence for confirmation.
04/10/17 KBCN no longer applicable to UKRFO LE04. For this scheme and Issue, refer to KBCN0919.
No high grade aggregates used on project - KBCN00098
Where no high grade aggregates will be used in a refurbishment scheme project, this credit is not applicable and will be filtered out of the assessment.
This CN supersedes CN 'Aggregates in existing applications', currently on the technical manual, as its applicability to the RFO schemes has been reviewed. The CN was developed for the New Construction schemes to account for situations where, for example, existing foundations are re-used in-situ, thus avoiding the need for new high grade aggregates. In the RFO scheme, existing structural elements are generally retained, therefore it would not be appropriate to account for the aggregate within these.
25/10/2016 Clarification on the N/A of current CN 'Aggregates in existing applications' added.
No opportunity for ecological protection or enhancement - KBCN0921
This Issue is not applicable to the assessment where it can be demonstrated that;
- There are no new or existing landscaping areas and therefore no need for ecological protection (ie when the ‘Protection of ecological features’ Issue is N/A)
AND
- There is no opportunity to make ecological enhancements (ie when the ‘Enhancing site ecology’ Issue is N/A). An example of such a case could be a retail building with a glazed shop frontage, where there are no other external elements or spaces for enhancement.
Evidence that there are no suitable external facades, roofs or other external areas within the developer’s control must be provided by the design team.
When both of the above conditions are in place and the two relevant scoping questions are completed in the scoring and reporting tool, this Issue will be filtered out of the assessment.
No refrigerant use – Part 4 only assessments - KBCN1540
Where there is no use of refrigerants in a Part 4 only assessment, this issue is filtered out.
3 credits are not awarded by default.
No refrigerant use – shell & core assessments - KBCN1058
The credits for Pol 01 can be awarded if the asset requires no refrigerants as per the criteria.
In speculative assessments, future tenant systems are unknown. To award the credits, evidence must show that the asset has been designed to operate without the need for air-conditioning or comfort cooling for the conditioning of occupied spaces. One way to demonstrate this is to achieve the ‘Free cooling’ credit.
Only refrigerants used for occupant comfort are assessed. Do not assess any refrigerant use for process-related functions.
21.09.2021 Wording amended for clarity
No unregulated energy consumption in the building - KBCN00066
Where there are no items, contributing to the unregulated (or equipment) energy consumption in the building, there is currently no mechanism to award credits. If, however, in this situation, significant contributors, not listed in the table, will be specified, the design team should justify how a meaningful reduction will be achieved for these contributors, in order to demonstrate compliance.
08/05/19 Wording amended to account for situations, where a meaningful reduction in unregulated energy can be demonstrated by other means.
18.05.2017 KBCN applicability removed for NC2011 and NC2013, for which compliance can be demonstrated via the three shell and core options, as per the technical manual.
No water fittings present - KBCN0449
Where the scope of works and tenanted areas do not include any water consuming components, Wat 03 issue can be excluded from the assessment. However, the issue is still applicable where there are water consuming components within tenanted areas, regardless of whether these are included in the scope of works.
Not enough rows in the Pol 01 calculator - KBCN1274
If additional rows are required in the calculator it is acceptable to add the specification of multiple models together in one tool, provided they are the same model and have all the same inputs for columns F to M. The weighting of the systems across the building is done by the System Capacity and Total Refrigerant Charge (columns E and F), so you would multiply each of these two figures by the total number of the system specified. This gives the contribution of the systems to the building's cooling capacity and charge. If further rows are still required please email
BREEAM@bregroup.com with a copy of the tool and specify the number of rows required.
Number of credits available - KBCN0749
In Issues 1.0 - 1.3, there is a publication error within the assessment criteria, which states the following:
“Note: up to a maximum of five credits are available from a combination of the following Accessibility Index and alternative transport measures criteria.”
The above is incorrect.
There are up to a total of 8 credits available for Tra01 (building type dependent) in this scheme:
Accessibility Index’ - up to 5 credits
‘Alternative transport measures’ - up to 3 credits
This will be corrected in the next manual re-issue
Obligation to provide a minimum number of car parking spaces exceeding BREEAM requirements - KBCN0401
Where it can be demonstrated (by documentary evidence) an obligation to meet a ’minimum car parking requirement’ which exceeds the BREEAM benchmarks is imposed by the planning authority, as long as no more than the stipulated minimum spaces are provided, a single credit can be awarded.
Occupancy calculation – Buildings with shift patterns - KBCN0431
In buildings with shift patterns, as shifts may overlap, the building users calculation should be based on the maximum occupancy of the building at any given time.
Occupant control – BMS and degree of control - KBCN0175
A Building Management System controlled set point with local override controls limited to a set range would satisfy the occupant control requirement so long as the temperature range available to building users is confirmed as appropriate for the building type and user profile.
Occupant control – spaces requiring user controls - KBCN0170
This guidance is intended to clarify the types of area for which user controls are required or would be considered beneficial.
Zoning is required in all areas of the asset where specified in the assessment criteria. Please refer to the specific requirements of the applicable BREEAM standard to interpret this guidance appropriately.
User controls required
Spaces where users are expected to have independent control over their environment.
- Owned spaces: small rooms for a few people.
For instance, cellular offices, owned spaces in residential assets.
- Temporarily owned spaces: where occupants expect to operate the environmental controls while they are there.
For instance, meeting rooms and hotel bedrooms.
- Shared spaces.
For instance, multi-occupied areas such as open-plan offices or workshops.
User controls not required
Spaces where users are not expected to have independent control over their environment.
- Managed spaces: where environmental control is expected to be centrally managed.
For instance, atria, circulation areas, concourses, entrance halls, function halls, restaurants, libraries, and shops.
- Occasionally visited spaces.
For instance, storerooms, bookstacks in libraries, aisles of warehouses, toilets.
14-Dec-2022 - KBCN applicability updated to include BIU. Wording clarified, and amended for compatibility with BIU criteria.
Off-site ecological enhancement - KBCN0651
BREEAM does not recognise enhancements which are not within the boundary of the site being assessed, as the aims of the land use and ecology section relate to the ecological value and biodiversity of the specific site under assessment.
However, off-site ecological enhancement can be accepted where:
- It is within the wider site, surrounding or adjoining the development.
- The land is currently under the ownership of the developer and intended to remain so (i.e. there are no immediate plans to sell);
- The Suitably Qualified Ecologist (SQE) confirms that the proposed ecological enhancements are appropriate and more effective than can be done solely within the red line boundary;
- The owner remains responsible for the on-going maintenance of the land.
Full justification and robust evidence must be submitted when relying on this approach.
BREEAM recognises that the red-line boundary drafted for planning purposes may not reflect the entire site within the control of the developer or building owner.
Off-site waste sorting / no dedicated on-site waste storage - KBCN0696
BREEAM assesses the
dedicated space for recyclable waste storage. Where this space does not exist:
For NC or RFO
The aim of the issue is met by provide evidence covering all points 1-4:
- A waste management plan which provides on-site storage between collections, adequately sized based on the frequency of collection.
- An on-going waste recycling contract.
- The typical recycling rates from the waste management company.
- A permanent internal or external space within the asset site boundary that can be converted to comply with all criteria requirements. Drawings must be provided showing how this space could be converted in future, including meeting all relevant criteria for:
• User and vehicle access,
• Area requirements for waste storage,
• Appropriate size and number of containers for the expected waste streams, and
• Space allowance for any additional waste processing requirements e.g. compactors, composting containers, water outlets etc.
This ensures that there is:
- A robust off-site waste management strategy,
- Proof of future convertibility for on-site waste storage.
BIU V6 Commercial only
The above approach for NC / RFO only applies to waste storage for construction fit-outs, which are temporary in nature. It does not apply to any other credits, and compliance cannot be met based on future commitments. This means that the above approach:
- Does not apply to recyclable waste storage.
Rsc 02 | Answers C + D
- Does apply to off-site sorting for construction waste arising from fit-out activities.
Rsc 02 | Answer E. Only points 1-3 apply - a future commitment for permanent storage facility is not required.
- Do not apply to the storage of reusable construction products
Rsc 02 | Answer F.
For BIU, new storage areas will be recognised once they are completed and assessed in future certification cycles.
22-Jan-2025 - Updated text to allow for permanent external spaces, aligning with KBCN1716. Scheme applicability updated.
18-Nov-2024 - Requirements for BIU projects clarified relating to all answers in Rsc 02. Title clarified.
09-Feb-2024 - Requirements clarified. Applicability updated to include construction waste storage for BIU V6 Rsc 02.
17-Jan-2024 - Scheme applicability updated.
16-Apr-2018 - Wording clarified.
Office equipment – mobile devices - KBCN00041
Mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, which are generally used without connection to an electrical power source, should be excluded from the assessment of the energy efficient equipment issue.
Devices which are not generally connected to an electrical power source when used are excluded from the 'office equipment' definition as they do not directly affect the unregulated energy consumption of the building.
On site fabrication - KBCN1292
Where concrete (or another construction product) is produced on site, there is no requirement to provide responsible sourcing certification for the end product. As in this case fabrication on site is effectively part of the onsite building process, the certification of the individual products (e.g. aggregates, cement), as delivered to site, shall be used in the assessment instead.
On-demand public bus services - KBCN1404
These can be recognised as follows:
- The location of the transport node should be determined as the nearest available pick-up point to the assessed building
- The frequency of the service should be considered as the published maximum wait time (or actual average wait time, if the service is established and this data is available)
- Such services, whilst they may serve multiple destinations, should be considered as a single route
- It must be demonstrated that information on the availability and how to access the service is made available to building users
This is limited to genuine on-demand bus services, which are operated as public transport with multiple pick-up and drop-off points and does not extend to private hire, taxi or other similar operations.
On-site LZC – whole site shared connection - KBCN1424
To be recognised in BREEAM, the on-site Low and Zero Carbon (LZC) technology must have a direct physical connection to the assessed asset.
OR
Where the LZC technology is;
- Located on the same site,
- Is owned and managed by the same organization as the assessed building, and
- Where it is impractical to physically connect the assessed building to the system,
It is acceptable to allocate the renewable energy generated proportionally as a calculation of the asset's predicted energy consumption compared to the total energy consumption of the whole site.
To allocate renewable electricity by proportional consumption:
- Obtain the total annual renewable electricity generated on-site.
- Exclude all renewable electricity which has been exported to the grid.
- Determine the respective electricity consumption of all assets on the whole site (predicted for new builds and measured for existing assets).
Where consumption data is missing, renewable electricity must not be allocated to the assessed asset. In this case, it is assumed that all electricity consumed is sourced from the grid.
17-Jan-2024 - Applicability BIU V6 Ene 13 removed, as this approach is not applicable to assessing the area of PV fitted.
21-Dec-2022 - Applicability to In-Use V6 confirmed.
Only lifts in building are for persons with impaired mobility - KBCN1330
Where the only lifts, escalators or moving walkways in the assessed development are for persons with imparied mobility with speeds no greater than 0.15m/s, and there are no lifts which fall within the scope of the criteria, the Issue should be filtered out of the assessment. Credits cannot be awarded by default.
Operational waste – Additional requirements for multi-residential buildings with individual bedrooms and communal facilities only - KBCN1519
These criteria are intended for situations where occupants of individual rooms have access to shared kitchens, which can be used to prepare food, regardless of whether central catering is also available.
In developments where all catering is managed centrally and no communal/shared kitchens are provided, these requirements do not apply.
If, for example, catering is managed centrally, but there are small satellite kitchens for staff to sort/reheat food for residents, the assessor must justify whether and to what extent recyclable waste will be generated in these kitchens and demonstrate that adequate recyclable waste storage provided as appropriate.
Operational waste facility – extension of definition – compliance principle - KBCN1716
The original intent in BREEAM was that an operational waste facility is a centralised, on-site permanent enclosed structure or dedicated internal space in the asset.
However, this approach is not always suitable for all asset types.
Compliance principle
The definition of operational waste facility is expanded to include
dedicated external spaces.
The principles for operational waste facilities are that they:
- Are adequately sized and equipped to manage expected waste streams.
- Are designed with the appropriate access and accessibility arrangements for all relevant users and vehicles.
- Are easy to find.
- Minimise disruption to users or neighbours during operation.
The table below shows how the original principles are adapted for dedicated external spaces.
BIU V6 Commercial only
This compliance principle also applies to the storage of:
- Construction waste for fit-outs.
Rsc 02 | Answer E.
- Re-usable construction products.
Rsc 02 | Answer F.
| Principle |
Compliance principle |
| Dedicated and permanent. |
This space can be a dedicated and permanent external space. |
| Adequately sized and equipped. |
External spaces must still meet relevant requirements for size, required waste processing equipment and water outlets for composting.
Where the asset contains multiple tenants or user groups with different needs, the waste facility can be multiple spaces, provided all of them meet the criteria. The minimum size calculation requirement is based on the combined area of all waste facilities. |
| Appropriate access and accessibility. |
The external space must meet requirements for size and access for all relevant users and vehicles,
Any external spaces must also be adequately lit through a permanent lighting solution that is fit for purpose. Compliance for this could be shown through meeting criteria in other issues relating to external lighting. |
| Easy to find. |
As well as permanent signs, external spaces can be marked out through permanent ground markings, bollards, or other permanent features. |
| Minimises disruption. |
Any external facilities must:
- Minimise light pollution and disruptive glare to neighbours, if the space is lit at night.
- Minimise any contamination and air quality issues arising from waste stored.
- Minimise disruptive noise during operation.
Justification and, where relevant, evidence of mitigation measures must be provided to show how these principles are being met. Evidence from other relevant assessment issues can be used. |
Operational waste requirement for catering – applicability - KBCN1162
The additional operational waste storage requirement for developments which include catering is generally only applicable where a commercial scale kitchen is present.
Where the design team can justify that there will be no significant waste streams from a modest facility, such as a small cafe, selling only drinks and pre-prepared snacks, the additional waste storage area identified in the default values does not need to be provided to meet compliance.
21-Jan-2026 Applied to NC V6 and V7 standards
Operational waste storage sizing - KBCN0560
The dedicated space requirements given in the technical manual are default guidance, for situations where it is not possible to demonstrate the required size based on known waste streams.
Compliance can, therefore, be achieved provided that it is clearly demonstrated and evidenced that there is adequate justification for the type of facilities & size of waste storage provided, and that the assessor is satisfied that the sizes and facilities meet the criteria based on the building type, occupancy and the likely waste volumes generated as a result of these.
Option 1 scoring based on robustness and extent of LCA - KBCN0674
For Option 1, BRE Global verifies the LCA tool's score within the Mat 01 calculator based on the rigour of the life cycle assessment tool and the extent it is used on the assessment. For this reason, as opposed to the UK New Construction schemes, the performance/scoring of building elements is not to be taken into consideration and Green Guide ratings for building elements are not linked to the scoring of the Mat 01 tool and credits achieved.
Please see KBCN0237 for further details on using the calculator with verified LCA tools.
Option 2 – number of credits available - KBCN0963
When choosing to assess under option 2 'Elemental assessment of environmental performance information', the online tool allows 'All other buildings' and 'Industrial' assessments to achieve a maximum of four out of six and one out of two credits respectively.
The exemplary credit is available for both options.
This is to recognise that option 2 is a less detailed and extensive way to demonstrate compliance than option 1 'Project life cycle assessment study', for which the maximum score of six credits can be achieved.
03/04/2018 KBCN wording amended to clarify the maximum number of credits available for different building types.
Option 2 – Use of Green Guide to Specification - KBCN0964
As per the relevant Compliance Note, the Green Guide to Specification can be used to demonstrate compliance with Option 1, as the Green Guide is a compliant LCA tool.
However, Option 2 is an elemental approach, for which the Green Guide cannot be used, as robust environmental performance information for the specific new element needs to be provided.
The Green Guide to Specification only provides generic rating and for this reason it cannot be used to demonstrate compliance with Option 2 criteria.
Other buildings specified fittings worse than baseline - KBCN00021
Where the performance of a sanitary fitting is worse than the baseline level, the baseline level as specified in the manual should be input as the level of performance in the Other Buildings calculator tab of the Wat 01 tool.
Outdoor foundations - KBCN0787
Outdoor foundations for lighting poles, bike racks, charging stations, etc., need to be included under hard landscaping, provided they are above the cut-off volume.
Park and Ride Schemes - KBCN0754
'Park and ride' bus services run from one or more car parks to a city centre or other destination to allow travellers to park their car at a convenient location and complete their journey by bus. These generally stop at transport nodes en route to allow passengers to board or alight.
Provided the service meets the aim of the Issue with reference to the guidance, they can be considered for this Issue in the same way as any other bus service.
Parking integral to development’s use - KBCN1145
Dedicated on-site parking which is integral to the function of the development can be excluded from the calculation of parking capacity. Examples could include, but are not limited to:
- Dedicated bays for police vehicles at a police station
- Parking for delivery vehicles at an industrial warehouse
- Holding bays for damaged vehicles at a vehicle repair centre
The spaces are only to be used for this purpose, and must have appropriate signage and / or markings.
Parking spaces with electric car recharging stations - KBCN00044
Electric car spaces should be included in the total number of car parking spaces calculation for maximum car parking capacity.
Whilst electric cars provide benefits in terms of reduced emissions, they do not directly reduce congestion which is one of the aims of this issue.
Part 1 applicability of ‘Commissioning’ and ‘Handover’ credits - KBCN00096
There is an error in the manual regarding the number of credits available in Man 04 to Part 1 only assessments.
Only assessment criteria 7 and 8, the 'Testing and inspecting building fabric' credit is applicable. The two commissioning credits (criteria 1-6) and the handover credit (criteria 9-10) are not applicable when undertaking a Part 1 assessment.
These requirements are beyond the scope of a Part 1 only assessment.
Part 2 and/or 3 assessment; floors and ceilings not affected by works - KBCN0682
For a Part 2 and/or 3 only assessment (i.e. Parts 1 and 4 do not form part of the assessment), where it can be shown that there are to be no changes or minimal reinstatement of the floor, ceiling and interior finishes, the credit can be awarded.
Part 2 Assessments & Thermal Zoning - KBCN0460
Some criteria related to thermal zoning and controls may not be applicable to Part 2 assessments.
These should however, be addressed as far as possible within the work to the core services and associated infrastructure, given the scope of works. Where compliance with any requirement is not possible, this should be justified by the design team in the evidence for this Issue.
10/02/2017 - This replaces the previous CN which stated, incorrectly, that the criteria relating to thermal zoning do not apply to Part 2 assessments. This approach now aligns with the BREEAM manual and the scoring & reporting tool.
Part new-build, part refurbishment projects – ‘original building area’ - KBCN0801
In the Scope section of the technical manual, under the heading 'Part new-build, part refurbishment projects', limits are set out for the proportion of new-build floor area which can be assessed as part of a refurbishment scheme.
For the purposes of this guidance, 'original building area' refers to the area of the original building which is retained and refurbished as part of the assessment. It therefore excludes any part of the original building which is to be demolished or not part of the refurbishment scheme.
The aim of these limits is to ensure that the vast majority of the development is certified against the appropriate scheme, whilst allowing a degree of flexibility to account for such mixed-scope projects.
Part new-build, part refurbishment projects – New-build areas inseparable - KBCN1180
Where the area thresholds given in the Scope section of the manual are exceeded, but new-build areas are integral to and inseparable from the refurbishment, separate assessments or a bespoke RFO/NC assessment may not be appropriate.
This typically refers to new build areas scattered around the floor plans, as in the example, rather than horizontal or vertical extensions linked to a specific part of the existing building.
In such cases, please submit comprehensive plans, clearly identifying the new-build spaces, along with a description of the project, to BRE for review.
24/06/2019 Applicability clarified
Part new-build, part refurbishment projects – Updated guidance - KBCN1187
As announced in July 2015 Process Note and in line with the New Construction technical manual, a simpler method of assessing small, part new-build, part refurbishment projects is now available, as per follows:
For developments that are a mix of new-build and refurbishment of existing spaces, the choice of scheme selection and application is determined according to the scope of the new-build and refurbishment works.
For smaller projects, where the total development area is less than 1000m², a single BREEAM assessment can be undertaken to cover both the new-build and refurbished areas. The choice of BREEAM New Construction or BREEAM Refurbishment and Fit-out scheme should be based on whichever (new-build or refurbishment) constitutes the majority of the assessed floor area.
For larger projects, a single New Construction assessment can be undertaken, though the refurbished areas have to comply with assessment criteria designed for new builds, which can be more challenging in some instances.
The option to carry out two separate assessments, or a single combined bespoke assessment remains, but it is recognised that these options may be overly onerous for smaller projects.
05/10/2018 Technical manual to be update accordingly in the next re-issue.
Passive design analysis – Parts 2 and 3 - KBCN0859
Whilst the majority of passive measures can only be influenced in the base-build, for a Part 2 and 3 assessment it is considered that those listed in the 'Passive design analysis' CN should be reviewed in terms of what can be done with the assessment scope (which may be limited to the last 4 measures for example). Where any of the listed items are not considered, as long as justification is provided in terms why these have not / cannot be considered, this would be acceptable.
Consideration should also be given to what passive design features were incorporated in the base-build and how these are carried through into the fit-out. For example, a passive ventilation strategy in the base-build, must be maintained in the fit-out, rather than sealing all the windows and installing air-conditioning.
In conclusion, in order to ensure a sustainable fit-out, full consideration must be given to how any passive measures from the base-build are maintained or enhanced and any additional measures which can be implemented in the assessment scope.
Passive design analysis – reference to Compliance Note - KBCN1166
The reference in the manual in criterion 2 is incorrect and should point to CN "Passive design analysis".
Technical manual to be amended in the next re-issue.
Passive design analysis where Hea 04 is not applicable - KBCN1236
Where Hea 04 is not applicable to the building type and options selected (for example an industrial building with no office areas), criterion 1 of Ene 04 is not applicable.
Playground or other specialist surfaces - KBCN0694
Where the hard landscaping surface is specified to meet safety related performance (e.g. non-slip or soft surfaces for playgrounds) or particular performance related requirements (e.g. specialist sports performance surfaces such as astro-turf, netball courts and running tracks), then these surfaces can be omitted from the assessment. The standard specification of surfaces for multi-use areas (e.g. cement, tarmac, asphalt) must still be assessed.
PMV and PPD reporting for mixed mode ventilation buildings - KBCN0632
When assessing buildings where both naturally ventilated and air conditioned spaces are included, reporting the PMV and PPD indices is required.
Pods or privacy booths used as workstations – Impact on view out - KBCN1697
Provided the space or room itself is compliant based on a more traditional furniture arrangement, the enclosure of workstations in booths or pods can be disregarded when considering compliance with the ‘View out’ criteria.
Point of use water heaters - KBCN0773
Small 'point of use' water heaters can be excluded from the sub-metering requirements.
Only major energy consuming systems that have a measurable impact on the operational energy consumption need to be included.
Post construction noise level testing - KBCN00043
Noise level measurements do not need to be taken at the post construction stage if the acoustician has accurately modelled the noise level from the plant, using manufacturer's literature, and site measurements taken at the design stage. Any attenuation measures specified by the acoustician in their report must be confirmed as being present post construction.
If the acoustician has been unable to model the noise level accurately, post construction measurements are needed to demonstrate compliance.
Calculations and recommendations from the acoustician are relied on to be accurate and in keeping with best practice; attenuation measures are assumed to be specified and installed correctly.
Post Occupancy Evaluation – Bespoke - KBCN0678
It is acceptable to use a bespoke POE providing that the assessor is satisfied that the methodology covers all relevant aspects of a compliant POE. The assessor should therefore refer to the further guidance on POE provided in the BREEAM technical manual for information on what a compliant POE methodology should contain, as copied below:
- The BCO guide to Post Occupancy Evaluation (POE), British Council for Offices, 2007
- BRE Digest 478, Building performance feedback: getting started, Building Research Establishment, 2003
- Guide to Post Occupancy Evaluation Report and Toolkit, HEFCE, AUDE & University of Westminster, 2006
Post-construction measurement – formaldehyde / VOC levels exceed limits - KBCN0258
If the measured formaldehyde / VOC concentrations were above the prescribed limits, the appropriate remedial action must be taken, as described in the IAQ Plan. The criterion requires confirmation of 'the measures that have or will be undertaken' however it does not specifically address re-testing. We would expect, however that the IAQ Plan should outline what remedial measures are appropriate depending upon the severity and type of the non-compliance with prescribed limits. Such measures may include re-testing as a matter of 'best practice'.
Where levels are found to exceed these limits, the project team confirms the measures that have, or will be undertaken in accordance with the IAQ plan, to reduce the TVOC and formaldehyde levels to within the above limits.
10-Oct-2022 - Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Made applicable to International NC V6.
Post-construction measurement – sampling methodology and KPIs - KBCN0380
When testing for VOCs post-completion and pre-occupancy, a representative sample of the building needs to be carried out. Each sample TVOC and formaldehyde measurement needs to achieve the threshold levels individually, either in the initial testing or after remedial measures have been implemented. This ensures that all tested areas of the building are below the limits, and that areas of non-compliance are not ‘averaged out’.
'When providing KPI test results for air quality post-construction / pre-occupancy within scoring and reporting tool, where the limits are exceeded and remediation and re-testing are carried out, the figure should be an average for the whole building post-remediation, as this is the key figure that reflects the building at its certified state'.
Where testing is not a requirement of the IAQ Plan and this is not carried out, the original testing figures should be entered and the assessment report should provide details of the remediation measures undertaken to reduce these to within the prescribed limits.
10-Oct-2022 Title amended to align with standard KBCN naming format for clarity and consistency. Scheme applicability updated.
06-Dec-2017 Amended to account for situations where re-testing is not required by the IAQ Plan.
Potential for natural ventilation – areas exempted - KBCN0806
For projects where the majority of a building's occupied spaces will meet the criteria to achieve the potential for natural ventilation credit, but a relatively small area will not comply due to functional requirements of the space, (e.g. a lecture theatre), the credit can be awarded where this approach can be justified.
The intention is to encourage the design of buildings where a strategy of (potential for) natural ventilation has been implemented as far as practically possible, given functional constraints.
Potential for natural ventilation – mechanically ventilated and mixed mode assets - KBCN1533
Scope of KBCN
This KBCN clarifies the associated compliance note for this credit.
- NC 2011 & 2013 - No CN, but the principle of this KBCN can be applied.
- NC 2014 v5.0 - CN 3.1
- INC 2016 v2.0 and INC V6 - CN 3.11
- RFO 2014 v2.0 - CN 7
- RFO 2015 v1.4 - CN 5.2
Clarification
Mechanically ventilated and mixed mode assets can potentially achieve the 'potential for natural ventilation' credit by:
- Meeting the relevant criteria for room depth and glazing area OR, where this is not possible:
- Show through modelling that the building has the potential to be ventilated entirely via a natural ventilation strategy.
For 2. the second paragraph of the CN allows flexibility in demonstrating adaptability to an entirely natural ventilation strategy.
An asset can allow for mechanical ventilation for ≤ 5% of its annual operating hours to boost ventilation rates, and (for this credit) can still be considered to be a fully naturally ventilated strategy.
≤ 5% mechanical ventilation rule
The focus of this credit is to demonstrate future adaptability to introduce fresh air into the asset for occupant comfort, so this requirement relates only to mechanical ventilation. Active heating / cooling is not considered.
≤ 5% is a weighted average over all of the asset's occupied spaces. The basis for the weighting will be determined by the modelling software used.
Scope and time scale of modelling
The modelling covers all occupied spaces. Where relevant, exclusions are allowed - see related KBCNs for details.
The modelling period is one year, during the asset's operating hours.
The modelling must be based on a plausible scenario that is realistic. This means that:
- Potential changes can be practically and reasonably achieved by future occupants.
For example, the adaptation strategy must not require new or modified openings in the building envelope or include significant or disruptive changes to the internal layout.
- The changes do not compromise the intended function or operation of the asset.
- For speculative assets, a realistic notional layout can be used. See KBCN0408.
- The modelling assumption does not need to factor in climate change.
The aim of the credit is prove the validity of a future naturally ventilated scenario - if and when this is carried out is outside the scope of the certification.
Potential for natural ventilation – shell only assessments - KBCN0408
Where compliance depends on a speculative layout which is unknown, it is the responsibility of the design team to demonstrate that it is feasible for a future tenant to achieve compliance in the relevant areas via the use of a notional layout.
This ensures that the shell allows the potential for compliance, and if this can be demonstrated the credit may be awarded.
Potential for natural ventilation – use of doors to comply - KBCN0690
Doors can only be used to demonstrate potential for natural ventilation where:
- They can be used to achieve at least 2 levels of ventilation control as required in the criteria AND,
- Using them does not cause accessibility or security issues during asset operation.
In all cases, the use of doors must be clearly and robustly justified by the Assessor.
19-Oct-2022 - Wording clarified. Scheme applicability updated.
Pre-demolition audit/(pre-refurbishment) on other structures and hard surfaces - KBCN00045
A pre-demolition/(pre-refurbishment) audit is required where any existing buildings, structures or hard surfaces are present on a development site.
The intent of the pre-demolition/(pre-refurbishment) audit is to ensure that any potentially useful materials are considered for re-use or diversion from landfill, not just materials resulting from buildings.
22.11.17 Reference added to the pre-refurbishment audit for RFO assessments.
Pre-demolition/(pre-refurbishment) audit requirement - KBCN0243
Where the site demolition/clearance does not form part of the principal contractor’s works, but has been undertaken by the developer for the purposes of enabling the assessed development, a pre-demolition/pre-refurbishment audit must be carried out and referenced within the SWMP as per the guidance.
Where justification and robust evidence can be provided, the following exceptions may apply:
- Where it can be demonstrated that demolition/clearance was carried out prior to the developer acquiring the site and no pre-demolition/pre-refurbishment audit is available.
- Where the demolition was expedited for health and safety reasons.
- Where the demolition has been carried out by the same developer, but as part of a significantly earlier site clearance, occurring prior to RIBA stage 0 and no less than 12 months ahead of the requirement being set to carry out a BREEAM assessment. In such cases it must be clearly demonstrated that the demolition was was unrelated to the current re-development.
This requirement seeks to encourage good practice by developers and design teams in relation to previously developed sites.
11/12/2019 Additional exception added to align with KBCN1257 and guidance re-structured for clarity
22 11 2017 Reference added to the pre-refurbishment audit for RFO assessments.
15 11 2017 Wording amended for clarity
Pre-refurbishment audit – definition of ‘competent person’ - KBCN0756
For the purposes of Wst 01, criterion 1b, a ‘competent person’ for the pre-refurbishment audit is someone who has knowledge of the value and condition of materials and what can or cannot be repaired. Although the ‘relevant definition’ is missing, it is effectively provided later in the sentence as someone who ‘has appropriate knowledge of buildings, waste and options for the reuse and recycling of different waste streams.’ A demolition contractor would be ideal for the role, but could also be the main contractor. To clarify, the 'competent person' does not have to be independent of the project.
11/09/2017 - Clarification on the removal of the independence requirement added.
This takes precedence over the technical manual, which will
be updated accordingly in next re-issue.
Pre-refurbishment/demolition audit – late development - KBCN0537
Where the pre-refurbishment/demolition audit has not been done at RIBA stage 2/Concept Design, as required in the criteria, the credit can still be achieved. Robust evidence must be provided confirming that the timing of the pre-refurbishment/demolition audit has not compromised its ability to influence the design, consideration of materials re-use and the setting of targets for waste management. Evidence must demonstrate that this allowed decisions to be made before the start of strip-out/demolition works.
26.07.2018 Applicability of KBCN extended to include the UKNC2018 scheme.
Prerequisite – Users with special hearing and communication needs - KBCN0969
Intent
Criterion 1c ensures that the suitably qualified acoustician has influenced the design of the asset to:
- Meet the acoustic requirements of users with special hearing and communication needs.
- Ensure that accessible acoustic design is considered where this is not adequately covered by local legislation.
What this should cover will depend on the asset type and expected users.
Asset users
The UK Department for Education document BB93
Acoustic design of schools: performance standards building bulletin 93 (February 2015) defines users with special hearing or communication needs as those with any of the following:
- Speech, language and communication difficulties.
- Visual impairments.
- Fluctuating hearing impairments caused by conductive hearing loss.
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- An auditory processing disorder or difficulty.
- Being on the autistic spectrum.
This list is not exhaustive, and the suitably qualified acoustician must consider typical asset users, along with the other points a-d when giving early design advice regarding room layout, sound insulation and reverberation times.
Accessibility features
The principles of accessible design are universal and could be applied in a wide range of assets. Additional features that could be relevant to accessible acoustic design include, but are not limited to:
- Designation of quiet zones.
- Hearing assistive technologies.
- Induction loop systems.
- White noise machines.
- Infrared and FM systems to provide direct audio to individuals with special hearing needs.
- Noise barriers.
The suitably qualified acoustician must use their professional judgement to determine the scope of any such features as part of the design. Where no features are applicable this must be clearly justified.
04-Sep-2024: Wording and intent clarified. Information on additional accessibility features added. Scheme applicability updated. Title updated.
01-Mar-2019: Amended to clarify that this is a 'typical' list of users, but does not impose a new requirement.
Prerequisite – Evidence requirements - KBCN1747
Confirmation of compliance with the standards or codes of practice required to meet the prerequisite should be provided by the relevant members of the project team, i.e. the system designer and/or the system installer, as appropriate.
This recognises the responsibilities of those designing and installing the system configuration. Evidence from the manufacturer is not required.
Prerequisite – Reused temporary site timber - KBCN1769
Timber formwork or scaffold boards, that are being reused and are verified as such, can be excluded from the criteria.
It is more sustainable to reuse existing timber than to potentially promote the use of virgin timber just to ensure responsible sourcing paperwork is available, which may be logistically hard to obtain for reused timber.
Presence detection – illuminated signs - KBCN1671
The requirements for presence detection do not apply to illuminated signs.
In BIU V6, presence detection requirements are included as part of automatic energy saving controls. All other requirements in this criteria must still be met.
Principal contractor or subcontractor no longer operational - KBCN0590
In situations where the principal contractor or other company involved in the project is no longer operational where, for example, the company has gone into administration, the assessor may be unable to obtain all the evidence to meet the requirements of BREEAM or HQM.
For some BREEAM Issues, it may not be possible to demonstrate compliance retrospectively, and in such cases, the relevant credits must be withheld.
However, in this situation, a lack of complete evidence will not, in itself, prevent the project from achieving a BREEAM rating and, where relevant, a prerequisite or minimum standard can be waived. For example:
INC NC V6 Man 03 Prerequisite - Legally harvested and traded timber
or
INC V6 Wst 03a – 1 credit to achieve an Excellent Rating
This is based on the project team demonstrating appropriate efforts to obtain the evidence from the company in administration and providing the following:
- Evidence of the company going into administration
- Evidence of compliance from the company in administration, where available
- Evidence of compliance from the date a new company was engaged
28 Oct 2024 - Title and general approach updated. Applied to NC V6.
Process Notes - KBCN0611
Process notes can be accessed by licensed assessors
here.
When a new process note has been released, you may be required to tick the box to confirm you have read the note to be able to access other documents in BREEAM Projects. To do this scroll to the bottom of the Process Note index page and tick the box and click next.

Process water to offset potable water demand - KBCN0586
Process water resulting from the building under assessment, can be considered for off-setting potable water demand from components that would otherwise be supplied using potable water, when in line with the criteria requirements for greywater systems.
Process water resulting from the building under assessment can be considered as a form of greywater for the purposes of off-setting potable water demand.
Process water to offset potable water demand - KBCN0586
Where it is demonstrated that it is safe to do so, process water resulting from the building under assessment, can be considered for off-setting potable water demand from components that would otherwise be supplied using potable water, when in line with the criteria requirements for greywater systems.
Process water resulting from the building under assessment can be considered as a form of greywater for the purposes of off-setting potable water demand.
21 Dec 2021 Additional wording added, requiring it to be demonstrated that process water is safe to use and KBCN applied to BIU standards.
Process: ‘Provisional’ registrations - KBCN0124
Projects with a ‘provisional’ registration against the Refurbishment and Fit-out schemes cannot be submitted for certification. Once licensed in the Refurbishment and Fit-out scheme any provisional registrations will need to be converted into full scheme registrations and these assessments can then be submitted for QA and certification.
Process: Registering RFO projects against 2008 and 2009 , where required contractually - KBCN00090
NC assessors will continue to be able to register under the building types for which they hold a licence using BREEAM 2008 or 2009 for Refurbishment or Fit Out. For example, an assessor who is licensed under NC Commercial (Offices, Retail, Industrial) will be able to register previous version 2008 Refurbishment or Fit Out assessments under Offices, Retail or Industrial providing there is contractual planning requirement in place to use that version.
A NC assessor would need to be licensed as a BREEAM RFO assessor to be able to assess refurbishment and fit-out projects.
Process: Registration date and applicable scheme manual issue - KBCN0708
Typically the scheme technical manual issue which is current when a project is registered should be used for the assessment. For example, if a BREEAM UK New Construction 2014 development was registered on 01/07/2016, the current issue of the scheme technical manual at that point would be issue 4.1, which was published on 11/03/2016 (the next issue 5.0 of the technical manual was published on 05/09/2016). However, it is permissible for the assessor to decide to use a later issue of the technical manual. The scheme technical manual version and issue used for the assessment should be clearly referenced within the assessment report.
Note that in any case, the same technical manual version and issue should be used for the entire assessment. It is not acceptable to assess different credits based on different issues of the technical manual and it is not acceptable to change issues between submissions of the assessment.
26 09 17 Clarification added that the 'Issue' of the technical manual may not be changed between assessment submissions
Proposing national best practice guidance on defining granular fill and capping as a high grade use - KBCN1138
Recycled aggregates used for granular fill and capping can only be considered ‘high grade’ if they:
- conform to specifications in national best practice guidance (refer to the ASWL).
- OR, where there is no national best practice guidance approved, new guidance can be proposed to BRE for approval:
- Specifications in national best practice guidance must include as a minimum, limits and requirements on the properties listed in Checklist A6.
- Specifications must be specifically for recycled aggregate for use as granular fill or capping.
- National best practice guidance is not required to cover test methodologies.
- OR, alternatively, the UK standard ‘Specification for Highway Works (SHW) Series 600 Earthworks’ and classifications as listed in the relevant definition section of the UK NC 2014 manual can be used.
If none of these apply, the recycled aggregates should be considered ‘low grade’ and excluded from the assessment of the Issue.
Protecting vulnerable parts of the building from damage – underground car parks - KBCN1331
Exposed elements, such as columns in an underground car park, should have been designed against structural damage from minor vehicle collision and, therefore, do not require any additional protection to meet compliance for this BREEAM Issue. Assessors should, however, consider whether additional protection is required at the vehicular entrance to underground car parks.
The requirements are intended to address the issue of damage to vulnerable parts of the facade, which would require repair/replacement in the event of minor vehicular collisions.
Public car parks - KBCN00092
Any public car parks in the vicinity of the assessed building, for which the building owners/operator are not providing some form of subsidy or an agreement with the car park operators to provide priority spaces for building staff, can be excluded from the assessment.
Raised access floors - KBCN00018
For the purposes of Mat 03, raised access floors should be considered as part of the floor structure.
HQM - Applies to HQM's Responsible Sourcing of Construction Products assessment issue.
Re-use and direct recycling of materials - KBCN0894
The ‘Re-use and direct recycling of materials’ criteria always apply, even where there is nothing being taken out of the building, i.e. there is no strip-out. This means that waste from the actual refurbishment works, i.e. the new products being installed, which may potentially be recycled or re-used, such as damaged products, off-cuts, spares, pallets, packaging - anything delivered to the site, can contribute to the requirements for these credits.
The ‘Re-use and direct recycling of materials’ criteria apply, regardless of whether the ‘Pre-refurbishment audit’ credit is applicable.
Re-used electrical equipment - KBCN0325
BREEAM does not currently recognise the reuse of electrical equipment as the most energy efficient option for compliance with this issue. If it can be demonstrated that such existing electrical appliances meet the criteria for inclusion in the relevant national or international energy efficient equipment schemes, these can be considered compliant.
If new equipment is procured in addition to the re-use of the old equipment, the existing equipment may be excluded from this assessment. In these situations the assessor must be satisfied that the new equipment would make a meaningful reduction to overall unregulated energy consumption.
This issue assesses the reduction of unregulated energy consumption in operation and does not currently assess embodied energy in the manufacture of equipment.
Recyclable, general and organic waste storage – space, labelling and segregation - KBCN1577
Strategies may vary according to the specifics of each project, their waste streams and collection arrangements.
- Any reference to ‘labelling’ refers to permanent markings or fixed, robust and weatherproof signage.
- Colour coding of bins to identify waste streams is not in itself compliant labelling.
The aim of these requirements is to encourage recycling, ensuring that it is correctly sorted and to prevent cross-contamination of waste streams.
Label the recycling area
This is required to alert building users and collection agencies to the location of the recycling facility.
Label each recyclable waste stream
This can be done by labelling the bins or their dedicated space within the recycling facility, or both. Mixed recycling bins and / or spaces are clearly labelled with their constituent waste streams.
General or organic waste have their own dedicated spaces
Sufficient space for general and, where relevant, organic waste is required in addition to meeting the requirements for recyclable waste. This does not have to be within a separate facility, but if combined with recyclable waste storage, there is greater risk of cross-contamination. The following requirements apply in this situation:
- For organic waste, see also additional hygiene-related requirements within the technical manual.
- In line with the requirement for the recycling area to be clearly labelled, general or organic waste must be stored in labelled bins and in a labelled, dedicated space within the combined waste facility.
If provision of waste bins is out of scope
Where the provision of waste bins is outside the scope of the developer, it is clearly not possible to label the bins. In this situation, the following compliance options are available:
- Provide compliant signage to the storage area and label bin spaces within the storage area according to the relevant waste streams.
- Where future waste streams are unknown, provide compliant signage to the storage area and a written commitment from the developer to ensure that the bins and/or bin spaces are labelled.
21-May-2024 - Link to KBCN0696 removed. Merged with KBCN1380. Minor clarification added on mixed recycling.
Recycled aggregate evidence prior to contractor’s appointment - KBCN0231
If the contractor has not been appointed at the time of submitting the Design Stage assessment, whilst it is imperative for the design team to demonstrate a firm commitment to meet the criteria and award the credit at this stage, a letter from the design team or developer to confirm that no contractor has been appointed should be submitted in lieu of the stated letter of confirmation. This should also be clarified in the Assessment Report.
BREEAM recognises that it may not be desirable to confirm the specification, source and availability of a particular recycled aggregate for a project where the contractor has not been appointed yet. This would restrict the contractor's ability to source the most economically viable recycled aggregate to meet the BREEAM criteria.
Recycled aggregates in concrete - KBCN0823
The relevant CN in the technical manual, which confirms that no concessions are given to the criteria, reads:
‘Where national building regulations limit the use of recycled aggregates in concrete (typically applicable to bound aggregate uses as listed), the onus for achieving this credit is on the unbound uses (please note that the total aggregate figure must still include the bound uses).’
To clarify, in the calculation, the percentage of recycled aggregates in both bound and unbound uses can be considered against the total high grade use for the project.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
Recycled materials in hard landscaping - KBCN0975
When recycled material is to be used for hard landscaping, the Green Guide rating will depend on whether the material comes from the same site or from another location.
Typically, on-site recycled material is treated with very little impact, or ignored, as there is little or no energy/material input in putting it in place. When recycled material is brought in from elsewhere, transport, as well as any processing the material has gone through to make it fit for purpose, will be taken into account.
If the assessor is in doubt, they need to submit a landscaping proforma along with any supporting documentation on the materials and their use and BRE will provide a rating and/or guidance.
Reduction of night time light pollution – Night-time operation - KBCN0697
Note: This KBCN supersedes INC 2016/INC V6 Pol 04 CN3.1
During hours of operation between 23:00 and 07:00, lighting required for operational reasons does not have to be modified for BREEAM compliance.
The aim of this Issue is to reduce light pollution by automatically switching off the external lighting or by complying with lower levels when the building is not in use.
23 Jan 2023 - Note added to address conflict with INC Pol 04 CN3.1. KBCN title updated for consistency - The technical manual will be updated accordingly in the next re-issue
08 Mar 2018 - Wording amended to add clarity.
Regenerative drives – requirement for specification - KBCN1253
Requirements for the specification of a regenerative drive for lift installations are subject to an analysis of resultant energy savings. However, where it can be demonstrated that this is not financially viable, accounting for payback over the service life of the installation, this option can be discounted.
Please also refer to other scheme-specific guidance relating to this requirement.
Remedial works – timing of acoustic re-testing - KBCN1164
The intent of CN "Remedial works" is that, where these are required, re-testing is carried out prior to handover and occupation.
However, it is permissible to carry out the re-testing post-occupation. This is provided any specific guidance for particular building types related test conditions have been met (for instance, it may be that some building specific guidance requires furniture or carpets to not be present during the testing).
Compliance cannot be achieved based on a letter from the SQA confirming that the contractor has followed their advice to achieve the required performance.
07.11.18 KBCN amended to allow for re-testing to be carried-out post-handover.
Reporting PPD and PMV Figures - KBCN0867
The PMV (Predicted Mean Vote) and PPD (Predicted Percentage Dissatisfied) values need to be entered into the scoring & reporting tool for data recording purposes.
The thermal modelling specialist should be able to provide values for both the PMV and PPD for the asset.
The values to report are the observed range of values for PMV and PPD:
- Across all occupied areas and,
- Across all expected occupied hours.
If the software or calculation method used does not generate these PMV / PPD metrics, they do not have to be provided.
[accordion]
[accordion_block title="Example"]
An asset has the following thermal comfort ranges across its occupied spaces:
- PMV ranges from -0.3 to +0.2.
Enter '-0.3 to +0.2' into the relevant field.
- PPD ranges from 3% to 10%.
Enter '3% to 10%' into the relevant field.
[/accordion_block]
[/accordion]
15.09.22 Wording and example clarified.
Responding to climate change – less than 12 credits available in Ene 01 - KBCN1829
The exemplary credit requirements for this issue require
8 credits to be achieved in Ene 01.
However, when using
Ene 01 Option 2 to assess energy performance, the available credits could be less than 12, depending on the Parts assessed.
In these cases, the requirement is to achieve
two thirds or more of available credits in Ene 01.
Adjusted requirements using Ene 01 Option 2
|
Part 1 only |
Part 2 only |
Part 3 only |
Parts 1+2 |
Parts 1+3 |
Parts 2+3 |
| Available credits in Ene 01 Option 2 |
3 |
8 |
1 |
11 |
4 |
9 |
| Requirement for Wst 05 |
2.00 |
5.33 |
0.67 |
7.33 |
2.67 |
6.00 |
No credits are available in Ene 01 for a Part 4 only assessment.
Requirements unchanged for Ene 01 Option 1
This two thirds requirement does not scale up for Option 1, where 15 credits are available. Where using this option, the requirement for Wst 05 remains at 8 credits.
Responsible construction practices – Multiple contractors on the same project - KBCN0352
It is the site that must comply with BREEAM issues rather than any individual contractor. Several different contractors may have obligations to meet compliance criteria. One of the contractors and/or site managers may have responsibility for ensuring compliance during site operations. It is ultimately the client/project team's responsibility to determine and demonstrate compliance.
Responsible sourcing – clarification for one credit - KBCN1594
The requirement for one credit can be achieved by
EITHER:
- Responsibly sourcing materials from 3 out of the 10 material categories listed in the Methodology OR
- Achieving ≥ 18% of the available RSCS points.
31-Jan-2024 - Wording clarified.
Retained external lighting - KBCN0782
All external lighting within the construction zone, whether retained without alterations, retained with alterations or newly specified, must meet the requirements of Ene 03 and Pol 04.
The aims of the two issues are to encourage the use of energy efficient external lighting and reduce night-time pollution and nuisance to neighbours from the assessed building. Even if new proposed lighting meets compliance, the existing lighting fixtures could have a high energy demand and result in night-time light pollution.
Reversible heat pump (VRF) providing both heating and cooling - KBCN0735
Where a reversible heat pump, which provides heating and cooling on reverse cycle with heat recovery, is used, the cooling capacity only should be used for the Direct Effect Life Cycle CO2e emissions (DELC) calculation.
The cooling capacity of heat humps is normally less than the heating capacity, so compliance against the criteria will be based on the more challenging DELC value calculated.
RGB LED lighting - KBCN0986
RGB LED lighting must be assessed against the average external lighting efficacy benchmark.
The current criteria do not completely rule out the use of RGB LED lighting as it can potentially be combined with other types of external lighting to meet the average efficacy benchmark.
Risk to Ecologist’s safety - KBCN0704
In some situations a significant safety risk may prevent a suitably qualified ecologist from attending the site to undertake a site survey. In these cases a desktop study can be used to demonstrate compliance, where the ecologist confirms that it is an acceptably robust substitute.
In these cases, the assessor must provide evidence to confirm the type of significant safety risk present.
Rounding the number of parking spaces - KBCN0602
Where the calculated number of car parking spaces is a fraction of a whole number, this should be rounded down to the next whole number to assess the issue.
Fewer parking spaces are preferable as the more sustainable solution.
RSCS summary score level for BES 6001 products - KBCN0955
For products certified under BES 6001, the rating score (between 5 and 7) can be found in the Green Book Live. This is the rating that needs to be entered in the Mat 03 calculator.
The RSCS score that is entered into the Mat 03 calculator comes from the relevant table in Guidance Note 18. However, for BES 6001, the score is per certificate because 6001 works at different levels of rigour.
Once you have found the product, by searching on the page below, click 'More..' on the right-hand side to reveal further details, including the BREEAM score level.
GreenBookLive Responsible Sourcing
Safe pedestrian routes – Definition, measurement and verification - KBCN0238
Definition
Safe pedestrian routes include sidewalks and safe crossing points, which may be controlled or, for example, be identified by tactile paving, a crossing island or a dropped curb. An element of judgement may be required, in which case justification should be provided.
Measurement
Distances could be measured, for example, along a sidewalk, across a road at a safe crossing point and along the sidewalk on the other side. The distance should not be measured diagonally across a road, following the most direct route.
Verification
The assessor’s site inspection is an important aspect of the assessment and may help to confirm that all relevant information is current and can include photographs of any key areas. This can also help to identify safe crossing points or hazards which may not be apparent from a desktop study. However, web-based evidence may also be used where the assessor is satisfied that it is robust and demonstrates that it is up to date.
Where web-based navigation maps (e.g. Google Maps/Street View) are used as supporting evidence, this must include:
• Dated and marked-up site plan or a web-based navigation map viewer highlighting:
• Current location and type of transport nodes and local amenities.
• Current route and distance from the building via a safe pedestrian route.
• Plan or map scale.
When using web-based evidence for post-construction stage, the assessor must, additionally, provide verification that the information provided for the nodes/amenities is still accurate and up to date.
29 Aug 2025 - Approach to web-based map data at post-construction stage updated and related wording amended accordingly
07 Mar 2024 - No changes have been made. This appears as 'updated' due to an administrative error.
11 Jan 2024 - Wording re-structured for clarity
19 Dec 2023 - Applicability to BIU V6 confirmed
Safety and security lighting – definition - KBCN0888
BRE does not provide a specific definition of safety and security lighting, as this could vary, depending on the project and location of the lighting. Together with the design team, the assessor is required to determine which lights are provided purely for safety and security purposes and which should be considered as general lighting.
Sanitary fittings used in religious practices – updated - KBCN1624
Such fittings should
not be included in the scope of this Issue. Please refer also to
KBCN0418
This guidance relates to fittings and facilities used in some religious practices, for example, for washing before prayer.
03 Nov 2023 - Updated. Previous guidance was incorrect and contradicted the approach outlined in KBCN0418
Scheme classification – Education - KBCN0398
The Education scheme classification criteria is tailored to the requirements of buildings that are likely to be used by large numbers of students, whose requirements differ slightly from the general population. Where a building on an education campus, or owned by an educational institution:
- is not used for teaching / study
- is primarily used by staff or other non-students
- and transport requirements differ from a standard Education building
The building may be assessed under a different, more appropriate scheme classification. Where it is unclear how this building should be assessed, a scheme classification query should be submitted.
Scheme classification based on anticipated occupancy & building use - KBCN0421
In the instance where there is potential for the building occupancy and use to change during the building lifetime, scheme classification should be based on the most likely occupancy and use of the building as anticipated at the time of the assessment.
Please refer to Guidance Note 10 (GN10) for further details
Scheme classification queries - KBCN0540
As the Operational Guidance clarifies ‘…A scheme classification requires the assessor, client or design team to submit floor plans showing the layout of the building(s) along with its intended functional areas and any other relevant information. BRE Global will then confirm the appropriate means of assessing the development, using either one or more standard schemes or by developing project-specific bespoke criteria…’
BREEAM Technical cannot definitively confirm a scheme classification in the absence of drawings.
Relevant information could also include specification of the scope of works, clarification of general building functions, spaces within them, as well as their management and access to the public.
Scope of ‘Building services’ location/use category - KBCN000001
'Building services' refers to the equipment and distribution systems specified for providing heating, power, ventilation, lighting, air-conditioning and domestic water services in a building. As a minimum, this location/use category should include the equipment and controls specified for the building services.
Refer to Guidance Note GN24: Demonstrating Compliance with BREEAM Issue Mat 03 issue for more information.
18/10/2018 Applicability to UK NC2018 removed; relevant guidance is included in the technical manual.
Scope of construction works included - KBCN0642
Only the scope of works the principal contractor is responsible for needs to be considered in the assessment of this Issue. This also includes works carried out by sub-contractors that are engaged by the principal contractor.
Scope of different parts – Error in compliance note - KBCN1261
CN3 Includes the following error:
- Where it reads: ‘Criteria 6 - 15 are not applicable’
- This should read: ‘Criteria 7 - 15 are not applicable’
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
Scope of energy efficient cold storage - KBCN00029
Technical guidance
The intent of the following wording in the technical manuals is to exclude self-contained refrigeration units.
NC 2018 Ene 05:
“The scope of this issue covers freezer or cold storage rooms which are integral to the building and served by the building’s own refrigeration systems.”
NC 2016 Ene 05:
"If the building contains no refrigeration systems or only refrigeration systems which stand-alone, i.e. are not integral to the building and served by the building services, this issue is not applicable to the assessment.
Clarification
The scope of this issue covers freezer or cold storage rooms which are integral to the building, and includes cooling systems that require commissioning and optimisation for the specific requirements of the cold storage space. This applies whether the cold storage space has a dedicated cooling system serving this space, or one which is connected to wider building cooling services.
"Kitchen and catering facilities", are excluded from this issue. They refer to commercial-sized, but self-contained, off-the-shelf units - these include large freezers, fridges, or stand-alone self-contained walk-in cold storage units. These types of units are manufactured as a self-contained product, and contain their own integral cooling systems - they operate according to manufacturer pre-sets, and do not require commissioning of the cooling system.
For this reason, these are not assessed under this issue, but they may still fall within the scope of the 'Energy efficient equipment' issue.
The guidance will be clarified in future reissues or updates of the technical manuals.
22-Feb-22 Wording clarified.
02-Jun-17 Wording clarified.
02-Dec-16 Wording clarified - no change to approach.
Scope of hard landscaping - KBCN0634
For the purpose of assessment, hard landscaping includes (but is not limited to) parking areas (including manoeuvring areas, lanes, roads within the parking area), pedestrian walkways, paths, patios. The definition excludes basement parking, access or approach roads and designated vehicle manoeuvring areas, balconies, roof terraces,specialist sports areas (running tracks, netball areas etc.) and retaining walls.
Scope of issue – clarification – fixed installations - KBCN1660
The scope of this issue covers noise from external building services (or 'fixed installations' as written in the manual) serving areas
designed for human comfort.
The noise impact assessment excludes:
- Noise from process-related plant.
- Noise from emergency or back-up plant which are not used during normal operation.
Scope of product assessment for VOCs - KBCN0871
For the purpose of this Issue, this covers any product installed or applied inside of the inner surface of the building’s infiltration, vapour or waterproof membrane or, where not present, inside of the inner surface of the building envelope’s interior facing thermal insulation layer.
Only products that are installed or applied in parts of the building where their emissions are likely to affect indoor air quality need to be assessed.
Scope of refurbishment varies: RFO Parts 1-4 - KBCN1635
Where the scope varies within a refurbishment project to the extent that the same RFO Parts are not universally applicable, the assessor should advise the project team of the following available options and register the assessment accordingly:
1. Undertake separate RFO assessments, according to the applicable RFO Parts for each area.
2. Undertake a single assessment based on the RFO Parts that are common to all areas.
Example
A project where the common areas are fully refurbished and fitted-out under Parts 1-4, and tenants' areas are subject to Parts 1-3, but not a Part 4 fit-out:
- Option 1 would require a Parts 1-4 assessment of the common areas and a separate Parts 1-3 assessment of the tenants' areas.
- Option 2 would allow a single assessment, but the fit-out of the common areas would be excluded, resulting in one assessment of all areas against Parts 1-3.
Scope of the criteria for lifts – Small service lifts (dumbwaiters) - KBCN1589
Small service lifts, of the type typically used to transport prepared food and crockery in restaurants (sometimes referred to as 'dumbwaiters'), fall outside the scope of this assessment issue.
Scope of the refrigerant leak detection system - KBCN0530
The refrigerant leak detection system is required to cover any part of the plant or pipework which contains refrigerant.
21/08/17 KBCN amended to include pipework containing refrigerant.
Scope: Building types not falling within the scope of the scheme - KBCN0544
For building types that are not included in the scope of the IRFO 2015 scheme, a Bespoke process will be required.
Information on the Bespoke process for buildings, communities and infrastructure projects is within guidance note
GN23 here.
The Buildings bespoke application form is available on the
Extranet here.
Scope: Part new-build, part refurbishment projects – unoccupied space - KBCN1670
The thresholds set for the permitted area of new build are intended for situations where this includes occupied space.
Where this is not the case, e.g. where the extended area is unoccupied warehousing, new build space up to 50% of the refurbishment area can be included in an RFO assessment.
Seasonal commissioning evidence - KBCN0818
Where the criteria require that seasonal commissioning activities are to be completed over a minimum 12 month period following the occupation of the building, it is accepted that completed records may not be available at the time of Final Certification.
In such cases, evidence of the appointment of a seasonal commissioning manager and schedule of commissioning responsibilities which fulfils the BREEAM criteria are acceptable to demonstrate compliance.
Seasonal commissioning of Solar Photovoltaics (PV) - KBCN0244
Solar PVs can be excluded from the requirements for seasonal commissioning. This is because commissioning at a particular time of the year will not affect the original commissioning of the system.
Self-contained dwellings / bedrooms with shared facilities – mixed recycling - KBCN1664
Where there is mixed recycling, the number of recyclables containers can be reduced to match the final waste streams being collected.
For example, the standard BREEAM requirement is
three recyclables containers per dwelling / communal facility.
- Where there are two waste streams (for example mixed paper, plastics and metals with a separate glass collection) then only two containers are required.
- Where there is only one waste stream, only one container is required.
The total combined storage volume requirements are the same as stated in the manuals.
To apply this KBCN, the project team must provide evidence to QA of the waste collection policies that apply to the asset.
Self-contained dwellings or units with individual utility meters - KBCN0199
Where self-contained dwellings or units covered by the assessment have their own individual energy supply and utility meter (e.g. water, gas or electricity), this supply can be excluded from the scope of the issue. All shared energy supplies and common areas under the responsibility of building management are still included in the assessment.
For example, if self-contained flats in an assisted living development have individual gas supplies with their own utility meter, this supply will be excluded from the assessment. However, the lighting and small power comes from a shared distribution board on each floor, in which case this shared supply will need to be sub-metered in accordance with the criteria.
This same principle applies to scenarios involving speculative industrial or retail units with capped services, where these units have their own utility meter.
12/09/2018 Applicable to Water Monitoring Issue where appropriate
27/09/2017 The word 'units' added to include a wider range of scenarios falling under this principle.
17/06/2022 Added other industrial / retail situations for further clarity on the applicability of this KBCN.
Services efficiency improvements in assessments against Part 1 only - KBCN1144
Where Parts 2 or 3 are not being assessed, improvements to the performance of the building services cannot be recognised, whether these be designed or consequential. In order to fully recognise the fabric efficiency improvements, however, where changes to the building services have been made, the post-refurbishment services performance values should be used for both pre-and post-refurbishment.
Where a project seeks recognition of improvements to the performance of the building services, this must be assessed against Part 2 or 3.
Setting of Responsible Sourcing Certification Scores (RSCS) - KBCN00017
Mat 03 credits require the majority of the materials used to be sourced with a high RSCS score. While maximum points (10) are available for reused materials the points available for RSCS's are typically less than 10. The available points are representative of the relative merits of each source while also providing some incentive for each scheme to improve and gain higher scores in the future.
The latest points scores for each RSCS route are available in the latest version of GN18.
Shared ecological enhancements - KBCN0656
A site-wide approach to ecological enhancements can be used on sites where multiple buildings share areas of soft landscaping. The enhancement benefits are applied to the individual building assessments within the site.
Similarly, where a building comprises more than one assessment, eg different floor assessments, a green roof on top of that building can be used to award credits for each assessment for which the Land use and ecology issues apply.
The benefit can be applied on a site-wide basis provided all developments are completed within the appropriate timeframe of a valid ecological survey.
Shell & core project: Completing as fully-fitted - KBCN0394
It is possible to complete an assessment as fully fitted following a design stage certification as a shell & core project. Whilst the assessment will reference much of the same evidence gathered for design stage, it must be re-registered and may be submitted as a fully-fitted Post-construction assessment.
17/04/18 Wording clarified
Shower with multiple shower heads - KBCN0855
To calculate the water use of a shower with more than one shower head, one of the following should be done:
- If all of the shower heads can be turned on at once, the flow rates should be added up.
- If the shower heads can only be used one at a time, the highest flow rate should be used
22 Feb 2024 - Applied to BIU, BREEAM NC and RFO standards
Showers and taps where use is physically time-limited – Calculating flow rates - KBCN1690
Where a timer is used to physically limit the use of showers or taps within a set period of time, this can be used as the basis for calculating a reduced flow rate.
For example, where use is limited to 2 minutes, 4 times per hour, for a shower or tap with a flow rate of 2 gallons/minute, the flow rate can be calculated as follows:
2 gallons/minute x 8 minutes/hour = 16 gallons/hour = 0.27 gallons/minute
Single function area and no separately tenanted areas – operational energy monitoring - KBCN00056
Where an asset has:
AND
- no significant energy uses that must be separately metered
AND
- no separately tenanted areas for sub-metering
Provided that the sub-metering by end-use credit is achieved, the sub-metering of ‘high energy load and tenanted areas’ credit can be awarded by default.
12-Aug-2025 - Title and wording clarified.
26-Mar-2024 - Wording clarified. Scheme applicability updated.
Solid concrete washout - KBCN00063
Solid concrete washout waste should be included in the waste resource efficiency benchmarks.
Space heating as major energy use - KBCN0939
Where possible, space heating should always be considered as a major energy use for sub-metering purposes.
Where space heating cannot be separated from hot water, this must be fully justified by the design team at QA.
See KBCN0329: Combined system for space heating/cooling and domestic hot water.
Where electric space heating is used, this in itself cannot be used as justification for combining the space heating along with lighting and small power unless there is a clear justification for doing so.
See KBCN0068: Combined sub-metering of electric heating and small power equipment.
Specialist assisted baths in care homes - KBCN0228
Specialist assisted baths in care homes or similar specialist applications can be excluded from the assessment of this issue.
Due to the specific access and care needs of users, it may not be possible to reduce the volume of specialist assisted baths.
Speculative floor finishes – Take-back and re-use policy - KBCN1702
Where a developer has an established written policy whereby unwanted floor finishes will be removed for re-use elsewhere prior to the tenant taking possession, this can be considered as meeting the aim of this issue.
This is only applicable to types of flooring which are suitable for re-use, can be easily removed and do not require the use of adhesives or other permanent means of fixing.
Additionally, the tenancy agreement must otherwise prohibit the removal of the flooring by the tenant
Evidence to support this approach would include:
• A copy of the take-back policy
• Details of the flooring type and material
• A copy of the tenancy agreement
Speculative office including floor finishes/suspended ceiling - KBCN0259
The requirements can still be met where a speculative development includes the installation of floor finishes/suspended ceilings provided a Lease Agreement will be implemented to confirm that tenants are not permitted to remove these finishes.
BREEAM recognises that incoming tenants may need to adapt ceiling finishes to suit the requirements of their fit-out. Therefore, where ceiling finishes are installed throughout, in line with Criterion 2, the following applies:
A tenancy agreement, applied to the first tenancy, should stipulate that ceiling finishes may only be modified where necessary, for example, to accommodate new partitions, lighting or other services, to replace worn or damaged components or to replace small, localised areas with a specialist ceiling to account for abnormal conditions, such as wet areas
Documentary evidence of this must be provided as evidence for the credit to be awarded.
18/04/2017 KBCN made applicable to NC 2016 and IRFO 2015
05/07/2018 Paragraph added to clarify the requirements of the tenancy agreement
SSM replacing BREEAM AP for on-site monitoring - KBCN0601
It is acceptable for a suitably qualified Site Sustainability Manager (SSM) to take over the monitoring of site impact role (Sustainability Champion (construction)) from a BREEAM AP.
In some instances it may be more appropriate for an SSM to carry out the role of the 'construction' Sustainability Champion. Therefore where a BREEAM AP has provided design input, an SSM could take over the role to complete the on-site requirements.
Stakeholder consultation – Building occupier unknown - KBCN0227
Where the building occupier is unknown, it is still possible to achieve the credit. The end user requirements must be assumed and considered by other project parties (e.g. client, design team, etc.) using their experience and judgement until such time as the occupier is known.
Stakeholder consultation – Definition of “independent third party” - KBCN0428
The definition of independent third party should be taken to mean that the party i.e. the individual(s) rather than the organisation undertaking the consultation is independent of the design process. BREEAM is not prescriptive about how to evidence this. It is the assessor's responsibility to collect robust evidence which proves this to be the case.
Stakeholder consultation – Existing shared facilities - KBCN0360
The consultation must include any existing shared facilities relied on to achieve compliance as well as the new facilities.
To ensure the shared existing facilities are appropriate and in line with the users' requirements.
Strip-out works - KBCN0578
Waste generated by strip-out works should be excluded from the Resource Efficiency credits, because the project cannot control the amount of waste that will be produced from strip-out works.
Sub-metering at least 90% of each fuel - KBCN0657
In a scenario whereby several energy consuming systems are not sub-metered because they account for less than 10% of the annual energy consumption (see Ene 02 methodology), and this results in less than 90% of the estimated annual energy consumption of that fuel being metered, the M&E consultant should review the metering strategy and advise which of these energy consuming systems would most benefit from sub-metering to make up the 90%.
This may be based on which of the energy consuming systems has the highest annual energy consumption, or which has the most potential for reducing energy consumption as a result of sub-metering. This will not necessarily have to mean that the energy consuming systems chosen have to have their own sub-meter, the M&E consultant may decide they would most benefit from metering alongside another consuming system. However ultimately 90% of each fuel must be metered.
Justification should be given within the metering strategy and the BREEAM assessment report as to which lower energy consuming systems were chosen to be sub-metered to make up the 90%, and how this was done to best suit the development (i.e. individual sub-meters or paired with another consuming system).
Sub-metering by calculation - KBCN0700
For simple sub-metering strategies, it is acceptable to calculate a single end-use by subtraction of known, sub-metered end-uses from the relevant main utility meter reading. For more complex strategies, where a BMS/BEMS is used, the software should be capable of calculating and displaying all required end-uses in line with the criteria.
Sub-metering of high energy load and tenancy areas – existing building systems - KBCN1341
Where a refurbishment assessment contains existing systems which are impractical to retro-fit in accordance with the sub-metering criteria, a practical alternative metering strategy may be acceptable (see also KBCN00071). Where existing systems cannot be retro-fitted, however, the credit is not awarded by default; this does not meet the intent of the guidance for additional metering beyond a whole building approach.
In all cases, suitable evidence should be provided to QA that demonstrates the inability to fully comply with the criteria, and that all practical means have been taken towards fulfilling the intent of the credit.
In refurbishment projects it is not always practical to undertake significant retro-fits to existing building systems. Where such changes require disproportionate effort in relation to the scale and complexity of the project, BREEAM will accept more practical solutions that still meet the intent of the credit.
Sub-metering technologies – Compliance principle - KBCN1561
Where it can be demonstrated that alternative sub-metering technologies can meet or exceed the capabilities of systems set out in the BREEAM guidance, subject to approval, these can also be considered compliant.
It is the role of the Assessor and the project team to provide evidence and justification in a compliance principle query (see
KBCN1555).
The following metering standards or technologies are currently recognized as alternatives to pulsed output meters:
- M-bus.
I.e. systems that comply with the EN 13757 series of standards.
Also includes systems complying with the OMS (Open Metering System) standards.
Submitting aftercare & post occupancy evaluation data - KBCN0589
Where credits have been awarded which require post-occupancy evaluation or an element of aftercare data collection (according to scheme requirements) from the building once operational and occupied, the data gathering must take place at the specified time and the findings reported to BRE.
The timing of this evidence gathering depends on the criteria of the BREEAM scheme having been undertaken. However, for all schemes, once the evidence is due for submission, it should be sent to BREEAM@bre.co.uk with the following title;
'
BREEAM Assessment Type Building Data
BREEAM Assessment Reference'
For example, a BREEAM 2011 New Construction assessment would use the following title when submitting their evidence;
'BREEAM NC 2011 Building Data BREEAM-1234-5678'
This KBCN replaces KBCN0695 for HQM.
Suitability of waste storage facilities - KBCN0186
In situations where direct vehicular access to the recyclable waste store is limited by logistics or if size is a problem, for example inner city locations, some flexibility to the application of the criteria is allowed.
The assessor can use their judgement on whether the storage space is appropriately sized and if the distance and changes in level via lifts or steps are acceptable. Convenience, H&S issues and the volume and type of waste likely to be generated must be considered. Where the assessor deems the arrangement to be satisfactory this would be acceptable.
Typically, ‘accessible’ is defined as being within 66ft of a building entrance. In some circumstances site restrictions or tenancy arrangements could mean it is not possible for the facilities to be within 66ft of a building entrance. If, in the opinion of the BREEAM assessor it is not feasible for the facilities to be within 66ft of a building entrance, their judgement can be used to determine if the facility is deemed to be ‘accessible’ to the building occupants and for vehicle collection.
Sustainability Champion role – Construction - KBCN0446
The intent of the Sustainability Champion role is to monitor and report on the project’s progress towards the relevant BREEAM target(s), over the course of the stated RIBA stages, in order to minimise the risks of possible non-compliance with the agreed BREEAM targets. To do this the Sustainability Champion should:
- Ideally be site-based, or visit the site regularly and be authorised to carry out inspection and monitoring of the works relevant to their role
- Monitor site activities with an appropriate level of frequency
- Report regularly to the principal contractor and attend relevant project team meetings, identifying potential areas of non-compliance and recommending actions to mitigate these.
Swimming pools - KBCN0812
Water use dedicated to swimming pools is considered an unregulated water use and should be included in the assessment of this issue.
Temporary Car Parking - KBCN0751
The number of car parking spaces should be based on the permanent parking spaces provided specifically for the development once fully operational.
Assessors should determine whether parking spaces should be considered 'permanent' or 'temporary', based on evidence provided by the design team.
Temporary ecological enhancements prior to development - KBCN00065
Where a site has been acquired but development is not scheduled to start immediately, it is possible to determine the baseline ecological value of the site at this point. Furthermore, to recognise where positive measures to enhance ecology have been taken to manage the site until development starts, these enhancement measures will not impact on the baseline value for the purposes of the BREEAM assessment, provided that the following have been met:
- Following acquisition of the site and prior to any site clearance which involves the removal of any relevant features, the ecological value of a site is recorded in accordance with the relevant BREEAM methodology by a suitably qualified ecologist (SQE) to establish the baseline.
- The SQE confirms and records details of the temporary ecological enhancement and management strategy being implemented on the site for the period prior to scheduled development.
- For a period of up to 10 years, the initial baseline determined for the site is valid for the purposes of BREEAM assessment.
- Any enhancements prior to scheduled development that are not being carried forward into the design, construction and operational phases can be disregarded for the purposes of establishing the baseline ecological value at development.
- The assessment report shall provide documentary evidence of the above for certification.
- Any enhancement and management practices implemented prior to scheduled development that will be maintained and continued through the design, construction and into the operational phase can contribute toward the awarding of credits via the BREEAM calculator tools.
Clarification: This guidance is currently under development. Please contact BRE Global with specific project details for confirmation of whether this approach may be used.
The aim of these issues is to demonstrate the impact that a project has had on the site ecology, but comparing the site pre and post development. BREEAM does not want to penalise sites that have put in temporary ecological enhancements that enhance the ecology while waiting for development to begin.
Temporary irrigation systems - KBCN0147
Temporary watering arrangements set up purely to allow plant species or a green roof to establish are acceptable for plants relying on natural precipitation during all seasons of the year. Where this is the case, the ecologist's report must confirm the plant species and the expected time for recommended plant species to establish themselves i.e. time period for temporary watering arrangements.
Temporary power solutions in noise impact assessments - KBCN0171
Plants such as standby generators that are only used temporarily are excluded from the noise impact assessment.
Testing and inspecting building fabric – Scope - KBCN1666
The criteria generally apply to 'Projects where the fabric of the building is being upgraded,...'
Where a project is only upgrading some areas of the building fabric, the criteria only apply to the upgraded areas.
Testing and inspecting building fabric – Untreated spaces - KBCN0972
Untreated spaces, which are not subject to compliance with statutory energy performance regulations, can be excluded from the scope of the 'Testing and inspecting building fabric/thermographic survey/air pressure testing' criteria.
Testing and inspecting the building fabric credit - KBCN0649
The requirements for this credit are to ensure continuity of insulation, avoidance of thermal bridging and air leakage paths. How this is achieved is up to the judgement of the suitably qualified professional.
The criteria are intended to afford the design team the opportunity to demonstrate that the above are met by whatever means are appropriate, which will generally be air-tightness testing and a thermographic survey.
Should the suitably qualified professional advise alternative means, the assessor must be satisfied and be able to demonstrate that all the above requirements have been met.
BREEAM seeks to be outcome-driven and does not, therefore, prescribe the specific testing methods to achieve the criteria in this Issue.
The importance of EPDs - KBCN0895
The publishing of a third party verified EPD by a manufacturer indicates a transparent, robust and credible step in the pursuit and achievement of real sustainability in practice. While an EPD in itself is not proof that a product is sustainable, it is a public declaration of the environmental impacts associated with specified life cycle stages of that product. A manufacturer or group of manufacturers, who carry out life cycle assessment (LCA) studies on their product(s) and publish the results in verified EPDs, help to create a knowledge base and an awareness of the environmental impacts quantified using standardised metrics. This allows benchmarking and the identification of improvement opportunities for the product’s environmental credentials. By implication, there are also opportunities for economic and social benefits to the manufacturer, such as the reduction in resource wastage through improvements in product design and manufacturing efficiency.
The reward for EPDs in BREEAM schemes promotes the above, while encouraging designers, procurers and other stakeholders to make decisions on the basis of robust and credible environmental data. This is one of the markers of BRE’s strategic approach to the selection and procurement of construction materials and products.
We recognise that there may be steep costs at the moment to small manufacturers wishing to publish verified EPDs for their products. This is a result of the maturity of the market and it is anticipated that as the awareness of the benefits of EPD increases, the increased uptake of EPDs will drive costs down.
Thermal comfort – Changing rooms - KBCN1133
Whilst thermal comfort in changing rooms may be considered as significant, such spaces are, generally, outside the scope of this Issue, as they would not fall within the definition of an 'occupied space'.
17/06/2019 - This supersedes the advice previously provided in this KBCN, which was published in error on 13/06/2018
Thermal modelling – full dynamic thermal analysis - KBCN1250
The software used to carry out the thermal modelling simulation at the detailed design stage needs to provide full dynamic analysis. For smaller and more basic building designs with less complex heating/cooling systems, an alternative less complex means of analysis may be appropriate. Further guidance on thermal modelling can be found in CIBSE AM11 Building energy and environmental modelling.
Thermal modelling for large scale projects - KBCN1171
In cases where the scale of the project makes it unfeasible to provide thermal modelling for every space, it is acceptable to demonstrate compliance with a representative sample of floors or rooms, ensuring any worst case scenarios are included.
Thermal modelling for Part 1 assessments - KBCN0944
Where a Shell Only (Part 1) assessment is being carried out, but the future servicing strategy is unknown, the thermal comfort credit is still applicable.
To assess compliance, the upgraded shell of the building shall be modelled with a typical servicing configuration which meets as a minimum:
- UK: Recommended minimum standards in the Non-Domestic Building Services Compliance Guide.
- International: relevant building services minimum standards within local building regulations, or Tables 6.8.1 A-K of ASHRAE Standard 90.1.
The thermal modelling credit can be awarded when the notional modelled system achieves the BREEAM thermal comfort criteria.
The intent is to ensure that thermal comfort is achievable with the proposed upgraded shell for any future occupiers. The details of the notional system could be passed on to future occupiers or servicing specialists to inform their servicing strategy.
Thermographic survey – Seasonal constraints - KBCN00031
Where seasonal constraints prevent the thermographic survey from being completed prior to certification at the post construction stage, the requirements can be satisfied with:
- Evidence that a Suitably Qualified Professional (SQP) has been contractually appointed
- Written confirmation by the SQP that the seasonal constraints prevent the survey at an appropriate time before certification
- The survey is scheduled to take place at the earliest opportunity after the handover, and
- There is a specific contractual agreement in place to remedy any identified defects before the defects liability period expires.
Thermographic surveys are designed to map the thermal efficiency of buildings and to detect areas where there are breaches in the thermal envelope. Surveys need to be conducted when temperature differences between the external areas of the building and surrounding air can be detected after the envelope is sealed. There may will be instances where the survey cannot be done before certification after the envelope is sealed and as such, the survey would take place after certification.
Thermographic survey – Standards for qualification of personnel - KBCN0689
Assessors can accept reports from thermographers who hold a suitable Infrared Thermographic Testing (TT) qualification under one of the following standards, depending on which one was current at the time of the thermographer's qualification:
- ISO 18436-7:2008
- ISO 9712:2012
- ISO 18436-7:2014
- ISO 6781-3:2015
13-Mar-2017 - Compliance note amended to allow the applicability of standards based on the time of the thermographer's qualification, rather than the BREEAM scheme version.
03-Nov-2021 - Above text added to issue 2.0 of the UK RFO 2014 technical manual. The text is still relevant to previous issues of the manual.
07-Mar-2023 - Updated title to clarify that this KBCN relates to standards for the qualification of personnel.
Thermographic survey for large and complex buildings - KBCN0405
In the case of large and complex buildings, it may be impractical for the thermographic survey and air-tightness testing to cover 100% of the building. The level of the survey should be decided by a Level 2 qualified thermographic surveyor. This could include, for example, airports, large hospitals and high-rise buildings.
Thermographic survey impractical - KBCN0150
In the case of large and complex buildings, it may be impractical for the thermographic survey and airtightness testing to cover 100% of the building. Where a complete thermographic survey is deemed impractical by a Level 2 qualified thermographic surveyor, the guidance in airtightness standard TSL2 (or relevant local standard) should be followed on the extent of the survey and testing. This could include, for example, airports, large hospitals, high-rise buildings.
Time critical requirements – Concept / Technical Design stages - KBCN1711
The intent of the criteria relating to project stages in BREEAM is to ensure that actions are taken at a time when they can have the intended influence.
Where projects are following these defined stages via a traditional procurement route, referring to the project programme and work stages are a robust and convenient way to demonstrate that the intent is met.
However, not all projects will follow these work stages. In such cases, the project can show that the intent is met by demonstrating that, for the relevant BREEAM requirement, the activity has happened when the project is at an appropriate stage of development.
Concept Design
The project stage at which fundamental aspects of the design are developed.
- What has happened already: the architectural concept is established.
- What is in progress: the design is undergoing spatial coordination and design development for detailed planning approval.
- Detailed planning approval is an approval that covers all major aspects of the asset's external appearance and form. Typically this means the detailed massing, external materials, and site layout are confirmed.
- Achieving outline planning permission does not mean that the project has left Concept Design. An outline approval is an approval for architectural concept but with many of the above details still missing, and yet to be developed.
Technical Design
Once a detailed planning application has been submitted, many aspects of the design will be fixed, and the project is at Technical Design stage.
- What has happened already: full planning approval has been granted.
- What is in progress: detailed spatial coordination and developed design information is being used to develop the information needed to construct the asset.
Depending on the procurement route, there may be an overlap between technical design and the construction phase of the works.
Additional guidance
Sometimes different aspects of the design might be at different project stages.
KBCN1156 gives detailed guidance on how to define the project stage for each construction element, based on the design information available for that element. Although it was originally written specifically to address Mat 01 LCA for UK NC 2018 and V6, it may be useful in other situations.
Time critical requirements – defining project stage by construction element - KBCN1156
This KBCN was originally written to specifically clarify BREEAM requirements for Mat 01 Concept / Technical Design LCA under UK NC 2018 and V6. However, the general principles may also be applicable to other assessment issues and schemes.
As a building design process passes through successive work stages, increasingly more aspects of the design become fixed. BREEAM criteria often require actions at, before or after specific project work stages, as these are the optimal stages to achieve the required sustainability outcome. When undertaken at a different stage, the criteria may be difficult to comply with, opportunities may be missed, options limited or costs may become prohibitive.
Knowing which stage your project is at
Where possible, BREEAM refers to industry-standard work stages, for example the RIBA plan of work stages. However different project teams can interpret these referenced stages differently.
Furthermore, many projects do not follow these stages in a simple linear fashion for all aspects of the design at the same time. For instance, the envelope design may be well advanced even to the point where installation has commenced before any specification decisions have been made on some interior finishes. As such, a project may not be at one project stage for all elements of the design at any one point in time.
This Knowledge Base compliance note is intended to provide supplementary information to enable projects to determine what stage they are at with respect to time critical BREEAM requirements, including where different elements are at different stages. Although project team members may be willing to offer their opinion on the stage the project has reached, this will often be subjective and hence inconsistent. Therefore, the process set out here looks at the currently available design information for the project (e.g. drawings, specifications) to determine the current work stage in relation to the issue under consideration. This provides a more objective, demonstrable approach for the assessor to follow.
Concept Design Stage
The RIBA definition of ‘Concept Design’ (RIBA stage 2) can be found here
https://www.ribaplanofwork.com/PlanOfWork.aspx . The core objective given is
‘Prepare Concept Design, including outline proposals for structural design, building services systems, outline specifications and preliminary Cost Information along with relevant Project Strategies in accordance with Design Programme. Agree alterations to brief and issue Final Project Brief.’
Table 1 and table 2 (in the link below) provide further guidance, specific to BREEAM, to help determine whether a project, or part of the project relevant to the issue/credit, is at ‘Concept Design’ stage. If there is ambiguity or uncertainty about the stage of the project, the assessor should check with the design team whether the design documentation (drawings, specifications, BIM etc.)
currently being produced by the design team will generally include the information listed.
It is possible for different aspects of the project to be at different stages in terms of how progressed the design is. For example, the substructure design may be at technical design or even installed while the internal partitions are still at concept design. Whether this matters depends on the issue/credit being pursued. The following steps take this into account.
Step 1
First, for the issue/credit being pursued, determine which of the relevant assessment scope items in table 1 and 2 are relevant. For example, if the issue/credit only relates to substructure, then only the substructure assessment scope items shall be considered. If the issue/credit is of a general nature concerning the whole project, then all the assessment scope items shall be considered.
Step 2
For the relevant assessment scope items from step 1, decide which of the following applies the most: -
- Where the items listed are in the process of being included in the design documentation, this indicates that the project, or part of the project being considered, is likely to be at the ‘Concept Design’ stage.
- If items listed are not in the process of being included, the project, or part of the project being considered, is likely to be at an earlier stage.
- If the existing design documentation already includes the items listed the project, or part of the project being considered, is likely to be at a later stage.
Please note that the items listed are indicative of the typical information produced at ‘Concept Design’ stage.
Technical Design Stage
The RIBA definition of ‘Technical Design’ (RIBA stage 4) can be found here https://www.ribaplanofwork.com/PlanOfWork.aspx . The core objective provided is ‘
Prepare Technical Design in accordance with Design Responsibility Matrix and Project Strategies to include all architectural, structural and building services information, specialist subcontractor design and specifications, in accordance with Design Programme.’
The following provides further guidance, specific to BREEAM, to determine whether a project is at the ‘Technical Design’ stage: The RIBA plan of work definition of ‘Technical Design’ clearly states that it should ‘
…include all architectural, structural and building services information, specialist subcontractor design and specifications…’. Therefore, it is a simpler task to determine whether the project, or part of the project relevant to the issue/credit, is at this stage. If there is ambiguity or uncertainty about the stage of the project, the assessor should check with the design team whether the design documentation (drawings, specifications, BIM etc.) currently under production by the design team (and the contractor’s specialist sub-contractors, if applicable) will, when finished, generally include all the final design information required for the construction works on-site.
Like concept design, it is possible for different aspects of the project to be at different stages in terms of how progressed the design is. The following steps take this into account.
Step 1
First, for the issue/credit being pursued, determine which of the relevant assessment scope items are relevant (the assessment scope items given in table 1 and 2 may be used, but the rest of the information in these tables relates to concept design).
Step 2
For the relevant assessment scope items from step 1, decide which of the following applies the most: -
- Where all the final design information required for the construction works on-site is in the process of being included in the design documentation, this indicates that the project, or part of the project being considered, is likely to be at the ‘Technical Design’ stage.
- If it is not in the process of being included, the project, or part of the project being considered, is likely to be at an earlier stage.
- If the existing design documentation already includes all the final design information required for the construction works on-site the project, or part of the project being considered, is likely to be at a later stage.
KBCN1156_IndicatorTables
06-Nov-2024 - Scheme applicability updated. Title amended. Explanatory note added.
17-Jun-2019 - KBCN updated to provide additional guidance
Timing of Ecological survey/report - KBCN0292
If the ecologist's site survey and/or report is completed at a later stage than required, the assessor would need to be satisfied that it was produced early enough for the recommendations to influence the Concept Design/design brief stage and leads to a positive outcome in terms of protection and enhancement of site ecology.
21/02/2017 Wording clarified.
Tools: Tracker+ - KBCN0760
Please note that Tracker+ is not a BRE-owned or managed reporting tool. For issues concerning Tracker + please contact the provider (Southfacing) as the BRE cannot advise on technical issues relating to Tracker+.
Tools: Use of reissued tools - KBCN0384
The most up-to-date version of an excel tool should be downloaded from the BREEAM Assessor's Extranet when a new assessment is started. If an updated tool is subsequently released then it will not be necessary to use the updated tool instead of the version already being used. The assessor can choose to use the updated tool if they wish.
When new tool versions are released, assessors are notified through the monthly Process Note. We would expect Assessors to review the 'Schedule of Changes' tab when an updated tool is released. If fundamental changes have been made to the tool and they will affect the results for the issue in question please contact BRE for guidance.
Tools: Weightings discrepancy on BREEAM Projects - KBCN0725
Completing the 'initial details' section of the BREEAM RFO pre-assessment or full assessment tool ensures that the appropriate issues and credits are filtered in or out of the assessment, depending on the project scope. This means that the weightings are also adjusted accordingly, so that the building environmental sections weightings' total always remains at 100%.
The BREEAM RFO weightings given in the relevant Table of the 'Environmental section weightings' section of the guidance, are for common projects types, purely as a starting guide and can be expected to vary significantly for real projects, depending on the applicability of issues and credits.
Technical manual to be updated accordingly in next reissue.
Total area of ground floor - KBCN00087
When determining the 'total area of ground floor (m2)', the Gross Floor Area (GFA) should be used, which includes the thickness of the external walls.
This is to align with Construction industry understanding.
Towel rails - KBCN00081
Towel rails cannot count towards the drying line requirements.
Clothes drying lines are provided to reduce the need to tumble drying clothes, which uses a lot of energy. Using towel rails to dry clothes would require the potentially damp towels to be stored while the clothes dry. This is inconvenient and therefore means the aim of the credit is less likely to be met.
Tram services - KBCN000004
Tram services are classified as train services when assessing transport accessibility.
Translation of standards for approval - KBCN0435
BRE Global can translate standards for the Approved Standards and Weightings List submission.
Please contact BRE Global in advance of submitting the Approved Standards and Weightings List, so that a proposal to cover the translation work can be arranged.
Transport of construction materials – Data and methodology - KBCN0413
To ensure comparability across assessments, the information completed in the scoring and reporting tool should be restricted to the minimum data specified in the technical manual.
For the purposes of this BREEAM Issue, the distances reported should be calculated from the point from which the products or materials were sourced, whether this be directly from a manufacturer or from a builders' merchant/distributor:
- For products or materials purchased directly from a manufacturer or quarry, for example, the distance should be calculated from the ‘factory gate’, including any intermediate transport.
- For products or materials, which are purchased from a merchant or distributor, only the distance from their depot should be reported.
Where products cannot be sourced locally, for example on small islands, the transport required to import the materials or products can be discounted, and only the local onward transport to the site recorded.
The aim of this requirement is to encourage developers to consider the impacts of transporting products and materials to site. As such, the criteria seek to address only those impacts, which can be influenced by the developer.
27.07.2018 Wording amended to add clarity.
Transportation analysis carried out by the lift manufacturer - KBCN0232
BREEAM recognises that lift manufacturers / suppliers are often engaged to provide such specialist advice. Where the assessor is satisfied that the analysis has been carried out correctly, the analysis can be submitted as compliant evidence.
Travel Plan – Confirmation of timing requirement - KBCN1665
The criteria require that 'a travel plan has been developed as part of the feasibility and design stages'.
To clarify:
Ideally, this will be completed and shared with the project team before the end of Concept Design Stage, so that sustainable transport options can be considered in the built form of the development.
However, in all cases, it must be demonstrated that the Travel Plan was undertaken at an appropriate stage in the design development to influence decisions on implementing sustainable transport measures.
Urinals – calculation of litres/bowl/hour - KBCN1010
A flushing frequency of two flushes per hour is used in the Wat 01 tool and should be applied when calculating the volume of water dispensed by urinals and compared against the water efficient consumption levels by component type for the Wat 01 issue. This method should be applied to calculate litres/bowl/hour.
For example, a 13.5 L cistern feeding 3 bowls which is flushed 2 times per hour: (13.5 L / 3 bowls) x 2 times an hour = 9 litres/bowl/h.
User controls – Thermal comfort - KBCN1813
The requirement for user controls does not mandate a specific type of control; e.g. local manual adjustment.
Where control is provided indirectly, e.g. via BMS or central management, the assessor must demonstrate that this approach meets the intent of the user comfort and accessibility criteria and is informed by end-user discussions or relevant design guidance.
Please refer to
KBCN0170 for clarification of the types of space requiring user controls.
Using BRE SMARTWaste tool - KBCN0236
BRE SMARTWaste may be helpful in demonstrating the construction waste benchmarks; however its use is not compulsory to achieve the credits.
Reference to the SMARTWaste tool has been included in the issue as an example of a tool that can be used to manage and monitor waste generated during construction.
Using water from natural underground sources to offset water consumption - KBCN00094
Water from natural underground sources (for instance aquifer water accessed via boreholes) cannot be used to offset:
- NC / RFO: potable water consumption.
- IU: utility supplied water consumption.
A significant amount of water used for public consumption is already drawn from aquifers. Private boreholes may be drawing water from the same sources as public utility companies.
27-Mar-2024 - Title and text updated to broaden definition. Scheme applicability updated.
Ventilation – applicability to Part 1 assessments - KBCN0974
The Ventilation credit is applicable to Part 1 assessments because there may be instances where the decisions made for the fabric and structure can have an impact on the ventilation strategy.
For example, if a natural ventilation strategy is to be used, the criteria related to ventilation standards and the distance between openable windows and sources of external pollution would be relevant.
11-Oct-2022 Title amended for clarity and consistency.
Ventilation – distance between air intakes and exhausts - KBCN0638
The minimum distance required between the building's air intakes and exhausts is described by
r.
- Where the exhaust is below (A), or at the same level (B) as the intake, r is a horizontal distance.
- Where the exhaust is above the intake (C), r is a 3-dimensional distance.
- r will vary depending on the scheme and criteria being assessed, and whether the exhaust is part of the assessed building or an external source of pollution.
Where the distance does not meet
r, the design team must either:
- Design in accordance with the relevant standard listed in the manual, which allows distances smaller than r in certain circumstances or,
- Use modelling to demonstrate no intake of exhaust air.
16-Aug-2024 - Applicability to INC 2016 and INC V6 removed as the guidance does not align with the criteria.
12-Jan-2023 - Value r clarified to account for different requirements in applicable schemes.
18-Nov-2022 - Requirements clarified. Title amended for clarity.
11-Oct-2022 - Scheme applicability updated. Wording clarified. Reference to EN13779 removed for international assessments, see KBCN1054.
Ventilation – E-cigarettes - KBCN1014
The use of e-cigarettes and vaporizers is considered equivalent to smoking.
A smoking ban must also include a ban on e-cigarettes and vaporizers.
11-Oct-2022 - Scheme applicability updated.
Ventilation – external requirement for window opening restrictors - KBCN1032
Opening restrictors to windows may sometimes need to be installed to meet:
- Health and safety requirements,
- Building regulations or,
- Legal obligations.
Where such external requirements are in force, these requirements cannot be used as a mitigating factor for meeting the BREEAM ventilation criteria.
Even with window restrictors, adequate ventilation can still be achieved.
Ventilation – filtration – non-residential assets - KBCN0797
Relevant specialist required
The design and specification of air filtration for mechanical ventilation requires the input and review of a relevant ventilation designer or specialist. It is their responsibility to interpret the requirements of this KBCN to align with local conditions.
Referenced standard
The requirements for air filtration in mechanical ventilation systems follows EN 16798-3:2017 Section B4.2. This standard replaces EN 13779:2007. See
KBCN1054.
Supply air quality
- For assessments using current standard EN 16798-3:2017 Section B4.2: The minimum supply air quality required is SUP2.
SUP 2 applies unless the asset’s function dictates even higher supply air quality. Please refer to a relevant specialist for further advice.
- For assessments using legacy standard EN 13779:2007 Annex A3: The default minimum indoor air quality category required is IDA2.
For international assessments where there is no relevant local guidance in the ASWL, the default non-domestic ventilation rates stated in the ASWL equate to an EN 13779 indoor air category of IDA2.
Outdoor air quality
The filtering required to achieve SUP2 is affected by outdoor air quality. Outdoor air quality (ODA) in both EN 16798-3:2017 and EN 13779:2007 are defined as:
- ODA 1: outdoor air that meets World Health Organisation (WHO) guidelines or national air quality standards.
- ODA 2 exceeds ODA 1 levels by factor of ≤1.5.
- ODA 3 exceeds ODA 1 levels by factor > 1.5.
As ODA definitions are relative to national air quality standards, these will depend on local regulations and the location of the asset. Please refer to the relevant specialist on how to correctly classify ODA for your asset.
18-Nov-2022 Title amended to differentiate between residential and non-residential filtration KBCNs.
06-Sep-2022 KBCN re-written and re-named to clarify BREEAM ventilation filtration requirements in relation to new ventilation standards.
Ventilation – single room MVHRs - KBCN1042
Single room mechanical ventilation heat recovery units do not need to show that the air intake and exhaust are a suitable distance apart.
However, the air intakes of these units must be located to minimise intake of other potential external pollutants.
11-Oct-2022 - Title amended for clarity and consistency. Wording simplified. Scheme applicability updated.
Ventilation – withdrawal of EN 13779:2007 - KBCN1054
Standard EN 13779:2007 has been withdrawn (01/02/2018) and in its place the following should be used:
- To replace EN 13779:2007 Annex A2 for location of the building's air intakes and exhausts - CEN/TR 16798-4:2017 Sections 8.8.1 to 8.8.4
- To replace EN 13779:2007 Annex A3 for filtration in HVAC systems - EN 16798-3:2017 Section B.4.2
- To replace EN 13779:2007 for providing fresh air into the building - ISO 17772-1:2017 Annex I or EN 16798-1:2019 Annex B.3 (using either Category I or Category II default design values)
Non-residential buildings: Both standards provide three methods for selecting design ventilation rates:
- Method 1: Method based on perceived air quality
- Method 2: Method using limit values of substance concentration
- Method 3: Method based on predefined ventilation flow rates
Dwellings (only applicable to the BREEAM International New Construction scheme): Both standards provide different options for selecting design ventilation rates:
- Total air change rate for the dwelling
- Extract air flows for specific rooms
- Supply air flows for specific rooms
- Design opening areas for natural ventilation
It is the design team’s responsibility to determine and apply the most appropriate method or option(s) for the project undergoing assessment.
Existing projects can continue to use EN 13779:2007 where applicable. Any new assessment registrations should use the replacements above.
11-Oct-2022 - Scheme applicability updated.
03-May-2020 - Typo corrected to clarify that 'EN 16798-1:2019 Annex B.3 'either Category I OR Category II default design values' are to be used.
10-Jan-2020 - KBCN updated to clarify methods for complying with new standards.
01-Sep-2019 - KBCN updated to reference new standard.
View out – alternative method of compliance for fixed workstations - KBCN1484
In relevant spaces that include fixed workstations* (such as a built-in cash registers or reception desks) an alternative method can be used. This is based on the number of compliant workstations.
For instance, where the requirement is for 95% of the relevant area to comply, 95% of the fixed workstations must have a compliant view out, rounded up to the nearest workstation.
Example
A retail assessment has 35 built-in cash registers, 95% of which must comply with the view out criteria.
35 x 0.95 = 33.25, rounded up to 34.
The requirement is met for this area if 34 registers comply with the criteria.
Where an asset includes a mix of relevant areas; both fixed workstations and flexible areas, compliance for the whole assessment must be demonstrated for all areas as appropriate, based on either area or number.
*freestanding desks and other items of moveable furniture cannot be considered as fixed workstations, regardless of whether their locations are pre-determined.
View out – Bedrooms in Residential and Residential institutions - KBCN1798
The 'View out' criteria are generally not applicable to bedrooms in assessments of Residential and Residential institutions (long-term stay and short-term stay), where the occupants are likely to be elsewhere during the daylight hours. Although a multi-purpose desk or work surface may often be provided in bedrooms for short-term working, study and other uses, this would not normally be considered as a dedicated workspace.
An exception to this would be where a separate dedicated office or study space is provided, for example within a bedroom suite. Please also refer to any building-type-specific guidance, as bedrooms in sheltered housing, for example, may be considered differently.
It is the role of the assessor to determine whether individual spaces should be determined as ‘relevant building areas’ in accordance with guidance provided.
View out – Calculating the glazing to wall ratio - KBCN1506
This should be calculated based on the glazed area of window, expressed as a percentage of the area of the external wall in which the window sits.
Where the ceiling height of the room is unusually high, relative to the window height, the wall area can be calculated based on a standard ceiling height for the building type.
View out – communal lounges, living rooms and bedrooms - KBCN1828
The default criteria for these space types requires relevant positions to be within 5m of an opening.
Where larger spaces are ≥ 50m2 NIA, the standard view out criteria for the relevant scheme is applied instead.
The 5m rule is intended for small scale domestic spaces where proximity to a view out is beneficial. This KBCN recognises that for larger relevant spaces in Residential, Multi-Residential and Residential Institution asset types, a scalable approach in line with commercial buildings is more appropriate.
View out – Corrections to Table - KBCN1136
The values for distance from window to workplace in the View out Table are incorrect. The Table should read as follows:
07-Oct-2025 - Applicability to INC V6 confirmed
View out – eye level - KBCN0581
BREEAM defines an adequate view out as being at seated eye level (1.2 – 1.3m) within the relevant building areas. However, where occupants will not have the option to be seated, for example in some industrial operational areas where the work being undertaken requires occupants to remain standing, the height of the view out can be changed accordingly to suit the eye level of occupants. All other view out requirements have to be met and clear justification provided for changing the height/level of the view out.
In some relevant building areas, occupants may not be sitting down to undertake tasks. Allowing the view out height requirements to be changed accordingly ensures building occupants gain maximum benefit from the view out.
View Out – First Aid Rooms - KBCN1104
The view out criteria do not apply to dedicated first aid or medical rooms in non-healthcare projects.
BREEAM recognises the need for user privacy in such areas and that these are intermittently occupied.
View out – internal view within an atrium - KBCN1240
Please refer to the guidance on this aspect in the relevant Definition or Compliance Note in the technical manual.
04-Mar 2026 - Content removed as it duplicates the guidance in the technical manual.
View out – no relevant areas - KBCN0876
If the scope of the assessment does not include any relevant building areas, as defined within the manual, the criteria for 'view out' can be considered as met by default.
Only spaces that fall within the definition of relevant areas and are within the assessment's scope need to be assessed.
View out – percentage area - KBCN0166
For the view out credit, compliance must be demonstrated for the percentage of the floor area in each relevant building area, rather than the percentage of the total relevant building area in the building.
09-Oct-2025 - Applicability to INC V6 standard confirmed.
14-Feb-2017 Wording amended to clarify that the percentage must be achieved for each 'relevant building area'.
View out – relevant areas - KBCN0268
The aim of the View Out criteria is to allow occupants to refocus their eyes from close work.
Relevant areas are spaces where close work in a fixed position is carried out for sustained periods of time.
The view out criteria are therefore not applicable to occupied areas such as meeting rooms, or other spaces where such close work is not being carried out.
Where rooms contain areas of different functions, only relevant areas should be assessed. In this case a notional line can be drawn on the plans and calculations made based on these relevant areas only.
However, spaces such circulation routes or other transient spaces within a relevant area can only be excluded if the route or area is clearly defined by the building layout. If this is arbitrary or based solely on a proposed furniture layout, it cannot be excluded. Features of the building layout which may be considered as dictating a function area would include, for example, the position of doors or fixed furniture such as a reception desk or canteen servery.
07-Oct-2022 Additional paragraph added to clarify how function areas must be defined.
21-Sep-2022 General principle of 'relevant area' added, and applicability of KBCN extended to BIU V6 Commercial.
View out – rooms used for security or other critical functions - KBCN1040
The View out criteria are not applicable to rooms containing security or critical systems or sensitive material, such as CCTV monitoring rooms.
Where it can be demonstrated that the presence of compliant windows would compromise a critical function of the space, the criteria can be considered not applicable.
19-Feb-2025 - Scheme applicability updated.
06-Mar-2018 - Published.
View out for commercial kitchens - KBCN1216
It is not necessary to provide a view out for commercial kitchens. This is because in such a space it is likely that kitchen staff will move around, doing various tasks. This makes the requirements for the view out to rest the eyes unnecessary.
Visitor car parking spaces for Other Buildings (Transport type 2) - KBCN0242
For developments such as hotels and visitor centres, which have a relatively small number of staff and large visitor numbers, the guest/visitor car parking spaces do not need to be assessed for this Issue where these are separate from the staff parking spaces. However, if the staff and visitor’s spaces are combined (and not clearly segregated) then all spaces must be accounted for within the calculation for maximum car parking capacity.
The aim of this Issue, 'To encourage the use of alternative means of transport...' is intended to apply to those commuting to the building on a regular basis.
21 06 2017 Wording amended to clarify the type of building and building-user covered by this KBCN.
Washer dryers - KBCN0699
Where a washer dryer is specified, the water consumption figure for the wash and dry cycle should be used.
The drying cycle of a washer dryer is taken into account because it usually uses water during this drying process (e.g. for cooling during the drying cycle) and in some cases, this water usage can be significant.
18-Nov-2022 - Updated to apply to BREEAM In-Use Version 6
Washing machines and dishwashers – Water consumption data - KBCN1571
The water consumption data used to demonstrate compliance may be based on the lowest full wash cycle (i.e. not a pre-wash cycle, for example).
Waste management practices - KBCN0247
16/04/2018 This compliance note is no longer valid as it does not fully explain how to approach this Issue. Please refer to the technical guidance and other compliance notes, such as KBCN0696, which deals with co-mingled recyclable waste.
The requirement to provide a dedicated space for the segregation and storage of operational recyclable waste, as well as relevant facilities (e.g. for large amounts of packaging and/or compostible waste), relates to the building, not the occupier or the local authorities. A dedicated space and facilities must be provided irrespective of the waste management practices of the relevant stakeholders.
The BREEAM certification relates to the building, not the occupier's or the local authorities' waste management practices. Therefore, the provision of a dedicated space and the relevant facilities is required to ensure the building's operational recyclable waste streams is diverted from landfill.
22/02/2017 Amended to include facilities (in addition to dedicated spaces)
Waste storage provision for catering - KBCN0755
As the manual states, the additional 2m2 per 1000 m2 of waste storage area provided for catering is measured against the "net floor area where catering is provided" and NOT the floor area of the catering facility.
Generally, a catering facility will serve building users throughout the building. If it can be demonstrated that this is not the case, for example if part of the development is subject to a separate tenancy, not served by the catering facility, the area calculation can be adjusted accordingly.
Where the net floor area is not indicative of the actual occupancy, the default values may not be appropriate. In such cases, the predicted waste streams should be calculated based on the actual occupancy and waste streams generated.
This requirement accounts for the increase in waste produced by building based on the likely number of building users served by the catering facility. Please note that these default calculations are only intended for use where it is not possible to determine accurately what provision should be made based on predicted waste streams.
15 06 2017 Wording updated to clarify
Wat 04 – Filtering correction - KBCN0999
The question below in the ‘Initial details’ section of the RFO tools has been corrected to allow the filtering of Wat 04 in accordance with the technical manual:
‘Does the building have or mitigate any unregulated water demand? e.g. irrigation or soft-landscaped areas requiring no irrigation, car washing, other significant process related?’
This will be announced in February's Process Note.
Water consumption calculation for push and automatic shut-off taps - KBCN00052
The water consumption of push and automatic shut-off taps can be calculated for input into the Wat 01 calculator using the following steps:
Step 1: Calculate the water consumption per person per use.
If a tap runs for less than 20 seconds per activation, assume it will be activated twice per person for the timed duration. For example, for a tap with a flow rate of 9 litres/min and a 15 second usage duration, the water consumed per person would be: 9 x 15/60 x 2 = 4.5 litres/min.
If a tap runs for 20 seconds or more per activation, assume one activation per person for the timed duration. For example, for a tap with a flow rate of 9 litres/min and a 20 second usage duration, the water consumed per person would be: 9 x 20/60 x 1 = 3 litres/min.
Step 2: Multiply the water consumption figure per person by 1.5 and enter this figure into the calculator tool.
Multiplying by 1.5 adjusts the consumption figure to compensate for the typical non times tap use of 40 seconds that has already been taken into account in the tool. Taking the first example above, if we multiply 4.5 litres/min by 1.5 we get 6.75 litres/min. When this is used in the tool as the flow rate specification, the consumption is 4.57 litres/person/day which more closely reflects the true level of water consumption for the push tap.
Water consumption calculation for sensor taps - KBCN0180
The water flow rate of sensor taps can be entered directly into the flow rate cells of the Wat 01 tool.
The amount of water dispensed by sensor taps for each use is determined by occupant demand in the same way as normal taps. Therefore, the default frequency of use will be applied in the Wat 01 tool and no adjustment calculation is needed for sensor taps.
Water fittings specification evidence at design stage - KBCN0420
For a design stage assessment, it is acceptable to provide data based on reasonable assumptions if the final specification of fittings is not yet available.
Water fittings used for a process related function - KBCN0418
Water fittings used for a process related function, e.g. low level ablution taps, laboratory / classroom taps, scrub-up taps, cleaners' sinks etc., should be excluded from the assessment of regulated water consumption.
Only kitchen taps and those used for general hygiene washing are to be included in the assessment of regulated water consumption.
04/08/17 Added low level ablution taps (typically used for religious purposes) to exemptions.
Water monitoring when only part of a building is under assessment - KBCN0548
When only part of the building is under assessment, there are two cases for achieving compliance with the requirement to specify a water meter on the mains water supply of the building:
If the whole building is under the same tenancy or ownership and management, then a meter monitoring the entire building is acceptable.
However, if the floors subject to assessment are separately tenanted, then a meter at the point of entry to the assessed areas is required.
Assessed areas have to be monitored separately for water consumption when only part of the building falls within the scope of assessment and where the assessed areas are separately tenanted.
Watercourse pollution from indoor parking - KBCN0545
If the design team can demonstrate that there will be absolutely no run-off from the indoor parking then the intent of the credit will be met. However, such proof would also have to demonstrate that no hydrocarbon spillage from vehicles found its way into the watercourse/sewer. It is likely that there would be water ingress from outside or that internal parking areas would have drains fitted and be cleaned regularly. In such conditions, the criteria are still applicable.
The intent of this criteria is to ensure no hydrocarbons run off to any watercourse.
Weather files – 50th percentile - KBCN0117
For the thermal simulation of climate change environments, where this not specified in the manuals, the 50th percentile weather file is used in all cases.
This applies also to the use of any alternative weather files or formats which are not listed in the manual. See
KBCN1182.
18-Dec-2024 - Title updated for clarity. Scheme applicability updated. Link to KBCN1182 added.
Weather files – alternative format or location - KBCN1182
If they achieve the aim of the credit, alternative weather file formats not listed in the manuals can be used instead of those referenced in the manual.
Format - current climate
The alternative weather files must include same variables as the specified weather files for each hour of the year e.g.:
- Dry bulb & wet bulb temperature,
- Wind speed & direction,
- Solar altitude & azimuth,
- Cloud cover etc.
For example, TMY (Typical Meteorological Year) is an accepted alternative format for BREEAM, meeting the requirements above.
The assessor or design team must verify this and ensure that meeting the BREEAM criteria does not become easier by using the alternative weather file.
Format - projected climate
These alternative files must be based on climate projections with equal or higher temperatures than those specified in the relevant criteria, setting an equally or more robust standard for overheating.
Where there are no suitable weather files available for projected climate change, use any one of the following:
To modify weather data for existing climates into the relevant future climate change scenarios required in the criteria.
Alternative location
Where the weather file for the nearest location for the project is not representative of the actual location’s climatic conditions, the project team can use the weather file from another nearby location which
is more representative.
This can take account of the climatic influences of altitude, prevailing wind, proximity to climate-moderating features, or heat island effect.
19-May-2025 - Added example alternative format. Added links to future climate change resources.
18-Dec-2024 - Merged with KBCN1013. Scheme applicability updated.
Weather files – files applicable internationally - KBCN0732
The technical manual refers to Prometheus, which is not applicable internationally for the
projected climate change scenario criteria.
Until an alternative has been formally approved, the following can be used:
Climate Change World Weather File Generator
ASHRAE weather data files
18-Dec-2024 - Title updated. Link updated.
WELL building standard – alignment with BREEAM - KBCN0737
Assessing health and wellbeing in buildings - Alignment between BREEAM and the WELL building standard
BRE and the International WELL Building Institute™ (IWBI™) are collaborating to promote health and wellbeing in the design, construction and operation of buildings and fit-outs, internationally. The two organisations announced their collaboration on 28 November 2016 with the aim to make it more efficient for clients and project teams to pursue both of their respective standards: BREEAM and the WELL Building StandardTM (WELL).
To simplify the process for project teams pursuing both assessment methods, BRE and IWBI have worked together to compare performance requirements, harmonise evidence and identify opportunities to streamline the process of achieving dual certification. This work demonstrates the significant synergies between the two methods and the efficiencies that exist between their respective assessment and certification processes. It forms a part of an ongoing collaboration between BRE and IWBI to work together to harmonise their approach to health and wellbeing in the built environment across their standards, research programmes and services generally.
View Briefing paper
here
Zoning and control – dimming - KBCN1018
Localised dimming controls installed in line with the criteria, along with a master on/off switch, can be considered as meeting the aim of the requirement for 'controls' in open plan offices.
The aim is for occupants to have local control over their lighting and maintain comfortable lighting levels.
Zoning and control – PIR in circulation spaces - KBCN0332
PIR controls can be deemed compliant in circulation spaces such as corridors. In this instance 'separate occupant controls' are not required.
The requirement for user control is so that the building users can have direct control over their immediate work environment to ensure it is suitable for their personal needs. In circulation spaces, occupancy is transient and PIR control in these spaces is acceptable.
Zoning and occupant control – access to lighting controls - KBCN00032
The relevant areas for the criteria apply only to areas where users are expected to have control.
For instance, this means that areas intended for the general public, or a shop floor would not be expected to have lighting controls.
The general principle which applies to user access to general environmental controls (heating, cooling, ventilation) may also apply to access to lighting controls. See
KBCN0170.
However, the the exact approach may differ between the two types of systems and assessor judgement must be used to determine compliance.
In all cases zoning is required in all areas of the asset where specified in the assessment criteria. Please refer to the specific requirements of the applicable BREEAM standard to interpret this guidance appropriately.
14-Dec-2022 - KBCN applicability updated to include BIU. Wording updated. Link to KBCN0170 created.
Zoning and occupant control – control via BMS - KBCN0703
Occupant control via a BMS is not normally considered a compliant BREEAM solution. Any solution that requires the action of a third party (eg facilities manager) is not considered under the control of the occupant. Solutions where all relevant building occupants have control via a user-interface via BMS may be considered compliant where the assessor is satisfied that the aim of the criteria are met.
User-control must be available directly to the occupant.
01/08/2017 - KBCN applicability to Thermal comfort Issue removed.
Zoning and occupant control – PIR detection systems - KBCN0335
The aim of the Health & Wellbeing category is to recognize ways to benefit occupants through giving them control of their lighting environment. Without manual overrides, presence or absence detection lighting controls (such as PIR detection systems) are not compliant with the criteria.
BREEAM recognises the energy efficiency benefits of detection systems in buildings through the Energy category. In some cases, the design team may have to prioritize one particular lighting strategy to the detriment of achieving a credit elsewhere.
Zoning and occupant control – PIR systems - KBCN0335
The aim of the Health & Wellbeing section is to recognise efforts to benefit the future occupants of the building and their user comfort and control. Therefore, without manual over-ride controls, PIR lighting controls are not compliant with the criteria.
BREEAM recognises the energy efficiency benefits of passive infrared sensor (PIR) systems in buildings through the Energy section. Therefore, in some cases it may be necessary for the design team to prioritise one particular lighting strategy to the detriment of achieving a particular credit.
18 09 2017 Wording amended to clarify the meaning.
Zoning and occupant control – whiteboards and display screens - KBCN1433
Whiteboards and display screens in dedicated teaching or presentation spaces require separate zoning and control for lighting, as specified in the criteria.
Lighting around whiteboards and display screens which are typically found in general office areas, meeting rooms, or in other generic spaces do not require separate zoning and control to meet the criteria. In such cases, the assessor should provide justification.
Whiteboards and display screens in dedicated teaching / presentation spaces are likely to be used frequently, and require appropriate zoning and control. An increasing number of offices and meeting rooms now include display screens - however separate zoning and control may not be appropriate.
Zoning and occupant controls – handheld remote controls - KBCN1243
Remote control light switches can be considered as compliant, on the basis that these are provided in sufficient numbers/locations to meet the aim of the criteria.
[KBCN withdrawn] ~ Areas assessed for formaldehyde and TVOC - KBCN1008
This KBCN is no longer applicable. Please refer to KBCN0871 for scope of 'Emission levels (products)' and 'Other information' section of the technical manual for scope of 'Emission levels (post-construction)'.
Superseded text:
Products applied or installed in parts of the building likely to affect the indoor air quality and impact the wellbeing of building users need to be assessed. Areas are not excluded on the basis of how long building users are present in those areas.
27-Feb-2018 - KBCN N/A due to ambiguity of applicability to criteria
[KBCN withdrawn] ~ BREEAM AP and BREEAM assessor – conflict of interest - KBCN0196
This KBCN has been withdrawn and replaced with the more detailed KBCN1708.
KBCN Withdrawn on 18th Oct 2024
An individual can be appointed as a BREEAM/HQM Assessor and BREEAM AP/Sustainability Champion for the same project, where the Assessor also holds current and applicable AP/Sustainability Champion credentials.
If this route is chosen, it must be made clear when submitting the assessment that both roles are being carried out by the same person and confirmed how potential conflicts of interest are identified and managed. This will mean, when appropriate, that the assessment can be escalated to a more detailed level of quality assurance checking.
[KBCN Withdrawn] ~ Confirmation of low flood risk without an FRA - KBCN0582
The KBCN has been withdrawn and is no longer valid.
This is because its content was created on the basis of a very specific case and should not be applied generally. The authority/organisation's confirmation is no more robust or detailed than reference to flood maps, which are not in themselves compliant without a FRA.
KBCN withdrawn on 31/03/17:
Where a national or local authority/organisation has confirmed, in writing, that the site has a low risk of flooding from all sources and that a Flood Risk Assessment (FRA) is not required then this is acceptable and the two credits can be awarded. The authority/organisation's written confirmation is a sufficient indication that an appropriate level of flood risk assessment has been completed. Please note that the use of relevant flood maps without this additional confirmation from the authority/organisation is not acceptable.
[KBCN withdrawn] ~ GN22 – Scheme version applicability - KBCN0646
Table 1 is for the use of any version of a scheme where the first version was released
pre-December 2015, and table 2 is for the use of any version of a scheme where the first version was released post-November 2015.
10-Oct-2022 This KBCN has been merged with KBCN0719. KBCN withdrawn.
[KBCN withdrawn] ~ No floor or ceiling finishes fitted - KBCN00046
Where the developer has not specified or installed any floor or ceiling finishes, the requirements are met.
This issue recognises where the potential for generating unnecessary waste of materials has been avoided.
16-May-2023 - Merged with KBCN1066. Withdrawn.
20-Dec-2017 - KBCN wording simplified to add clarity.
[KBCN withdrawn] ~ VOC product types – other - KBCN0698
Where a product does not appear to fit into any of the defined VOC product types listed in the manual this does not mean it is automatically exempt from being assessed. If it is similar to one of the listed product types and clearly could have an impact on VOC levels it should normally be assessed.
In such cases the supplier/manufacturer should seek to demonstrate that their product meets the equivalent standards required for the closest matching product type.
19-Oct-2022 - KBCN replaced by KBCN0872.
[KBCN withdrawn] ~ VOC testing – alternative methods for compliance for paints and varnishes - KBCN0492
Manufacturers' calculations of VOC content, based on the constituent ingredients, can be used to demonstrate compliance with the testing requirement for paints and varnishes instead of ISO 11890-2:2013.
11-Oct-2022 - KBCN is withdrawn because it is a duplicate of KBCN0452.
[KBCN withdrawn] ~ Wat 04 – Refurbishment and Fit-Out assessments - KBCN0913
This KBCN has been withdrawn and is no longer valid. Please refer to
KBCN0999 for relevant guidance.
KBCN guidance superseded.
KBCN withdrawn on 30 01 2018:
Where there are no landscaped areas within the refurbishment or fit-out zone/within developer control, ie there is no irrigation system, and there are no other unregulated water demands for the building, the Issue is filtered out. On BREEAM Projects the exclusion is activated by answering ‘NO’ to the two relevant questions.
Where there are soft landscaped areas, but no irrigation systems specified and there are no other unregulated water demands for the building, the credit can be awarded by default, to recognise that the need to provide an irrigation system has been designed out. On BREEAM Projects, respond with ‘NO’ to the unregulated water use question and ‘YES’ to the one on soft landscaping.
[Withdrawn] – multiple assessments – site-wide certificate - KBCN0874
Where developments on a site are assessed under multiple BREEAM registrations, but there is a requirement for an overall, site-wide BREEAM rating, an additional certificate can be produced for the whole development.
For further details of this service and applicable fees, please contact the BREEAM technical team.
04-Dec-2023 - Withdrawn.
17-Apr-2018 - Amended to clarify.
[Withdrawn] – Weather file location - KBCN1013
Content merged with KBCN1182.
In accordance with the guidance provided in CIBSE AM11, in instances where the weather file for the nearest location does not represent the most appropriate climatic conditions for the actual location, it is permissible to use the weather file from another, nearby location, which more closely matches the climate at the actual location.
This can take account of the climatic influences of height above sea level, a coastal location or other local, climate-moderating features such as mountains, woodland, lakes, prevailing wind direction or urban heat island effect.
18-Dec-2024 - Content merged with KBCN1182.
[Withdrawn] Labeling and signage – Where provision of waste bins is out of scope - KBCN1380
[This KBCN has been merged with
KBCN1577].
Where the provision of waste bins is outside the scope of the developer, it is clearly not possible to label the bins. In this situation, the following compliance options are available:
- Provide compliant signage to the storage area and label bin spaces within the storage area according to the relevant waste streams.
- Where future waste streams are unknown, provide compliant signage to the storage area and a written commitment from the developer to ensure that the bins and/or bin spaces are labelled.
See also
KBCN1577
It is recognised that the bins may be provided by the tenant, local authority or waste management company after the time of certification.
21-May-2024 - Withdrawn. Merged with KBCN1577.
22-Mar-2023 - Updated to align with KBCN1577 and to clarify applicability to all assessment types where providing bins is out of scope.
Information correct as of 9thMarch 2026. Please see kb.breeam.com for the latest compliance information. To use either the EN 17037 or IES-LM-83-23 option, the methodology within Guidance Note 50 must be followed. In addition, the minimum percentage area to comply, dependant on the building type and space type, must be met in accordance with the criteria within the relevant BREEAM issue. To calculate the percentage of assessed area that complies, follow KBCN0471 or KBCN1081.
Example:
A school using the International New Construction V6 scheme, has used the IES-LM-83-23 sDA method to calculate the daylight performance. The nominal level is achieved in all occupied spaces. The minimum area to comply is set at 80% as per table 10 and 12. As 100% of occupied spaces meet the nominal level, 2 credits can be met.
To use either the EN 17037 or IES-LM-83-23 option, the methodology within Guidance Note 50 must be followed. In addition, the minimum percentage area to comply, dependant on the building type and space type, must be met in accordance with the criteria within the relevant BREEAM issue. To calculate the percentage of assessed area that complies, follow KBCN0471 or KBCN1081.
Example:
A school using the International New Construction V6 scheme, has used the IES-LM-83-23 sDA method to calculate the daylight performance. The nominal level is achieved in all occupied spaces. The minimum area to comply is set at 80% as per table 10 and 12. As 100% of occupied spaces meet the nominal level, 2 credits can be met. 





